IJCRR - 5(1), January, 2013
Pages: 106-114
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
IN VITRO EVALUATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL EFFECT OF FRESH GARLIC EXTRACT AND ITS INTERACTION WITH CONVENTIONAL ANTIMICROBIALS AGAINST ESCHERICHIA COLI ISOLATES
Author: Vishal Gaekwad, N.A. Trivedi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Escherichia coli (E. coli) is the most common etiological agent, for causation of uncomplicated urinary tract infection. At the same time it is one of the bacterial strains account for wide range of antimicrobial resistance. Garlic (allium sativum) possesses antimicrobial activity against wide variety of organisms. In the present study antimicrobial activity of fresh garlic extract (FGE) was assessed by well diffusion as well as tube dilution method and effects of combination of ampicillin and ciprofloxacin with FGE were studied by well diffusion method against the clinical isolates of E Coli spp. FGE per se produced dose dependent increase in zone of inhibition. In the combination study, addition of FGE with various concentrations of ampicillin (2.5-20mcg/ml) resulted in marked further increase in zone of inhibition than that produced by ampicillin per se at the respective concentration. While combining different concentrations of ciprofloxacin with FGE, ciprofloxacin 1.25mcg/ml with 20mg/ml and 40mg/ml of FGE produced synergistic effect. This study suggests possibility of concurrent use of antimicrobial drugs and FGE in treating infections caused E. coli spp. Further detailed pharmacokinetic and in vivo studies of garlic are required.
Keywords: Garlic; Ampicillin; Ciprofloxacin; Antimicrobial activity; E Coli
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Antimicrobial resistance is the ability of a microorganism to survive when exposed to antimicrobial drugs against which it was previously sensitive1 . Infections caused by resistant micro-organisms often fail to respond to the standard first line treatment, resulting in more expensive therapies, prolonged illness, prolonged treatment, prolonged hospital stay and greater risk of death. Overall increases health-care costs and the financial burden to families and societies. E. coli is the gram –ve bacterial organism most commonly recovered in the clinical laboratories and has been incriminated in infectious diseases involving virtually every human tissue and organ system. However, this organism which was once susceptible to all major class of antimicrobials, is now becoming a therapeutic challenge due to release of Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL).2, 3 Most strains of E. coli were highly susceptible to ampicillin when it was first introduced in early 1960’s but now percentage of E. coli resistance to ampicillin reaches up to 40-50 %2 .
Ciprofloxacin is the fluorinated 4-Quinolone having broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. It is a potent bactericidal agent used widely for E. coli infections2 . However resistance to E. coli is increasing may be up to 30-50% according to community based surveillance by WHO in India4 . As emergence of resistance is a natural process of evaluation for the microorganisms, the only answer mankind has against this is, rapid and faster discovery of more and more potent antimicrobials. Over the past 20 years, there has been much interest in the investigation of natural products as sources of new antibacterial agents. Garlic (Allium sativum) is coming up as one of such promising source of antimicrobial agent. Garlic is a perennial bulb-forming plant belonging to family Liliaceae.
Various ancient literatures have suggested use of garlic for variety of treatment for preventing common cold, malaria, cough and tuberculosis and sexually transmitted diseases, wound infection etc5 . Various modern literatures also suggest antimicrobial activity of garlic against variety of gram +ve, gram -ve organisms as well as against fungi and viruses5-11. This broad spectrum of activity has been attributed to the phytotherapeutic sulphur compounds (eg. Allicin and Thiosulfinates) present in varying concentrations in garlic5, 9 .So, this study was aimed to evaluate antimicrobial action of Fresh Garlic Extract (FGE) and assessing its in vitro interaction with ampicillin and ciprofloxacin against E. coli spp.
MATERIALS AND METHODS Preparation of Garlic Extract Garlic was purchased from the local market; garlic bulbs were peeled, weighed 100gm and cleaned. Cleaned cloves were surface-sterilized by immersing them into 70% (v/v) ethanol for 60 seconds. After letting the residual ethanol on surface evaporate, garlic bulbs were homogenized aseptically in sterile mortar and pestle, allowed to stand for ten minutes and filtered through Whatman filter paper No. 1. This Fresh Garlic Extract (FGE) was then collected in the sterile bottle and stored in refrigerator. This extract was considered as the 100% concentration of the extract. The concentrated extract was further diluted with sterile distilled water12. FGE once prepared was used for 4 days.
The concentration of FGE was calculated as the total weight of garlic per milliliter. 100 grams of raw garlic yielded an average of ~ 7ml of juice. This extract was considered as the 100% concentration12. Every time 100% FGE was inoculated on MacConkey’s agar for 24hrs to check for its sterility.
Sample Collection Escherichia coli species isolated in the Microbiology laboratory of Medical College, Baroda from the samples of urine collected from the different clinical wards of the S.S.G. Hospital, Baroda during the period of November 2010 to October 2011 were used.
Isolation of Pure Culture A flame sterilized nichrome inoculating loop was used to inoculate the infective material on MacConkey’s agar. The inoculum was spread into four quadrants of the plate by turning the plate at 90 degree angles. The loop was sterilized between each successive quadrant streak. The purpose of this technique was to dilute the inoculum sufficiently on the surface of agar medium so that well defined colonies of bacteria known as colony forming units can be obtained13 . The pure colonies thus obtained were confirmed by standard biochemical tests.
Preparation of Standard Inoculum Pure colonies were picked up with the help of flame sterilized inoculating straight wire from MacConkey’s medium and emulsified in a test tube containing peptone water and kept for 20-30 minutes. The turbidity was matched with 0.5 McFarland standards (containing 1×107 CFU/ml) approximately against a sheet of white paper. The turbidity was adjusted to the proper density as the McFarland by adding sterile saline or more bacterial inoculum.
(I) Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of FGE
(I a) By Well Diffusion Method 8, 14-16
Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA) was prepared according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Himedia); then media was poured in media plates of 9-10 cm diameter and depth of agar was kept about 3-4 mm. With a sterile cotton swab the standard inoculum was spread evenly over the plate successively in three directions and over the rim, to obtain even inoculum. The plate was allowed to dry for 3-5 minutes. 4-5 wells of 6mm were cut on the surface of the agar. 100μl of 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 35%, 50%, 75% and 100% solutions v/v of fresh garlic extract was added to different wells. Different dilutions of fresh garlic extract were prepared by adding 30µl of sterile distilled water. One well was filled with sterile distilled water which served as a control. The plates were incubated at 37?C for 18-24 hours. The zone of inhibition was measured by a scale to the nearest mm including well diameter.
(I b) By Macro broth dilution technique 8, 14-15 Experiments were performed by using macro broth dilution method where in 100µl of different dilutions (5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 35%, 50%, 75% and 100%) of fresh garlic extract was added in 2ml of Mueller Hinton Broth. 1 ml of standard inoculums of the microorganism was added to each tube. A tube of the growth medium without garlic extract served as a growth control and uninoculated tube of medium was incubated to serve as a negative growth control. After 18-24 hours of incubation at 37?C, tubes were examined for turbidity, indicating growth of the microorganism. From these samples, we calculated Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC). The MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of garlic extract that completely inhibited the visible growth of the organism6, 8, 11
(II) Determination of the combined activity of Fresh Garlic Extract (FGE) and conventional antimicrobial agents using Well-diffusion method
Ampicillin and ciprofloxacin were purchased from Hi-Media Laboratory Ltd., Mumbai (India). Antimicrobial effect of serial dilutions of, ampicillin (2.5-20µg/ml) and ciprofloxacin (1.25- 20µg/ml) were assessed per se as well as in combination with different concentrations of FGE (5-160mg/ml) on E. coli spp. using well diffusion method. Agar plates of Mueller Hinton agar medium were swabbed using cotton swab with standard inoculum culture of the E. coli spp.
The plates were allowed to dry for 3-5 minutes. Five wells of 6mm in diameter were punched in the agar. The wells were filled up with different concentrations of FGE and conventional AMAs alone or in combination keeping the total volume in each well to 30µl11, 12, 16, and 17. Serial dilutions of ampicillin (2.5, 5, 10, 15, 20mcg/ml) and ciprofloxacin (1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20mcg/ml) were prepared by using sterile distilled water as diluents. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 18-24 hour. The antibacterial activity was assessed by measuring the zone of inhibition (mm).
CLSI guidelines were used to label E. coli ‘sensitive’, ‘intermediate sensitive’, or ‘resistant’ to ampicillin and ciprofloxacin18 . Synergism effect is defined when combined zone of inhibition is increased by 5mm compared to the individual drug11, 16. Antagonism effect is defined when combined zone of inhibition is less than that produced by individual drug19 .
RESULT In the present study we evaluated antimicrobial activity of FGE alone and in combination with conventional antimicrobial agents, ampicillin and ciprofloxacin on Escherichia coli spp. Total 45 samples of E. coli spp. were isolated from microbiology laboratory of the Medical College; Baroda from the samples of urine from the different clinical wards of the S.S.G. Hospital, Baroda, during the period of November 2010 to October 2011.
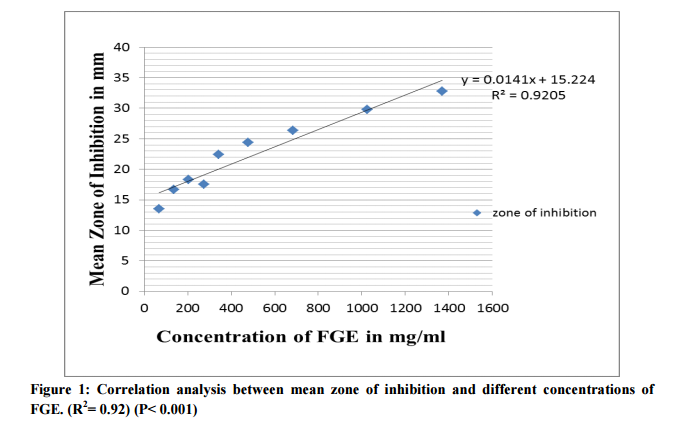
Evaluation of antimicrobial effect of FGE Different concentrations of FGE produced statistically significant dose dependent increase in zone of inhibition compared to control. (Table 1) 10% and higher concentrations of FGE produced mean zone of inhibition more than 15mm while 100% FGE produced mean zone of inhibition 32.8± 3.2mm. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) was determined using macro broth dilution method using 15 isolates of E. coli spp. Mean MIC of FGE was 134.53mg/dl. Figure 1 shows the correlation analysis between mean zone of inhibition and different concentrations of FGE. Increase in zone of inhibition positively correlates with increase in concentration of FGE. (R2= 0.92) (P< 0.001) From this correlation mean MIC value of FGE 134.53mg/ml is correlated with 17.12mm zone of inhibition.
Effect of combination of ampicillin and FGE on E coli spp using well diffusion method:
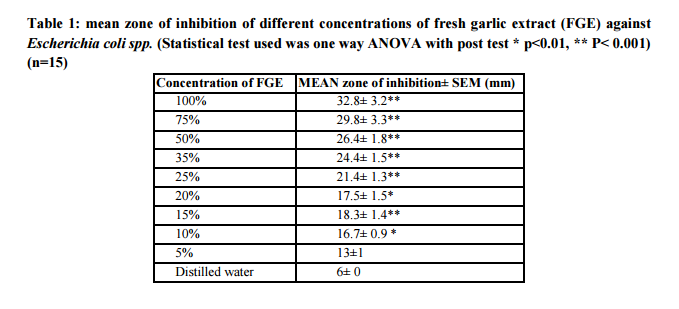
Table 2 shows zone of inhibition produced by combination of FGE with different concentrations of ampicillin (2.5-20mcg/ml). As shown in the table, the addition of different concentrations of ampicillin to FGE produced minimum further increase of 1-2mm in mean zone of inhibition than that produced by the same concentration of FGE per se. However, addition of FGE to different concentrations of ampicillin (2.5-20mcg/ml) produced marked further increase in mean zone of inhibition (9-10mm) than that produced by ampicillin per se at the respective concentration. Addition of 80mg and higher concentrations of FGE to ampicillin 2.5mcg/ml and higher makes the E. coli spp. intermediate to sensitive the combination.
Effect of combination of ciprofloxacin and FGE on E. Coli spp. using well diffusion method:
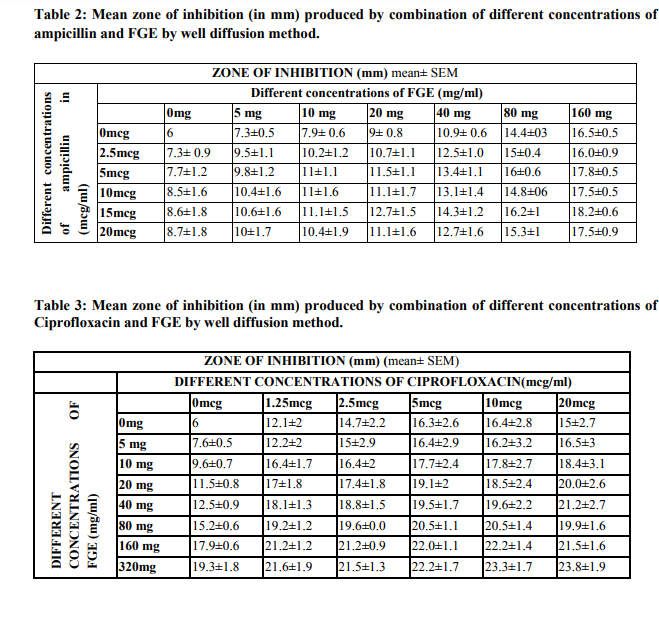
Table 3 shows effect produced by addition of ciprofloxacin (1.25-20mcg/ml) to different concentrations of FGE (5-320mg/ml). As shown in table, addition of ciprofloxacin to different concentrations of FGE produced marked further increase in mean zone of inhibition than that produced by FGE alone at the said concentration.
The rise in mean zone of inhibition (8-9mm) by combination was maximally observed at FGE concentration 40mg/ml and lesser concentration, while at 80mg/ml and higher concentration of FGE plateau is observed. Further addition of varying concentrations of ciprofloxacin produced lesser increase in mean zone of inhibition (3- 4mm). Varying concentrations of FGE alone per se produced dose dependent statistically significant increase in mean zone of inhibition. E. coli spp. were intermediately sensitive to FGE 80mg/ml and higher concentrations. However, addition of ciprofloxacin 2.5- 5mcg/ml made the combination sensitive to FGE. As shown in the table ciprofloxacin per se at different concentrations produced mean zone of inhibition of 12 to 16mm, making E. coli spp. intermediate sensitive to ciprofloxacin.
However, addition of FGE to varying concentrations of ciprofloxacin further increased the zone of inhibition than that produced by ciprofloxacin alone at the said concentration making it sensitive to E. coli even at lower concentrations. Combination of ciprofloxacin in concentration as low as 1.25 and 2.5mcg/ml with FGE 160 and higher concentrations produced zone of inhibition of 21.2mm and higher making it sensitive to E. coli. E. coli was intermediate sensitive to ciprofloxacin 5mcg/ml concentration per se. However addition of 80mg/ml and higher concentrations of FGE made E. coli sensitive to the combination.
DISCUSSION The continuous spread of multidrug-resistant pathogens has become a serious threat to public health and a major concern for infection control practitioners worldwide. In addition to increasing the cost of drug regimens, this scenario has paved way for the re-emergence of previously controlled diseases and has contributed substantially to the high frequency of opportunistic and chronic infection cases in developing countries. The slow pace of newer antibiotic development and emergence of resistance developed the need to explore nature, in search of phytotherapeutic agents with novel targets and mode of actions.
Garlic has had an important dietary and medicinal role for centuries. Most of its prophylactic and therapeutic effects are ascribed to specific oil and water-soluble organosulfur compounds (allicin and thiosulfinates). There are extensive literatures on the antibacterial effects of various garlic preparations6-8, 10-12,20 . Deresse Daka et al (2009)7 assessed antibacterial effect of crude preparation of garlic on diarrhea causing bacteria (E. coli, salmonella and shigella strains). The study found that, at the concentration of 30- 37.5 mg/ml garlic has a bacteriostatic effect and at concentration higher than 37.5mg/ml garlic has bactericidal effect, which was comparable with cotrimoxazole, ciprofloxacin and chloramphenicol.
Also, in a study done by B.A. Iwalokun AO et al6 , antibacterial activity of aqueous garlic extract by well diffusion and macro broth dilution method was characterized by inhibition zone of 20.2-22.7 mm and minimum inhibitory concentrations ranged from 15.6-48.3 mg/ml for gram positive organisms. In the present study antibacterial effect of FGE alone and in combination with conventional drugs ampicillin and ciprofloxacin against E. coli was studied. Antimicrobial susceptibility when assessed using well diffusion method, showed dose dependent increase in zone of inhibition ranging from 13mm to 32mm which is comparable to studies done by Iwalokun 6 and durairaj 8 . FGE concentration of 10% and higher have significant antimicrobial activity with mean zone of inhibition ≥ 16mm. All 15 E. coli spp. were sensitive to FGE showing maximum zone of inhibition up to 32mm zone of inhibition with 100% FGE.
In present study mean MIC value of FGE found was 134mg/ml which is higher than that stated in above studies. Variations in composition of garlic and genetic disparity among bacteria or different species may be responsible for such inconsistency. In routine microbiology practice, zone of inhibition in mm is used to define the antimicrobial sensitivity as it is cumbersome and time consuming to study MIC every time. Therefore a correlation analysis was done between different concentrations of FGE with the zone of inhibition obtained, which showed a strongly positive correlation (R2 =0.92) between zone of inhibition obtained and concentration of FGE used.
From this correlation analysis we observed that mean MIC of 134mg/dl correlated with 17.12 mm zone of inhibition. Few studies have been conducted to determine antibacterial effect of garlic in combination with conventional antimicrobials. Plaksha et al 12 studied the antibacterial effect of garlic extract on streptomycin resistant Staphylococccus aureus and E. coli strains solely and in combination with streptomycin. Finding shows garlic extract had significant antibacterial activity and combination with streptomycin produced increase in sensitivity to both Staphylococccus aureus and E. coli strains.
Mei-Chin Yin et al 10 had assessed the inhibitory effects of aqueous garlic extract, garlic oil and four diallyl sulphides against four enteric pathogens and their interactions with conventional antimicrobials. Most interactions of four antibiotics (meropenem, ceftazidime, imipenem and gentamicin) with diallyl polysulphide, determined as FIC index, showed synergistic or additive effects. In the present study, addition of FGE with ampicillin resulted in additive effect by well diffusion method. Out of 15 E. coli spp. used, 13 were resistant to ampicillin. According to CLSI guidelines ampicillin sensitive strains of E. coli should produce ≥17mm zone of inhibition at 10mcg/ml concentration18. In present study even with 20mcg/ml concentration this zone of inhibition cannot be achieved which is even not a tolerable dose in vivo.
Different concentrations of FGE (5-160mg/ml) produced dose dependent increase in zone of inhibition and with 160mg/ml produced zone of inhibition >16 mm. Combinations of FGE and ampicillin produced additive effect. Zone of inhibition produced by combination was 9-10mm more than that produced by ampicillin per se. However, it was only 2-3mm more than that produced by FGE per se. Addition of FGE 80-160mg/ml to ampicillin concentration as low as 2.5mcg/ml makes it intermediate sensitive to E. coli. However, at higher concentrations of FGE (80-160mg/ml) there is masking of effect of ampicillin. When different concentrations of ciprofloxacin was combined with FGE, combination makes E. coli spp. completely sensitive to ciprofloxacin even at the concentration as low as 1.25 and 2.5mcg/ml which is lower than MIC of ciprofloxacin (5mcg/ml). Combination of ciprofloxacin 1.25mcg/ml with 20mg/ml and 40mg/ml FGE produced synergistic effect producing additional rise of >5mm than produced by any of drug alone.
Thus combinations of FGE with these antibiotics not only help to regain the sensitivity of the older less toxic and comparatively cheaper drugs, but also reduce the dosage required for the therapy. FGE may probably retard the development of resistance to these important antimicrobial agents. In evaluation of antibacterial activity of garlic reported by various studies the mean zone of inhibition remains identical in various studies 6-8 , however there is marked variation in MIC value obtained by different studies. MIC value reported from garlic extract ranged from 35-320mg/ml by various studies. The probable reason for such variation is, variations in composition of garlic and genetic disparity among bacteria or different species. Standardization of garlic extract used by isolation and purification of the active component is necessary.
So, this study suggests the possibility of use of antimicrobial drugs and garlic extracts in combination for treatment of infections caused by E. coli strains. However, it is hard to predict synergistic effects in vivo on the basis of the presented in vitro evidence alone because data from the in vitro study may not be extrapolated in in vivo drug efficacy as in vitro can not reflect the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic features of antimicrobial agents after it has been ingested.
CONCLUSION In conclusion, FGE as a sole agent is having significant antimicrobial effect against E. coli spp. in in vitro studies. Moreover, there is a possibility of concurrent use of antimicrobial drugs and Fresh garlic extract in treating infections caused E. coli spp. This may help to not only regain the sensitivity of older less toxic agents but also reduce the dosage required for the therapy. Further detailed pharmacokinetic and in vivo studies of garlic are needed.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The authors are thankful to Department of Microbiology, Medical College Baroda for their support and valuable guidance for carrying out this work. Authors acknowledge the great help received from the scholars whose articles cited and included in reference of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and book from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. Authors are grateful to IJCRR editorial board members and IJCRR team of reviewers who have helped to bring quality to this manuscript.
References:
1. WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance. February 2011; Available from: ttp://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs 194/en/.
2. Bruton L, Chabner B, Knollmann B. Goodman and Gilman's The pharmacological basis of therapeutics2011.
3. Fauci As, Kasper DL, Longo DL, Braunwald E, Hauser s, Jameson L, et al. Harrison's Principles of internal medicine. seventeenth edition ed2008.
4. WHO. Community-Based Surveillance of Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in Resource-Constrained Settings Report on five pilot projects2009.
5. Organization WH. WHO monographs on selected medicinal plants 1999.
6. B.A. Iwalokun AO, 2 D.O. Ogbolu,3 S.B. Bamiro,4 and J. Jimi-Omojola2. In Vitro Antimicrobial Properties of Aqueous Garlic Extract Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Candida Species from Nigeria. Journal of medicinal food. 2004;7(3).
7. Daka D, Awole M. Assessment of the Antibacterial Effect of Crude Preparation of Garlic (Allium Sativum) on Diarrhea Causing Bacteria: An In Vitro, study. asian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2009;1(1):12-4.
8. Durairaj S, Srinivasan S, Lakshmanaperumalsamy P. In vitro Antibacterial Activity and Stability of Garlic Extract at Different pH and Temperature. Electronic Journal of Biology. 2009;5(1):5- 10.
9. Goncagul G, Ayaz E. Antimicrobial Effect of Garlic (Allium sativum) and Traditional Medicine. Journal of animal and Veterinary Advances. 2010;9(1).
10. Yin M-C, Chang H-C, Tsao S-M. Inhibitory Effects of Aqueous Garlic Extract, Garlic Oil and Four Diallyl Sulphides against Four Enteric Pathogens. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis. 2002;10(2):120-6.
11. Ahmad I, Aqil F. In vitro efficacy of bioactive extracts of 15 medicinal plants against ESbL-producing multidrug-resistant enteric bacteria. Microbiological Research. 2007;162 264-75.
12. Palaksha M, N., Ahmed M, Das S. Antibacterial activity of garlic extract on streptomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli solely and in synergism witj streptomycin. Journal of Natural Science, Biology and Medicine. july 2010;1(1).
13. Dini C, Fabbri A, Geraci A. The potential role of garlic (Allium sativum) against the multi-drug resistant tuberculosis pandemic: a review. Ann Ist Super Sanità. 2011;47(4):465-73.
14. Mackie, Cartney M. Mackie and Mc Cartney Practical Medical Microbiology. 14th ed. Collee JG, Marmion B, P., Fraser A, G., Simmons A, editors: Churchil livingstone; 2007.
15. Scott B. Bailey and Scott's Diagnostic Microbiology. 12th ed. Forbes B, A., Daniel FS, weissfeld A, s., editors: Mosby elsevier; 2007.
16. Adwan G, Mhanna M. Synergistic Effects of Plant Extracts and Antibiotics on Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Clinical Specimens. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research. 2008;3(3):134-9.
17. Ahmed Z, Khan SS, Khan M, Tanveer A, Ahmad Lone Z. Synergistic Effect of Salvadora persica Extracts, Tetracycline and Penicillin Against Staphylococcus aureus. African Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. 2010;2(1-2):25-9.
18. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disc Susceptibility Tests, NCCLS. january 2002;22(1).
19. Eja ME, Arikpo GE, Enyi-Idoh KH, Ikpeme EM. An evaluation of the antimicrobial synergy of Garlic (Allium sativum) and Utazi (Gongronema latifolium) on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Malaysian Journal of Microbiology. 2011; Vol 7(1):49- 53.
20. Egbobor ME, Asikong BE, Abriba C, Arikpo GE, Anwan EE, Enyi-Idoh kh. a comparative assessment of the antimicrobial effects of garlic (allium sativum) and antibiotics on diarrheagenic organisms. southeast asian j trop med public health. 2007;vol 38 s( No. 2).
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License