IJCRR - 5(4), February, 2013
Pages: 61-72
Date of Publication: 28-Feb-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF SHORT TERM HATH YOGA ON LUNG FUNCTION, AEROBIC CAPACITY AND QUALITY OF LIFE IN HEALTHY YOUNG INDIVIDUALS
Author: Foram Dhebar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Yoga is one of the most common methods used as mind body therapy. Hath yoga, one of the many forms or paths of yoga, focuses on overall fitness through pranayama, asana, and meditation. Anxiety and stress are the major problems of the modern world particularly of youth and college going students. There are very few studies on effect of hath yoga on lung function and aerobic capacity of healthy young individuals and there is paucity of data on effect of yoga on quality of life in the same group. Objective: The objectives of the study were to see the effect of short term hath yoga on lung function, aerobic capacity and quality of life in healthy young individuals. Methodology: Study design: experimental study Sample size: 60 volunteers A: experimental group and B: control group. Study setting: students of the college of physiotherapy. Method Hath yoga for 4 weeks,5 days in a week for 60 minutes; including 5 minutes of relaxation-savasana and makarasana, 5 minutes of pranayam, 5-10 minutes warm up, 25-30 minutes asanas (Ardh Paschimotasana, Paschimotasana, Yogamudra, Ardhmatsy endrasana, Uttitakumarasana, Tadasana) 5-10 min savasana, cool down period. Subjects of control group were in waiting list. After 4 weeks control group was taught same hath yoga poses. Peak expiratory flow rate, 12 min walk distance, SF-36 scores were taken as pre and post data. Result: The result shows that there is statistically significant improvement in PEFR, 12 MWD, and component of SF-36 after 4 week of hath yoga practice in healthy young individuals compared to a control group at 5% significance level. Conclusion: The conclusion of the study is that Short term Hath yoga improves lung functions, aerobic capacity and quality of life in healthy young individuals compared to control group.
Keywords: hath yoga, lung function, aerobic capacity, quality of life
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is a group of diverse medical and health care systems, therapies and products.1 The American public´s use of complementary and alternative medicine increased substantially during the 1990s.2Complementary and alternative medicine includes techniques such as aromatherapy, massage, yoga, etc. Yoga is one of the most common methods used as mind body therapy. Yoga is a Sanskrit word which means “the unity of body and mind.” Yoga is an ancient Indian practice; first described in Vedic scriptures around 2500 B.C. which utilizes mental and physical exercises to attain “Samadhi”, or “the union of the individual self with the infinite”.3 Yoga is cessation of thought waves in mind.
Hath yoga, one of the many paths of yoga, focuses on overall fitness through breath control exercises (pranayama), yoga poses (asana), and meditation. Practitioners of yoga therapy integrate yoga concepts with western medical and psychological knowledge for example, by using body awareness and breathing activities, physical posture and meditation with an understanding of pathological condition such as back pain or depression4 whereas traditional yoga practice is primarily concerned with personal enlightment of people without understanding of pathology. Yoga since long has been used to reduce the physical symptoms of chronic pain, improves fitness and for meditation. Yoga also may help individuals deal with the emotional aspects of chronic pain, reducing anxiety and depression. Although yoga is historically a spiritual discipline, it has been used clinically for therapeutic intervention. The number of publications on its clinical application has greatly increased over the past 3 decades 5 . In literature there are many articles of use of yoga in variety of condition such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, breast cancer, low back pain, migraine, epilepsy.6-10 Even though there have been numerous studies on yoga and disease, there have been few on healthy subjects. Several studies have been conducted in the geriatric population to see improvement in balance and fitness, but very few on healthy young subjects.11 Anxiety and stress are the major problems of the modern world particularly of youth and college going students. Stresses have very negative effects on fitness and health. Poor health negative feelings lead to various physical and psychological problems. Stressful life can lead to poor quality of life and fitness. There are studies on yoga and disease related stress, anxiety and effect on well being but very few on healthy young individuals’ fitness aspect. Some studies found improved lung function in condition such as asthma, Bronchiecstasis etc.12- 13 there are very few studies on effect of hath yoga on lung function and aerobic capacity of healthy young individuals and there is paucity of data on effect of yoga on quality of life in the same group. Hence the need of this study to determine whether yoga practice over a short duration of 4 weeks would result in a change in lung function, aerobic capacity and quality of life in healthy young individuals.
MATERIAL AND METHADOLOGY
Study design
A randomized controlled trial Study setting The study was conducted at the College of physiotherapy. Duration of study The total duration of the study was 6 months. Sample size and design 60 healthy volunteers were randomly divided in to 2 groups 1) Experimental group (yoga group)-30 individuals 2) Control group-30 individuals Inclusion criteria Gender- male and female Age-18 to 25 years BMI within normal limits Having full range of motion of all joints Exclusion criteria Those who were doing regular exercises previously Having any history of acute or chronic diseases History of Smoking and drinking Data collection and procedure Material Consent form. Data collection sheet Yoga mats Paper, pencil, pen Apparatus Stop watch Peak flow meter Weighing machine Measure tape Outcome measure Peak expiratory flow rate14 12 min walk distance15 SF-36 questionnaire16 Procedure 68 volunteers, 18-25 years of age were recruited from the undergraduate students of the college of physiotherapy. According to inclusion exclusion criteria 60 volunteers were included in the study. All subjects were explained the study and written consent informed form was taken. Then they are randomly divided in to 2 group’s .group A: experimental group and group B: control group. General characteristics (age, sex, height, and weight and body mass index) were collected. On the first day of study, both groups came to training room and their pre intervention data were collected: 12 min walk distance, peak expiratory flow rate and SF-36 score. Experimental group performed hath yoga for 4 weeks, 5 days in a week. Some important guidelines and precautions for practice of asanas were explained such as Take light snacks 1 hour before yoga class. Evacuate bowel and bladder. Dress should be loose and comfortable. Ladies should not do asana during menstruation. Breathing should be done through nose only. Avoid jerky movements while doing asanas. Exhale during all forward bending movements in which the chest and abdomen are being compressed, and inhale during all movement in which the chest and abdomen is being expanded. Do not force your body to achieve final pose. Each yoga session was taken between 7.30 to 8.30 a.m. for 60 minutes; including 5 minutes of relaxation with savasana and makarasana, 5minutes of pranayam consisting of alternative nostril breathing while maintaining of half lotus pose (ardh padmasana).(Photograph 1) Then 5-10 minutes of warm up focused on slow dynamic muscle movements with dynamic lunges, shoulder/arm circling, and neck rolling. This was followed by 25-30 minutes of asanas consisting of following poses: ArdhPaschimotasana (photograph 2) Paschimotasana (toe touching in long sitting) (photograph 2) Yoga mudra ArdhPaschimotasana (photograph 3) Ardh matsyendrasana (sitting and twisting pose) (photograph 4) Uttita kumarasana (cat and camel pose) (photograph 5) Tadasana (toe standing with arm elevated) (photograph 6) Session was ended with 5 min of relaxation with savasana and cool down period. At the end of 4 weeks post exercises data were collected. Statistical tests were used to compare the data of both groups. Level of significance was kept at 5%. Subjects of control group were in waiting list. After 4 weeks control group was thought same hath yoga poses.
RESULT
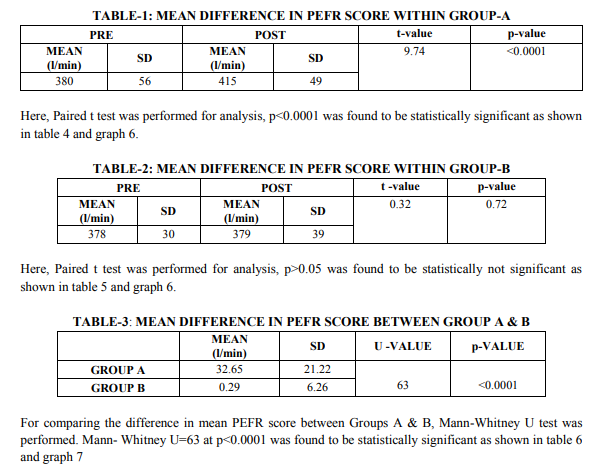
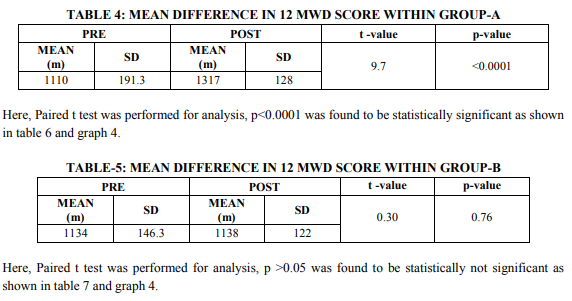
The present study comprised of two groups of 30 subjects in each group. Group A was experiental group and Group B was Control group. Group A was given Hath yoga training, while Group B was kept in waiting. All selected subjects completed the study satisfactorily. Subjects were evaluated at end of four weeks. The results of the 60 subjects were analyzed by using Graph pad Prism-5. Graph 1, 2 shows the mean age, body mass index values having no statistical difference. Here paired t test was used for statistical analysis of within group A and B peak expiratory flow rate and 12 MWD
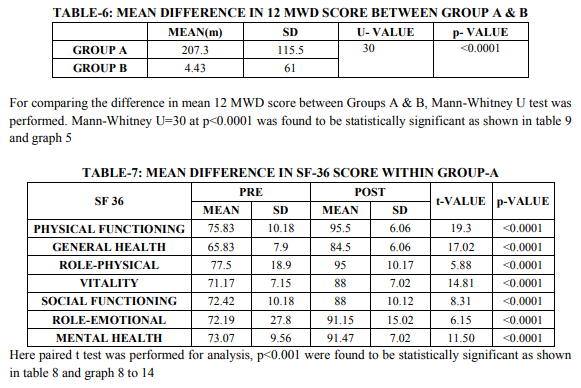
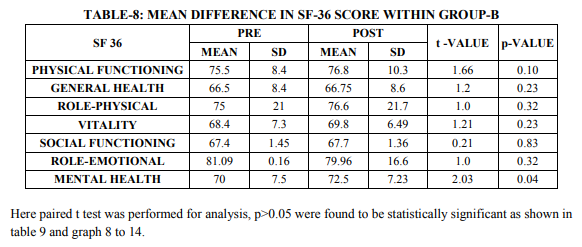
Group A showed statistically significant difference in PEFR (table 1 and 2) and 12 MWD (table 4 and 5) at the end of 4 weeks of Hath yoga practice at 5 % level of significance compared to group B (control group) For comparing the difference in mean PEFR score and 12 MWD Score between Groups A and B, Mann-Whitney U test was performed and found statistically significant (table 3 and 6) In this study subjects were healthy individuals who had no complain of pain and hence pain subscale of physical component was not evaluated. Group A showed statistically significant difference in SF 36 score at the end of 4 weeks of Hath yoga practice p0.05) in physical functioning, general health, rolephysical, vitality, social functioning, roleemotional, and mental health (table 7 – 9)
DISCUSSION
The result shows those 4 weeks of hath yoga practice in healthy individuals can significantly benefit in improving lung function, aerobic capacity and quality of life compared to a control group. This is similar to findings by Yadav RK et al., in a study on 60 healthy young females; where a significant increase was demonstrated in forced vital capacity, forced expiratory volume in 1 second and peak expiratory flow rate.17 Mandanmohan et al. also demonstrated that short-term Yoga practice increased skeletal muscle strength and lung volumes in children.18 Joshi LN et al. found that short term pranayam practice increased respiratory sensation, maximum expiratory pressure and flow rate.19 Respiratory function depends on many factors including nervous system, respiratory muscle strength, and lung dimension. Yoga recognises three methods of breathing: Diaphragmatic, Intercostal, Clavicular 20 According to Chitlow, of these three, diaphragmatic breathing is the most efficient as it uses the least energy and enables the most absorption of oxygen. This is because the surface area of the lungs is greater in the lower lobes resulting in higher quantities of oxygen circulating around the body.21 Yoga stabilizes autonomic equilibrium with a tendency towards parasympathetic dominance rather than stress-induced sympathetic dominance. According to Ernst, Yoga therapy readjusts the autonomic imbalance, controls the rate of breathing and relaxes the voluntary inspiratory and expiratory muscles, which results in decreased sympathetic reactivity.22, 23 Thus; Yoga increases respiratory efficiency, balances activity of opposing muscle groups and slows dynamic and static movements. Pranayama may have psycho physiological benefits by increasing the patient’s sense of control over stress and thus aids in reducing their autonomic arousal factors. Five positions of Hath-Yoga used in this study have been reported to predominantly affect prime mover and accessory respiratory muscle such as external and internal intercostal muscle, pectoral, latisimusdorsi, erector spine, rectus abdominals, serratus anterior and diaphragm.24 Halvorson stated that performing Yoga stretching and balancing movement can lead to improvements of muscle strength and flexibility of all these muscles.25 and thus improve PEFR as seen in present study. The result of this study, showed statistically significant difference in 12 min walk distance at the end of 4 weeks of Hath yoga practice in group A Similarly Balasubramanian and Pansare also reported significant increases in cardiorespiratory endurance after 6 weeks of regular yoga practice. However, the authors had estimated VO2max using the Astrand- Rhyming Step Test.26 In contrast Blumenthal et al. and Raju et al. directly measured VO2max by the analysis of expired gases and reported no significant changes resulting from yoga practice27 .However, the sample population in these two studies consisted of healthy older individuals (ages 60–83) and elite athletes, respectively. Cardiac function in normal young volunteers has been studied in a randomized controlled trial in 24 school children, which was designed to determine whether pranayama had any effect on ventricular performance by measuring systolic time intervals and cardiac autonomic function tests. After 3 months training, parasympathetic activity was seen to be increased and sympathetic activity decreased .28 A study by Bhattacharya on 30 healthy young men also demonstrated improvement in oxidative status and the antioxidant pathological processes following yoga practice leading to an increase in aerobic capacity which could justify the changes seen in present study. 29 The result also suggests improvement in subjective well being and score of SF 36 scale. In this study subjects were healthy individuals who had no complain of pain and hence pain subscale of physical component was not evaluated. As shown in this study, Group A showed statistically significant difference in SF 36 score at the end of 4 weeks of Hath yoga practice. According to Madanmohan, Savasana, the relaxation part of yoga practices, has shown to enhance the ability to withstand stress30 Kamei T et al studied changes in brain waves and blood serum cortisol during yoga exercise and increase in alpha waves and decrease in cortisol level have been reported.31 In vivo evidence has been provided for regulation of conscious states at a synaptic level by yoga nidra 32 . Harinath K et al. studied on the effects after 3 months of hath yoga practice on cardiorespiratory performance, psychological profile and melatonin secretion. They showed improvement in these profiles and increase in plasma melatonin, indicating that yoga could be used as a psycho physiologic stimulus to increase endogenous secretion of melatonin, which in turn might be responsible for improved sense of well-being33 . Prasad concluded the state of the mind and that of the body are intimately related. If the mind is relaxed the muscles in the body will also be relaxed. Stress produces a state of physical and mental tension. Yoga physical postures and breathing exercises improve muscle strength, flexibility, blood circulation and oxygen uptake, as well as hormone function, In addition the relaxation helps to stabilize the autonomic nervous system with a tendency towards parasympathetic dominance. The physiological benefits which follow help the yoga practitioner become more resilient to stressful conditions34 . The limitations of the study were Predominant female individuals were included as participants. Direct estimation of aerobic capacity was not performed. Future Research can be conducted on healthy young individuals to measure relation between quality of life and stress and also can be done in geriatric population to see effect on fitness and quality of life
CONCLUSION
The conclusion of the study is that Short term Hath yoga improves lung functions, aerobic capacity and quality of life in healthy young individuals compared to control group So, clinically it can be implicated to be used to improve physical and psychological fitness in healthy individuals.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I am thankful to Dr. Pankaj Patel, Dean N.H.L. Medical College for giving me an opportunity to do the study. I am grateful to Dr. Neeta Vyas, Principal of S.B.B.College of Physiotherapy, for providing me all facilities for my work, without which it would not have been possible to complete this project. I would like to express my deep sense of gratitude to my respected teacher Dr. Megha Sheth, Lecturer; for her invaluable guidance. I also express my gratitude to all the staff members of S.B.B. College of Physiotherapy for their assistance and help in carrying out this project work I will be failing in my duty if I do not thank my all the subjects, who participated in my study and spent their valuable time. I owe thanks to my family andfriends who shared my anxiety and believed in my abilities specially Amruta Chauhan, Maharshi Trivedi for their support in carrying out this study. I acknowledge the great help received from the scholars whose articles cited and included in references of this manuscript. I am also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. I am grateful to IJCRR editorial board members and IJCRR team of reviewers who have helped to bring quality to this manuscript
References:
1. John A. Why patients use alternative medicine: Result of a national study. JAMA. 1998; 279: 1548-1553.
2. Eisenberg DM, Davis RB, Ettner SL, et al. Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990-1997: Results of a follow-up national survey. JAMA.1998; 280:1569-1575.
3. Lidell L. The Sivananda Companion to Yoga. New York, NY: Simon and Schuster Inc.; 198
4. Worthington V. A History of Yoga. London, UK: Routledge and Kegan Paul; 1982.
5. Khalsa SB. Yoga as a therapeutic intervention: a bibliometric analysis of published research studies. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 2004, 48(3):269–85. 5,
6. Oken BS, Kishiyama S, Zajdel D, Bourdette D, Carlsen J, Haas M, Hugos C, Kraemer DF, Lawrence J, Mass M. Randomized controlled trial of yoga and exercise in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2004; 62: 2058-2064.
7. Dash M, Telles S. Improvement in handgrip strength in normal volunteers and rheumatoid arthritis patients following yoga training. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2001; 45: 355-360.
8. Alyson B. Moadel, Chirag Shah Rosett, Melanie S. Harris, Sapana R. Patel, Charles B. Hall, and, Judith Randomized Controlled Trial of Yoga Among a Multiethnic Sample of Breast Cancer Patients: Effects on Quality of Life. American Society of Clinical Oncology Oncol 2007; 25:4387-4395.
9. P.J. John, PhD; Neha Sharma, MSc; Chandra M. Sharma, MD, DM; Arvind Kankane, MD et al. Effectiveness of Yoga Therapy in the Treatment of Migraine Without Aura: A Randomized Controlled Trial Headache 2007;47:654-661
10. Jayasinghe SR. Yoga in cardiac health (a review). European journal of cardiovascular prevention and rehabilitation, 2004, 11(5):369–75
11. Brown KD, Koziol JA,Lotz M.A. et al. Yoga based exersice programe to reduced the risk of fall in seniors: a pilot study J Alter Complement medi. 2008; 14; 454-7. 11,
12. Nagarathna R, Nagendra HR: Yoga for bronchial asthma: a controlled study. BMJ, 1985; 291: 1077–79 12
13. Visweswaraiah NK, Telles S et al. Randomized trial of yoga as a complementary therapy for pulmonary tuberculosis. Respirology, 2004; 9:96. 13,
14. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network and The British Thoracic Society (2003) British Guideline on the Management of Asthma - Annex 8: Personal Asthma Action Plan"
15. Cooper, K. H. (1968) A means of assessing maximal oxygen uptake. Journal of the American Medical Association 203:201- 204.
16. McHorney, CA, et al;The 36 item short form health survey (SF-36) test of data quality, scaling assumption, and reliability across diverse patient groups. Med Care 32:40,1994.
17. Yadav RK and Das S. Effect of yogic practice on pulmonary functions in young females. Indian J Physiol Phamacol 45:493- 496, 2001.
18. Mandanmohan, Jatiya L, Udupa K, and Bhavanani AB. Effect of yoga training on handgrip, respiratory pressures and pulmonary function. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 47: 387-392, 2003.
19. Joshi LN, Joshi VD, and Gokhale LV. Effect of short term “Pranayam” practice on breathing rate and ventilatory functions of lung. Indian J Physiol Phamacol 36:105- 108, 1992
20. Gilbert C. Yoga and breathing. J Bodywork Mov Ther 3:44-54, 1999.
21. Chaitow L and Bradley D. The structure and function of breathing. In: Multidisciplinary Approaches to Breathing Pattern Disorder, edited by Chaitow L, Bradley D and Gilbert C.Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2002, 1-41.
22. Ernst E. Breathing techniques-adjunctive treatment modalities for asthma? Systematic review. Eur Respir J 2000; 5: 969–972.
23. Ram FSF, Holloway EA, Jones PW. Breathing retraining for asthma. Resp Med 2003; 97:501–507.
24. Levenson C. Breathing Exercise. In: Clinics in Physical Therapy: Pulmonary Management in Physical Therapy, edited by Zadai C. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1992, p 135-156.
25. Halvorson C. Stretching to breathe: Can yoga help your asthma? Asthma Mag 7:27- 29, 2002
26. Balasubramanian B, Pansare MS. Effect of yoga on aerobic and anaerobic power of muscles. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991;35(4):281–282.
27. Raju PS, Madhavi S, Prasad KVV, et al. Comparison of effects of yoga and physical exercise in athletes. Indian J Med Sci. 1994;100:81–87
28. Udupa K et al. Effect of pranayam training on cardiac function in normal young volunteers. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 2003, 47(1):27–33. .
29. Bhattacharya S, Pandey US, Verma NS. Improvement in oxidative status with yogic breathing in young healthy males. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 2002, 46(3):349–54.
30. Madanmohan et al. Modulation of cold pressor-induced stress by shavasan in normal adult volunteers. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 2002, 46(3):307–12.
31. Kamei T et al. Decrease in serum cortisol during yoga exercise is correlated with alpha wave activation. Perceptual and motor skills, 2000, 90(3 Pt 1):1027–32.
32. Kjaer TW et al. Increased dopamine tone during meditation-induced change of consciousness. Brain research. Cognitive brain research, 2002, 13(2):255–9.
33. Harinath K et al. Effects of hath yoga and omkar meditation on cardio-respiratory performance, psychologic profile, and melatonin secretion. Journal of alternative and complementary medicine, 2004, 10(2):261–8.
34. Parshad O et al. Role of yoga in stress management. West Indian medical journal, 2004, 53(3):191–4.



|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License