IJCRR - 5(4), February, 2013
Pages: 31-36
Date of Publication: 28-Feb-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
INHIBITION OF CANDIDA BIOFILMS BY PYOCYANIN: AN IN-VITRO STUDY
Author: Bhattacharyya S., Gupta P, Banerjee G., Jain A., Singh M.
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Objectives: Invasive candidiasis has an attributable mortality of 10-49%. It is associated with biofilm formation over indwelling devices. Biofilm-associated upregulated drug efflux makes treatment expensive and ineffective. Hence low-cost alternatives inhibiting Candidal biofilm formation are needed. Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibits growth of Candida albicans in vitro. This study aimed to detect whether secreted products of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, especially Pyocyanin, affect biofilm production by Candida albicans and C.tropicalis. Methods: P. aeruginosa strains were incubated overnight at 37\?C in Luria broth and centrifuged. Supernatant was filtered by syringe filter (pore size 0.22\?m). Yeast isolates were grown overnight in YPD broth (Yeast Extract-Peptone-Dextrose). Turbidity was adjusted to 106 cells/ml in YPD and culture filtrate. Then 100 \?l of both suspensions were dispensed in wells of flat-bottomed 96-well microtitre plate with normal saline as negative control. Wells were washed after incubation of 90 minutes at 37\?C with Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and reloaded with 100 \?l of respective liquid media. This was repeated after intervals of 24 and 48 hours. Wells were stained with 1% safranine in 95% ethanol, washed with PBS and observed under inverted microscope. Optical density was measured spectrophotometrically. Methods were repeated with filtrate, preheated at 100\?C for 20 minutes and Pyocyanin extracted from P. aeruginosa broth culture with the help of Chloroform and acidified water. Results: Biofilm formation of Candida albicans and C. tropicalis was significantly reduced by culture filtrate, both plain and heated, and Pyocyanin. Pyocyanin was found non-toxic to host cells. Conclusions: Pyocyanin can be utilised in vivo to inhibit device-associated biofilm formation by these pathogens.
Keywords: Biofilm, Candida spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pyocyanin.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Invasive candidiasis is a major disease concern in developing countries. Candida albicans is the most commonly isolated species [Colombo et al., 2003]. However, in regions like South America, Candida parapsilosis and C. tropicalis are the leading agents of candidemia [Colombo et al., 2003]. This disease entity has an attributable mortality in the order of 40-49% without treatment, which varies from region to region [Ahmad et al, 2012]. It is associated with formation of complex microbial communities known as biofilms over indwelling devices like central venous catheters[Sun et al., 2012].Treatment of invasive candidiasis is difficult owing to biofilm-mediated increased drug efflux[Jabra-Rizk et al., 2004]. Among the antifungal agents available, only Echinocandins and Amphotericin B lipid formulations have shown consistent activity against Candidal biofilms [Kuhn et al, 2002] . However, Amphotericin B can be severely nephrotoxic to the host and Echinocandins are prohibitively costly to be used routinely [Deray, 2002 and Morris and Vilman, 2006]. Hence, there is urgent need of less costly natural products and other alternatives against invasive candidiasis .Some workers have studied the effect of secreted products of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on inhibition of biofilm formation by Candida albicans in vitro [Holcombe et al, 2010]. Keeping these things in mind, our study was aimed at detecting the effect of culture filtrate of P. aeruginosa, both plain and heated, and Pyocyanin, in particular on biofilm formation by Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis in vitro.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This was a laboratory-based observational study, carried out in the Department of Microbiology, KGMU, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India. The study was conducted from July 2011 to June 2012.
Isolation of microorganisms:-
Routine microbiological culture media like 5% sheep blood agar and MacConkey agar plates were used to culture Pseudomonas aeruginosa from different samples like pus, sputum, urine and others. To isolate Candida spp. from various clinical samples like blood, pus and urine, Saboraud’s Dextrose Agar (SDA) with Emmon’s modification (pH 7.0) was used. Ten (10) each of C. albicans and C. tropicalis and 10 isolates of P. aeruginosa were randomly selected for the study. P. aeruginosa isolates were identified by Non Lactose-fermenting colonies on MacConkey Agar, positive Oxidase reaction and Citrate utilisation tests and blue green diffusible pigment(pyocyanin) production along with fruity (corn-taco) odour of the colonies on solid media[Ferguson et al., 2007, and Gaby and Hadley, 1957]. Candida albicans isolates were identified by positive Germ tube test, growth above 42°C and terminal chlamydospore production on Corn meal agar with Tween 80(Dalmau technique) at 25°C after 48 hours of incubation[Raju and Rajappa, 2011]. Candida tropicalis isolates were identified by wavy pseudohyphae along with budding yeasts on corn meal agar with Tween 80 at 25°C after 48 hours, positive fermentation of Glucose, maltose and sucrose (all in 2% concentration, w/v)but not lactose and negative germ tube test [Fungal descriptions]. Test for Biofilm formation in Candida spp.:- The microtitre plate model, as proposed by Ramage et al, was employed for biofilm formation and its inhibition in vitro [Ramage et al., 2001]. At first, yeast isolates were grown in YPD Broth (1% Yeast Extract, 2% Peptone, 2% Dextrose, w/v) overnight at 37°C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were incubated overnight in LB or Luria Broth (1 colony suspended in 2 ml LB) and then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes. After that, the culture supernatant was filtered by passing through a membrane filter (syringe filter) of pore size 0.22 µm (Micro-Por Minigen Syringe Filter, Genetix Biotech Asia, New Delhi).This filtrate was divided into 2 parts. One part was left unheated and the other was heated to 100°C for 20 minutes in a water bath and subsequently cooled. Then yeast cell turbidity was adjusted to 106 cells/ml in- a) YPD, b) P. aeruginosa unheated filtrate, and c) P. aeruginosa heated filtrate. About 100 µl of each set of suspension was dispensed in separate wells of a flat-bottomed 96-well microtitre plate (Nunclon A/S, Kampstrupvej, Denmark). Sterile normal saline was added in a well as negative control. After incubating for 90 minutes at 37°C, the wells were washed thrice with Phosphatebuffered saline (PBS, pH 7.2) to remove nonadherent cells and wells were reloaded with respective sterile liquid substrates. Washing and reloading was repeated at intervals of 24 hours and 48 hours. After 48 hours, wells were washed thrice with PBS and stained with 100µl of 1% safranine (w/v) in 95% ethanol for 1 minute. After washing off excess stain with PBS, the wells were observed under inverted microscope under 200X magnification [Ramage et al.,2001]. Subsequently their readings (optical densities) were also measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450 nm UV light (iMark MicroPlate reader, BioRad, USA). The first round of tests were carried out with Candida albicans ATCC 90028 and C. tropicalis ATCC 750 strains and then with randomly selected clinical isolates. All tests were carried out three times (in triplicate). In a second set of experiment, Pyocyanin was extracted from Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates by the method described by Vinckx and co-workers [Vinckx et al., 2001]. Briefly, 1 loopful Pseudomonas aeruginosa colony was grown overnight at 37°C in 5 ml Peptone water containing 1% Glucose(w/v), and then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes. To the cell free supernatant, equal volume of chloroform (Ranbaxy SRL, New Delhi, India) was added and it was again incubated at 37°C overnight after thorough shaking. After that the chloroform phase was purified from the bottom and to it, equal volume of acidified distilled water (pH: 4) was added. After another incubation overnight at 37°C , the watery phase was separated out in a sterile test tube and its pH brought to 7.0 (neutral pH) by adding 1 M NaOH to it. The resultant solution was purified extracted pyocyanin and its fluorescence was checked in an Ultraviolet hood. Yeast isolates were suspended in- a) YPD, and b) pyocyanin and turbidity of both was adjusted to 106 cells/ml. Then 100 µl of both suspensions were dispensed in wells of Microtitre plate and incubated similarly at 37°C. Wells were washed with PBS and reloaded with respective liquids. After final washing and staining, wells were observed microscopically and readings were noted spectrophotometrically at 450 nm wavelength. The toxic effects of pyocyanin, if any, were observed by inoculating shell vials coated with Hep-2 (Human laryngeal epithelioma) cell line monolayer, incubating at 37°C and observing vials under inverted microscope every 6 hours.
RESULTS
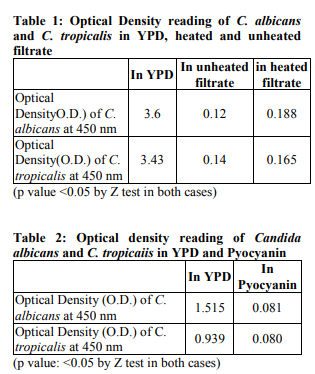
As observed by both the methods (microscopically and spectrophotometrically), biofilm formation in Candida albicans and C. tropicalis was significantly reduced by crude culture filtrate of P. aeruginosa, both heated and unheated, in vitro. The difference in mean values (O.D. readings) of yeasts in YPD and the culture filtrate were calculated by Z-test of significance [Mahajan, 2010]. The differences were found to be highly statistically significant. Mean O.D. of Candida tropicalis in YPD, unheated and heated filtrates were 3.43, 0.14 and 0.165 respectively (p<0.05). The corresponding readings for Candida albicans were 3.6, 0.12 and 0.188 respectively (p<0.05). The results were reproducible when the experiments were done in triplicate. The results have been shown in Table 1. Pyocyanin also showed significant inhibition of biofilms of Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis. The mean O.D. of C. albicans in YPD was 1.515 while that in Pyocyanin was 0.081. The corresponding figures for Candida tropicalis were 0.939 and 0.080 respectively. The results have been shown in Table 2.
DISCUSSION
Invasive candidiasis is now considered the fourth most common cause of bloodstream infection(BSI) worldwide, representing 11% of all cases of BSI [Festekjian et al., 2010]. Attributable mortality in this condition ranges from 10-54%, other than factors like significant morbidity and increased hospital stay [Festekjian et al., 2010 and Eggimann et al., 2011]. Among all the species belonging to the genus Candida, C. albicans is the most common agent causing invasive disease in Europe, but in North and South America as well as in India, species other than C. albicans have become commoner [Eggimann et al., 2011, and Kothari and Sagar, 2009]. Invasive candidiasis is associated with formation of complex, structured microbial communities also known as biofilms, on indwelling devices such as intravascular catheters [Uppuluri et al., 2011]. In fact, studies have shown that Candida spp. is the commonest fungal species associated with biofilm formation [Ramage et al., 2005]. Treatment is difficult in these settings, owing to factors like ability of cells within biofilms to withstand host immune defences, defective drug penetration through biofilms and upregulated drug efflux pumps [Jabra-Rizk et al., 2004, Ramage et al., 2005, Matinez and Fries, 2010]. Therapy can be initiated with Amphotericin B and Echinocandins, although this is often problematic since the former has been documented to be nephrotoxic in about 50% cases and the latter group is too expensive to be used in regular practice [Deray, 2005, Morris and Villman, 2006]. Hence there is imminent need of developing low-cost compounds and natural products that inhibit biofilm production and resultant pathology in invasive candidiasis. A few naturally derived compounds, like secreted products of Aspergillus flavus (Aspirochlorine or organochlorine derivatives), have been found to inhibit growth of Candida albicans [Klausmeyer et al., 2005]. Recent research has also shown that secreted products from Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibit biofilm formation in Candida albicans [Holcombe et al., 2008]. These compounds, being non-toxic to the host cells as found in our sudy, can be precoated on the surface of indwelling devices, to disrupt biofilm formation in Candida spp. in vivo too. Furthermore, in the face of emerging candidemia due to Candida spp. other than C. albicans, the efficacy of P. aeruginosa culture filtrate and especially Pyocyanin in inhibiting biofilm of C. tropicalis is also important. Other workers have reported that Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth itself can inhibit growth and biofilm formation in Candida albicans and C. tropicalis when cocultured in vitro [Bandara et al., 2010]. Since C. tropicalis is becoming increasingly resistant to fluconazole and voriconazole in the Indian scenario at least, the effectiveness of these secreted factors in the filtrate implies that it can be used in biofilm-associated C. tropicalis infection [Kothavade et al., 2010, Eggimann et al., 2011]. Such inhibition of Candidal biofilm formation has also been reported in other bacterial products. Some authors have shown such inhibition by bacterial Lipopolysachharide (LPS) of Serratia spp. and Klebsiella spp., although LPS of some Gram negative bacilli can also enhance Candidal biofilm formation in some cases [Bandara et al., 2010]. In case of our study, this inhibitory effect of culture filtrate of P. aeruginosa was found to be unaltered by high temperature, and hence can be used in febrile states also. This inhibitory effect was presumably due to Pyocyanin, a phenazine compound secreted by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In a mixed environment, Farnesol, a quorum-sensing molecule produced by Candida albicans has been shown to downregulate Pyocyanin production by P. aeruginosa by significantly downregulating the transcription of the pqsA gene. This is possibly a mechanism by which the yeast pathogen protects itself from the toxic effects of Pyocyanin, an iron scavenger and a putative virulence factor of P. aeruginosa [Peters et al., 2012]. So far, the toxic effects of Pyocyanin on Candidal biofilm have not been studied and this study, to the best of our knowledge, is the first one in this regard. The factor in crude filtrate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibiting Candidal biofilm formation was found to be thermostable, a property shared by pyocyanin [Denning et al., 1998]. This compound can further be analysed and assayed in order to study inhibition of Candidal biofilm formation in vivo, too and can pave a way for development of new antifungal agents inhibiting biofilm formation by these yeast pathogens. Thus new anti-biofilm compounds can be synthesized.
CONCLUSION
Pyocyanin can be utilised in vivo to inhibit device-associated biofilm formation by these pathogens.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are sincerely thankful to Dr Deepak Kumar, Junior Resident, Department of Microbiology, KGMU, and Mr Mayank Agnihotri, Junior technician, Mycology section, Department of Microbiology, KGMU for their timely advice and whole-hearted support.
References:
1. Ahmad S, Khan Z. Invasive candidiasis: A review of nonculture-based laboratory diagnostic methods. Ind J Med Microbiol 2012;30:264-69.
2. Bandara HMNH, Lam OLT, Watt RM, Jin LJ, Samaranayeke LP. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides variably modulate in vitro biofilm formation of Candida species. J Med Microbiol 2010;59:1225-34.
3. Bandara HMNH, Yau JYY, Watt RM, Jin LJ, Samaranayake LP. RPseudomonas aeruginosa inhibits in-vitro Candida biofilm development. BMC Microbiology 2010; 10:125-134.
4. Colombo AL, Perfect J, DiNubile M, Bartizal K, Motyl M, Hicks P, Lupinacci R, Sable C, Kartsonis N. Global distribution and outcomes for Candida species causing invasive candidiasis: results from an international randomized double-blind study of caspofungin versus amphotericin B for the treatment of invasive candidiasis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Inf Dis 2003;22: 470-74.
5. Denning GM, Wollenweber LA, Railsback MA, Cox CD, Stoll LL, Britigan BE. Pseudomonas Pyocyanin Increases Interleukin-8 Expression by Human Airway Epithelial Cells. Infect Immun 1998;66(12):5777-5784.
6. Deray, G. Amphotericin B nephrotoxicity. J Antimicrob Chemother 2002; 49 Suppl.S1:37-41.
7. Eggimann P, Bille J, Marchetti O. Diagnosis of invasive candidiasis in the ICU. Ann Int Care 2011;1:37-47.
8. Ferguson D, Cahill OJ, Quilty B. Phenotypic, molecular and antibiotic resistance profiling of nosocomial Pseudomonas eruginosa strains isolated from two Irish Hospitals. J Med Biol Sci 2007;1.
9. Festekjian A, Neely M. Incidence and Predictors of Invasive Candidiasis Associated with Candidemia in Children. Mycoses 2011;54: 146–153.
10. Fungal descriptions. mycologyonline.edu.
11. Gaby WL, Hadley C. Practical Laboratory Test for the identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 1957; 74:356.
12. Holcombe LJ, McAlester G, Munro CA, Enjalbert B, Brown AJP, Gow NAR, Ding C, Butler G, O’Gara F, Morissey JP. Pseudomonas aeruginosa secreted factors impair biofilm development in Candida albicans. Microbiology 2010; 156: 1476–86.
13. Jabra-Rizk MA, Falkler WA, Meiller TF. Fungal Biofilms and Drug Resistance. Emerg Inf Dis 2004.; 10: 14–19.
14. Klausmeyer P, McCloud TG, Tucker KD, Cardellina JH, Shoemaker RH. Aspirochlorine Class Compounds from Aspergillus flavus Inhibit AzoleResistant Candida albicans. J Nat Prod 2005; 68:1300–1302.
15. Kothari A, Sagar V. Epidemiology of Candida bloodstream infections in a Tertiary Care institute in India. Ind J Med Microbiol 2009;27:171-172.
16. Kothavade RJ, Kura MM, Valand AG, Panthaki MH. Candida tropicalis: its prevalence, pathogenicity and increasing resistance to fluconazole. J Med Microbiol 2010; 59: 873–880.
17. Kuhn DM, George T, Chandra J, Mukherjee PK, Ghannoum MA. Antifungal Susceptibility of Candida Biofilms: Unique Efficacy of Amphotericin B Lipid Formulations and Echinocandins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2002;46: 1773–1780.
18. Mahajan BK. Sampling Variability and Significance. In Methods in Biostatistics For Medical Students and Research Workers. 7th Ed 2010. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. New Delhi. 114 .
19. Martinez LR, Fries BC. Fungal Biofilms: Relevance in the Setting of Human Disease. Curr Fungal Infect Rep 2010;4:266–275.
20. Morris MI, Villman M. Echinocandins in the management of invasive fungal infections, part 2. Am J Health-System Pharm 2006; 63:1813-20.
21. Peters BM, Jabra-Rizk MA, O,May GA, Costerton JW, Shirtliff ME. Polymicrobial Interactions: Impact on Pathogenesis and Human Disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 2012;25: 193-213.
22. Raju SB, Rajappa S. Isolation and Identification of Candida from the Oral Cavity. ISRN Dentistry 2011.
23. Ramage G,Saville SP, Thomas DK, LopezRibot JL. Candida Biofilms: an Update. Eukaryot Cell 2005;4:633–638.
24. Ramage G, Walle KV, Wickes BL, LopezRibot JL. Standardized method for in-vitro antifungal susceptibility testing of Candida albicans biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2001; 45:2475-79.
25. Sun Y, Yu S, Sun P, Wu H, Zhu W, Liu W, Zhang J, Fang J, Li R. Inactivation of Candida Biofilms by Non-Thermal Plasma and Its Enhancement for Fungistatic Effect of Antifungal Drugs. PLoS ONE 2012;7: e40629.
26. Vinckx T, Wei Q, Matthijs S, Cornelis P. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa oxidative stress regulator OxyR influences production of pyocyanin and rhamnolipids: protective role of pyocyanin. Microbiology 2010; 156: 678–686.
27. Uppuluri P, Chaturvedi AK, Srinivasan A, Banerjee M, Ramasubramaniam AK, Kohler JR, Kadosh D, Lopez-Ribot JL. Dispersion as an Important Step in the Candida albicans Biofilm Developmental Cycle. PLoS Pathogens 2010 ;6:e1000828.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License