IJCRR - 8(24), December, 2016
Pages: 33-40
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MIGLITOL AND ACARBOSE ADD ON THERAPY INTENDED FOR BETTER GLYCAEMIC CONTROL IN TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Author: Lopamudra Dhar Choudhury, Ranjan Basu, Tanmay Biswas, Apurba Mukherjee, Anup Kumar Das
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objectives: This study was done to find out the comparative efficacy of Miglitol and Acarbose as add on therapy in patients of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Methods: This is a prospective, randomized, patient controlled, open label comparative study involving Type 2 diabetes patients, aged between 35-70 years of either sex of hyperglycaemic with PPBS >180mg%, FBS < 200mg% even after treatment with glimeperide 4mg and Metfomin 2g for at least 3 months.
Results: Miglitol produced a mean reduction of PPBS of 34.12 \? 4.89% and Acarbose produced a mean reduction of PPBS of 30.61 \? 5.86% whereas reduction in HbA1C with Miglitol was 0.58 \? 0.05 g% ad that of Acarbose was 0.47 \? 0.09 g% .The P value in both the cases were > 0.05 signifying Miglitol to be better than Acarbose in terms of glycaemic controlin type 2 D.M.
Conclusions: Type 2 Diabetes forms a significant share of the Diabetic load in India where cereals in the form of carbohydrates form the staple diet of most Indians. Thus \a glucosidase inhibitors like Miglitol and acarbose are sure to play an important role as an add on therapy when first line drugs like sulphonylurea and biguanides fail to control the hyperglycaemia and they have minimum adverse effects, with more or less similar efficacy with Miglitol being better than Acarbose..
Keywords: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Hyperglycaemia, PPBS, HbA1c, Miglitol, Acarbose
Full Text:
Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a large and growing health problem and appears to be associated with urbanization, sedentary lifestyle and dietary habit. The world Health Organization (WHO) has estimated that the global prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing rapidly and India bears a sizeable burden of this epidemic.
The term diabetes mellitus describes a metabolic disorder of multiple etiology, characterized by chronic hyperglycemia with disturbances of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action or both1.Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a progressive disease and once diagnosed, the treatment pathway involves an increasingly complex combination of treatments as the disease worsens2. Therapy however should be individualized according to the degree of hyperglycaemia3.
There are three modalities to Diabetes care. First is aimed at lifestyle modification including physical activity and dietary restrictions. Second involves use of drugs which increase insulin availability like sulphonylurea or insulin secretagogue Repaglinide. Third modality is use of agents that increase insulin sensitivity like Biguanides and Thiazolidinedione or drugs which reduce insulin requirement like α glucosidase inhibitors3. Compared with sulfonylurea, AGIs seem to be inferior with respect to glycemic control, but they reduce fasting and postprandial blood glucose as well as insulin levels4.
The primary objective in the management of type 2 diabetes is glycaemic control along with management or prevention of micro and macro vascular complications. Epidemiological evidence strongly implicates postprandial hyperglycaemia, but not fasting hyperglycaemia, as an important contributor associated with the development of macrovascular complication in type 2 DM5. Techniques that can improve postprandial control include lowering the carbohydrate, encouraging physical activity after meals, adding α glucosidase inhibitors with meals and using rapidly acting insulin analogues5,6. Alpha glucosidase inhibitors (acarbose, miglitol and voglibose) are agents which specifically target post prandial blood sugar level7.When administered along with the first bite of a carbohydrate rich diet, carbohydrate absorption is shifted more distally in the intestine, allowing the sluggish insulin secretory dynamics of Type 2 diabetics to catch up with the carbohydrate absorption, thereby counteracting the post absorptive glucose rise8. These oral antidiabetic agents also have action on the fasting blood glucose level, gastrointestinal hormones and body weight. Thus their efficacy and safety needs to be compared for their therapeutic applications.
Materials and Methods
A prospective, randomized, patient controlled, open label comparative study was done on 50 Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients attending the Diabetic OPD at R.G.KAR Medical College and Hospital starting from July, 2004 and completed with 18 months’ follow for each patient, up till May, 2006. Type 2 diabetes patients, aged between 35-70 years, of either sex, hyperglycaemic with PPBS >180mg%, FBS <200mg% even after treatment with glimeperide 4mg and Metfomin 2g for at least 3 months, were taken into study after proper consent and ethical clearance from the local Ethical Committee.
Patients with abnormal LFT, blood urea or creatinine levels, with h/o inflammatory bowel disease, peptic ulcer, carcinoma, irritable bowel syndrome, any other concurrent drug therapy or life threatening complications, pregnant or lactating were excluded from the study. Type-1 Diabetes patients and Type-2 Diabetes patients on monotherapy or multi-drug therapy with other drug combinations/insulin therapy were also excluded from the study. Sample size was estimated to be 50 with 25 patients in each arm.
At the first visit, patients’ history, general clinical examination, fasting and post-prandial blood sugar levels (assessed by standard glucose oxidase method] and HbA1C levels were noted.
Selected patients were randomly assigned in 1:1 ratio to either of two groups, (25 each). 25 such patients [group A] were advised to take 25mg Miglitol twice daily along with first bite of food at lunch and dinner while 25 patients (group B) were advised to take 25mg acarbose twice daily along with first bite of food at lunch and dinner, as add on therapy.
Patients of each group were advised to attend OPD regularly at 8-12 weekly intervals, with FBS and PPBS reports for dose titration of the test drugs as required. The other parameters like HbA1c, urea and creatinine, blood aspartate transaminase and blood alanine transaminase levels were assessed at 3-6 monthly interval at their follow up visits. Patients with any abnormality regarding blood urea / creatinine, AST or ALT levels were excluded from the study.
According to PPBS levels, in follow up visits, the frequency of the α glucosidase inhibitor was increased to thrice daily or dose titrated upto 50mg. History of any flatulence, diarrhoea, loss of appetite or any other adverse report were noted at each visit. All parameters under study were screened at 6-8 monthly interval and again at the end of the study period. Treatment failure patients were planned to be treated with either thiazolidinediones or nocturnal intermediate acting insulin or a combination of short acting and intermediate acting insulin in addition to combined glimeperide and metformin therapy. Any episode of hypoglycaemia was planned to be managed by instant administration of oral glucose.
Group A patients were ultimately administered 25mg of Miglitol thrice daily while group B patients were given 50mg of Acarbose thrice daily to attain the targeted PPBG level.
The study period was terminated at the completion of 18 months for each patient and the periodically collected data were statistically analyzed for significance.
Statistical Methods : All statistical analysis were performed by using SPSS software , version 16 and data have been summarised as counts and percentages. Paired proportions have been compared using Paired t test and the p value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant .
Results
Comparison of collected data regarding PPBS and HbA1C of patients of either group at first visit, to that obtained at last follow up shows the following results :
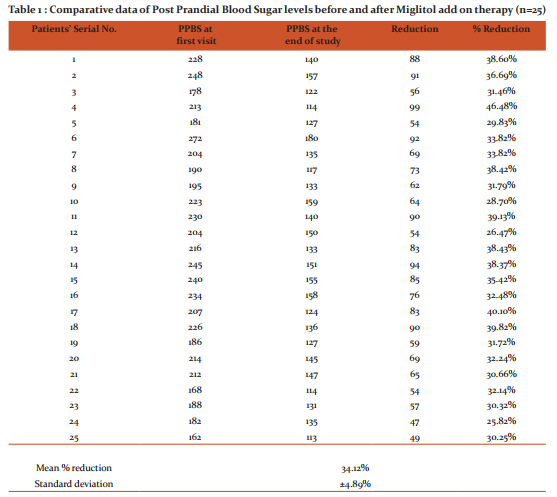
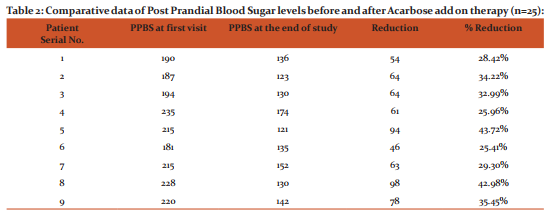
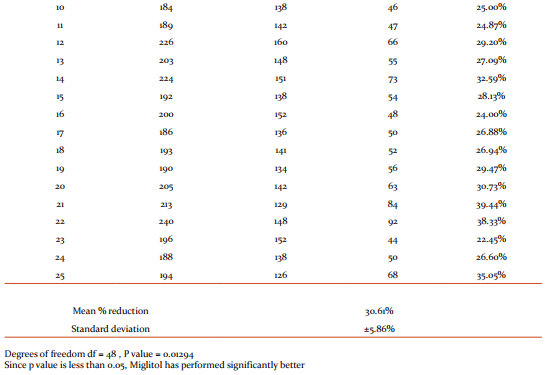
Miglitol as add-on drug titrated to a maximum dose of 25mg thrice daily over 18 month period produced a mean reduction of PPBS of 34.12 ± 4.89% (Table -1). Acarbose as add-on drug titrated to a maximum dose of 50mg thrice daily over 18 month period produced a mean reduction of PPBS of 30.61 ± 5.86% (Table -2).
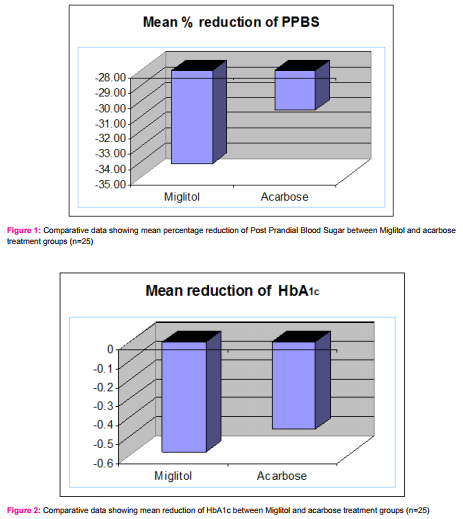
Since the sample size in each group were < 30, t-test was used to analyze the differences between the two readings. The p value obtained was 0.01293, which is less than 0.05. This shows that the efficacy of Miglitol is significantly better than Acarbose (Figure 1).
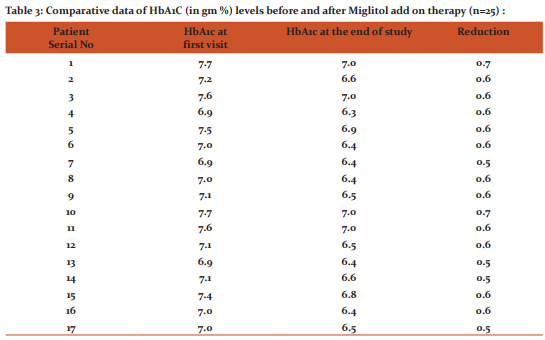
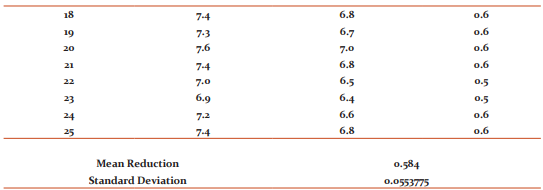
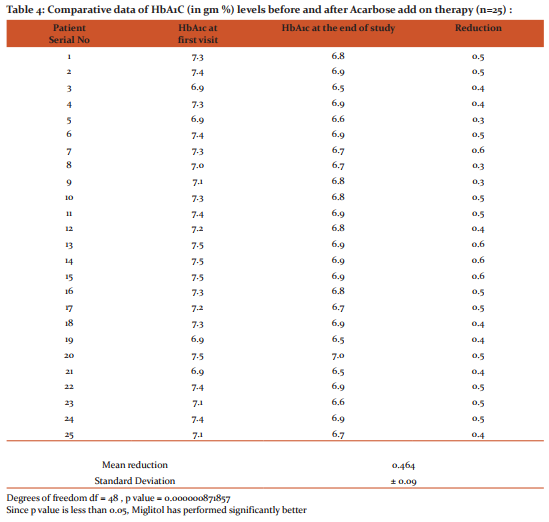
Comparison of the HbA1C readings of patients at the initial phase of study to the data derived at the end of study shows that the mean reduction in HbA1C with Miglitol was 0.58 ± 0.05 g% (Table 3) while that of Acarbose was 0.47 ± 0.09 g% (Table 4) . The p value obtained using t-test was 0.0000008, hence highly significant . This re-emphasizes that the efficacy of Miglitol is significantly better than Acarbose (Figure 2) .
Discussion
Results of PPBS of both groups when compared from initial to subsequent and final visits were found to be better with Miglitol than Acarbose (Table 1 and 2). As most patients complained of diarrhoea following 50mg of Miglitol, the dose was limited to 25mg thrice daily. Patient tolerability with 50mg of Acarbose was better except for flatulence. As dose response with Acarbose was less compared to Miglitol, the dose of Acarbose was increased to a maximum of 50mg thrice daily. LFT showed slight increase with Acarbose after 6 months of therapy but both blood urea, creatinine as well as blood AST, ALT levels were within limits with Miglitol. The main adverse effect following Miglitol therapy was diarrhoea, while both flatulence and diarrhoea were noted with Acarbose. In most patients diarrhoea subsided with continuation of therapy. There was no reported incidence of weight gain, rather most patients under therapy reported about 2-5kg weight loss over the 18 months study period. A few probable symptoms of hypoglycemia was reported in two patients with 50mg Miglitol but was not confirmed biochemically. The symptoms subsided on taking oral glucose tablets as advised.
As per results of the study, it can be stated that alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are safe and efficacious drugs as add on therapy in Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients already on combination therapy of sulphonylurea and metformin. Both α-glucosidase inhibitors, Acarbose and Miglitol are effective in lowering PPBS as well as HbA1c, but efficacy and tolerability of Miglitol was proven to be better than Acarbose.
Previous study by Rybka J. et. al. shows that compared to placebo, Acarbose decreases HbA1c by 0.7% and Miglitol by 0.68% 4 whereas in our study we find Miglitol has decreased HbA1c by 0.58% (Table 3) while Acarbose by 0.48% (Table 4) as minimum dose add on therapy to Glimeperide 4mg and Metformin 2g.. With acarbose dosages higher than 50 mg thrice daily., the effect on Glycosylated Hb remains the same, but the occurrence of side effects increases4 .Similar response was noted on this study.
Clinical trials with Miglitol, in 50-100mg three times daily in type 2 diabetes patients has been found to produce consistent improvement in glycaemic control over a 6-12 month period. Miglitol may prove particularly beneficial in elderly patients and those with hepatic impairment or mild to moderate renal impairment or in whom other oral antidiabetic agents are contraindicated9. Miglitol is a 1-deoxynojirmycin derivative, structurally resembling a glucose molecule which reversibly inhibits intestinal a glucosidase enzymes responsible for the digestion of carbohydrates to absorbable monosaccharides10. In a previous study, Miglitol in combination with metformin used in Type 2 Diabetes patients produced better glycaemic control in respect to fasting and postprandial blood glucose as well as HbA1c levels10. In this study dose of Miglitol kept to minimum was found to be effective when given in addition to Metformin and Sulphonylurea. Hypoglycaemic episodes were not reported during clinical studies with Miglitol at therapeutic doses but miglitol produces a significant depression of post-peak blood glucose compared to placebo or acarbose11,12,13 Acarbose a tetra-saccharide compound is only minimally absorbed after oral administration and is associated with a relatively high incidence of gastrointestinal symptoms secondary to fermentation of unabsorbed carbohydrates14. Miglitol, a 1-desoxynojirimicin derivative, structurally related to glucose and considered second generation α-glucosidase inhibitor, is well absorbed from the small intestine13,15. It was speculated that absorbable α-glucosidase inhibitors such as miglitol would have a lower propensity for gastrointestinal adverse effects16. Absorbable α glucosidase inhibitors can exert an inhibitory effect on non-intestinal α glucosidases present in various cell types but there is little risk of inducing unwanted side-effects when Miglitol is administered at an oral dose of 1mg/Kg body weight17. Miglitol effectively enhances postprandial GLP-1 release and suppresses plasma GIP secretion and significantly lowers feelings of hunger, inducing sensations of satiety in obese-type 2 diabetic patients18. Alpha glucosidase inhibitors must be taken with meals, in which carbohydrates make up a minimum of 40% of the diet, for these agents to be effective19. India is a agriculture based country where maximum people have rice/ wheat as their staple diet. Long term administration of a- glucosidase inhibitors did not induce any appreciable degree of carbohydrate malabsorption20. One drawback of acarbose treatment is an association with hepatotoxicity21, though it was not observed in this study, perhaps due to the minimum dose used.
Conclusion
Type 2 Diabetes forms the greatest burden and holds a significant share of the Diabetic load in India. India being an agriculture based country, cereals in the form of carbohydrates form the staple diet of most Indians. Thus α glucosidase inhibitors are sure to play an important role as an add on therapy when first line drugs like sulphonylurea and biguanides fail to control the hyperglycaemia in these type of patients.
As these drugs have minimum adverse effects, with more or less similar efficacy, they can be included in the oral antidiabetic therapy as second line or add on drugs to control the PPBS in majority of Indians who consume a carbohydrate based diet.
Acknowledgement
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
- Powers A,D’ Alessio D. Endocrine Pancreas and Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes Mellitus and Hypoglycaemia. In ,Laurence Brenton(ed).Goodman and Gillman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th edition, USA, McGraw Hll Companies, 2011;p1238-73.
- Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davdson MB, et al. Medical management of hyperglycaemia in Type 2 diabetes. A consensus statement of American Diabetes Association and the European Association for study of Diabetes. Diabetes care 2009;32:193-203.
- Lesley J. Scott and Caroline M. Spencer; Miglitol a review of its therapeutic potential in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus ; Drugs:2000 March 59(3);521-549
- Rybka J, Goke B, Sissmann J; European Comparative Study of 2- α glucosidase Inhibitors, Miglitol and Acarbose; Diabetes 1999 May:48 Suppl.1;101
- Ceriello A, Colagiuri S,Gerich J, Tuomilehto J. Guideline for management of postmeal glucose.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2008;18:S17-S33.
- Sudhir R, Mohan V. Postprandial hyperglycaemia in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus.Treat Endocrinol 2002;1:105-16.
- Monami M, Lamanna C, Marchionni N, Mannuci E, Comparison of different drugs as add on treatments to Metformin in Type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis,Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2008;79:196-203.
- Scheen AJ.Is there a role for alpha-glucosidase inhibitors in the prevention of Type 2 diabetes mellitus? Drugs 2003;63:933-51.
- Scott LJ; Spencer CM; Miglitol: A Review of its Therapeutic Potential in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Drugs, Vol 59, No, 3, March 2000, pp 521-549(29)
- Jean-Louis Chiasson, Lisa Naditch; The Synergistic Effect of Miglitol Plus Metformin Combination Therapy in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes.Diabetes Care June2001:24(6):989-994
- Johnston PS, Coniff RF, et al; Effects of the Carbohydrate Inhibitor Miglitol in Sulfonylurea-treated NIIDM Patients. Diabetes Care January 1994 ; 17 (1):20-29
- Bastyr EJ, III Stuart CA, Brodows RG, Schwartz S et al. Therapy focused on lowering postprandial glucose, not fasting glucose, may be superior for lowering HBA1c. Diabetes Care 2000; 23;1236-41.
- Jean-Pierre JE Sels,Maya SP Hujiberts, Bruce HR Wolffenbuttle; Miglitol, a new α-glucosidase inhibitor;Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy Nov1999:1:149-156
- Kingma PJ et al; α glucosidase inhibition by Miglitol in NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care 1992 Apr;15:478-83
- Johnston PS. Coniff RF. Hoogwer BJ et al. Effects of the carbohydrate inhibitor miglitol in sulfonylurea treated NIDDM patients.Diabetes Care 1994 Jan:17:20-9
- Joubert PH,Ventor HL et al.The effect of Miglitol and Acarbose after an oral glucose load; a novel hypoglycaemic mechanism.Br J Clin Pharmacol 1990 Sep;30:391-6
- Reuser AJ, Wisselaar HA et al; An evaluation of the potential side effects of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors used for the management of diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Invest 1994 Aug;24 Suppl3:19-24
- Lee A et al; The effects of miglitol on glucagon like peptide-1 secretion and appetite sensations in obese type 2 diabetics. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2002 Sep;4(5):329-35
- Lebovitz HE, Oral therapies for diabetic hyperglycaemia Endocrinal Metab Clin North Am 2001, 30.909-33
- Peter S Johnston, Peter U Feig, Robert F Coniff, et al, Chronic treatment of African-American Type 2 Diabetic-Patients With α glucosidase inhibition. Diabetes Care March 1998;21(3):416-422
- Fujimoto Y. Ohhira M. Miyokawa N, Kitamori S, Kohgo Y; Acarbose–induced hepaticinjury.Lancet1998, Jan31, 351 (9099) :340
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License