IJCRR - 5(8), April, 2013
Pages: 53-62
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH NON-COMPLIANCE OF DIRECTLY OBSERVED TREATMENT-SHORT COURSE FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN A RURAL AND A TRIBAL VILLAGE OF ANDHRA PRADESH-A COMPARATIVE STUDY
Author: Maseer Khan, Manohar Mogili
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: TB is the number one killer infectious disease in developing countries. In 1990 World Health Organization (WHO) report on the Global Burden of Disease ranked TB as the seventh most morbidity-causing disease in the world and expected it to continue in the same position up to 20201.DOTS as the most systematic and cost-effective approach to revitalize the TB control programme in India has been formulated.Non adherence is found to be the major problem in DOTS therapy. Objectives:1)To study the socio-demographic factors of the study population. 2) To compare reasons for non-adherence/non compliance to DOTS in Tribal TB unit (TU) of Dhammapeta and TB unit (TU) of Nandigama (rural TB unit). Study design: The present study is an observational, prospective and community based study. Study population: All newly diagnosed sputum smear positive TB cases under DOTS- Strategy were selected The study population consisted of 174 in rural area and 107 in tribal area. Study period: The study was conducted from 01.04.2006 to 31.04.2007 (including follow-up). Results: In the age group of 15-49 years, the treatment interruption was more in the tribal area (70.73%) when compared to rural area (64.96%). In rural areas the most common factors for non adherence is adverse effects (40.24%), lack of personal interest (31.70%) followed by work load (30.48%).In tribal area the most common factors for non adherence is adverse effects (37.60%), work load (25.64%) followed by lack of personal interest (24.78%). Conclusion: the present RNTCP should develop Information, Education, and Communication package for the target group of patients.
Keywords: DOTS, non-adherence, defaulters
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
TB is the number one killer infectious disease in developing countries. In 1990 World Health Organization (WHO) report on the Global Burden of Disease ranked TB as the seventh most morbidity-causing disease in the world and expected it to continue in the same position up to 20201.
WHO estimated that 1.86 billion people were infected with tuberculosis each year? 8.74 million Develop tuberculosis and nearly 2 million die. This means that someone somewhere contracts TB every four seconds and one of them dies every 10 seconds 2, 3. India accounts for nearly one-third of the global burden of tuberculosis and two-thirds of the total cases in South-East Asia. Nearly 40 percent of the Indian population is infected with the TB bacillus. In1993, WHO declared TB as a global emergency. Every year, 1.8 million new cases of TB occur in the country, of which about 0.8 million are highly infectious New Smear-Positive pulmonary TB cases.4 The disease is most prevalent in the age group 20 to 50 years. About 415,000 deaths occur each year, more than 1,000 every day, or two every three minutes 4.
Despite the National TB Control Programme (NTP) being in existence since 1962, no appreciable change in the epidemiological situation of TB in the country has been observed. To rectify lacunae, the Government of India, decided to give a new thrust to TB control activities by revitalizing the NTP, with assistance from international agencies. In1993 the Revised National TB Control Programme (RNTCP) thus formulated and adopted the internationally recommended directly Observed Treatment Short-course (DOTS)-Strategy, as the most systematic and cost-effective approach to revitalize the TB control programme in India10.
Implementation of RNTCP in Andhra Pradesh:
Andhra Pradesh is the fifth largest state in India with a population of over 80.43 million. About 4,47,523 TB suspects examined, total of 1,07,051 TB patients registered on RNTCP DOTS treatment and 44,867 NSP patients registered on RNTCP DOTS for four quarters of 2006.5 The RNTCP was initially pilot tested in Hyderabad and Medak districts during 1995-96.The Programme extended to six more districts namely Ananthapur Chitoor, Mahabubnagar, Rangareddy, Srikakulam Vijianagaram in 2000 -2001. Cuddapha, Guntur, Nellore, Prakasam joined RNTCP fold in 2002, and Adilabad, Badrachalam, East.Godavari, Khammam, Kurnool, Krishna, Nalgonda, Nizambad, Visakhapatnam, Waragal and West.Godavari districts implemented RNTCP in the year 2003. Karimnagar was the last district to implement RNTCP in the state in 2004.2
The analysis of the RNTCP data over a one-year period from 3rd quarter 2002 to 3rd quarter 2003, shows that the performance in terms of case detection and cure rates in a sample of predominantly tribal districts in the tribal-dominant states of India, was similar to the rest of India.7
Tribal TB unit (TU) of Dhammapeta was the first TB unit (TU) of Andhra Pradesh which achieved 98% of new sputum positive cure rate for the year 2005.8 Where as in rural TB unit (TU) of Nandigama of Krishna district treatment outcome of new sputum positive cases for the year 2005 showing cure rate 85.6%.9 Due to this difference in the new sputum positive cure rate, it was decided to compare the reasons and the factors which showed the tribal unit (98%) to be more effective than the rural TB unit (85.6%).
Objectives:
- To study the socio-demographic factors of the study population.
- To compare reasons for non-adherence/non compliance to DOTS in Tribal TB unit (TU) of Dhammapeta and TB unit (TU) of Nandigama (rural TB unit)
Non compliance to self administered multi drug tuberculosis treatment regimens is common and is the most important cause of failure of initial therapy and relapse. Non-compliance may also result in acquired drug resistance, requiring more prolonged and expensive therapy that is less likely to be successful than treatment of drug susceptible tuberculosis.12
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design: The present study is an observational, prospective and community based study
Study population:
Inclusion criteria: All newly diagnosed sputum smear positive TB cases under DOTS- strategy for the period between 01.04.2006 to 30.09.2006 (i.e. 2nd and 3rd quarter of R.N.T.C.P calendar) were selected because of theire highest priority due to their role in infection spread and in whom treatment outcome is evaluated most correctly by following smear conversion
Study setting: Tribal TB unit (TU) of Dhammapeta of Khammam district and rural TB unit (TU) of Nandigama of Krishna District of Andhra Pradesh was selected.
Sample size and selection: All newly diagnosed sputum smear positive TB cases under DOTS- Strategy were selected as study subjects for the period between 01.04.2006 to 30.09.2006 (i.e. 2nd and 3rd quarter of R.N.T.C.P calendar). The study population consisted of 174 in rural area and 107 in tribal area.
Study period: The study was conducted from 01.04.2006 to 31.04.2007 (including follow-up).
RESULTS
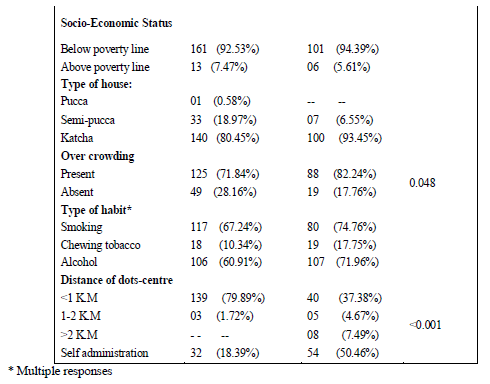
In the present study among rural area out of 174 subjects, 138 were males and 36 were females, whereas in tribal area out of 107 subjects 73 were males and 34 females. Majority of the study subject belong to 15-49 years age group in both rural (65.53%) and tribal area (68.22%). 52.29% and 71.96% of the study subjects in the Rural and tribal area were found to be illiterates. Most of them were agricultural labourers. Housing standards were poor in the study population in rural area, 80.45% of cases are residing in katcha houses where as it was more in tribal (93.45%) area. 90% of study population were living below poverty line. 72% of rural subjects and 82% of the study population were living in Overcrowded houses. Among study population, 7.49% patients were traveling >2KM for their treatment in tribal area, which is more, when compared to rural area.
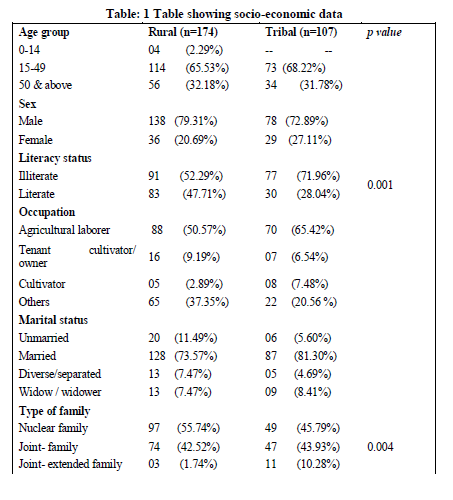
In the present study, out of 174 subjects, 44.82% were cured, 25.88% were Treatment completed, 9.19% died, and 5.17% were failure and 14.94% were defaulters after treatment in the rural area. Out of 107 subjects, 39.25% were cured, 22.44% were Treatment completed, 6.54 % died, and 4.67% were failure and 27.10% were defaulter after treatment in tribal area.
Treatment outcome was found to be better in rural areas (44.82%) when compared to tribal area (39.25%).Defaulters rate was more in tribal area (27.10%) when compared to rural area (14.94%)
Similarly in a study done N. Pandit et al 11 it was noticed that, Majority of study population (85%) was in age group of 15 - 55 years, which is the productive age and 50% of patients were labourers.81% of patients were from socio-economic class IV and V, lower socio economic class.
Gopi PG, et al12noticed that, 39% were aged 45 years or more and it was noticed that, 71% of the cases were males, 39% of the TB cases were illiterate.35% were unemployed in their study. They also noticed that among TB cases 41% were smokers and 31% were alcoholics.
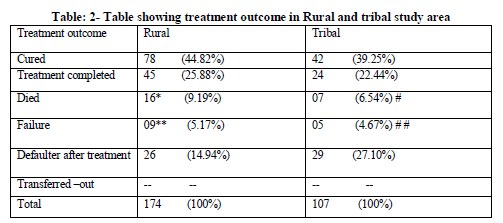
In rural area: *Among 16 deaths, 9cases were Defaulters, ** among 9 failure cases, 5 were Defaulters.
In tribal area: # Among 7 deaths, 6 cases were Defaulters, # # All 5 failure cases were defaulters.
During the treatment period, the total interruption was more in tribal area (76.62%) when compared to rural area (67.33%).
Among this, interruption was more in rural area (33.31%) when compared to tribal area (19.61%) in intensive phase but in continuous phase treatment interruption was more in tribal area (53.26%) when compared to rural area (31.60%).
Among the total treatment interrupted cases, defaulters were more in tribal area (37.37%) when compared to rural area (22.98%).
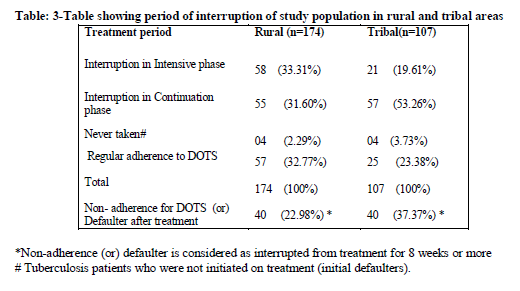
Reasons for treatment interruption included both patient and program factors. In rural areas the most common factors for non-adherence is adverse effects (40.24%), lack of personal interest (31.70%) followed by work load (30.48%).In tribal area the most common factors for non adherence is adverse effects (37.60%), work load (25.64%) followed by lack of personal interest (24.78%).Migration and false beliefs were other reasons for non-adherence which were comparatively more in tribal area.
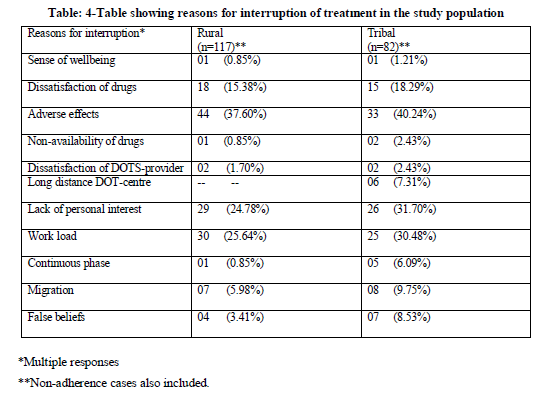
In the age group of 15-49 years, the treatment interruption was more in the tribal area (70.73%) when compared to rural area(64.96%). This is the productive age group who are usually the bread earners for their families, so once they become asymptomatic they tend to resume their regular activities and thereby neglect the treatment. The treatment interruption was more among rural males (82.05%) when to tribal males (74.39%) whereas treatment interruption was more in tribal females (25.61%) when compared to rural females.
The treatment interruption among agricultural laborers was more in tribal area (65.85%) when compared to rural area (47.87%).The treatment interruption among cultivators was more in tribal area (7.32%) when compared to rural area (0.86%). Among the patients who chew tobacco, the treatment interruption was more in tribal area(17.07%) when compared to rural area(7.69%). the treatment interruption was more in tribal area(73.17%) when compared to rural area (66.67%) among alcoholic patients.
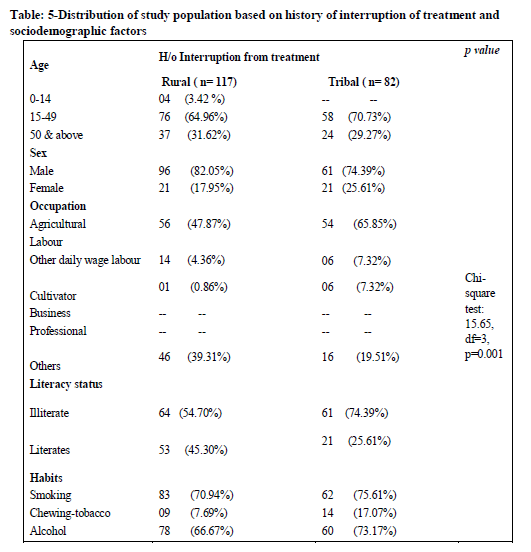
Defaulters were more in productive age group when compared to other age group. In the tribal area 42% of male patients were defaulters when compared with female patients (24%).75% of Defaulters in tribal area were found to be illiterates
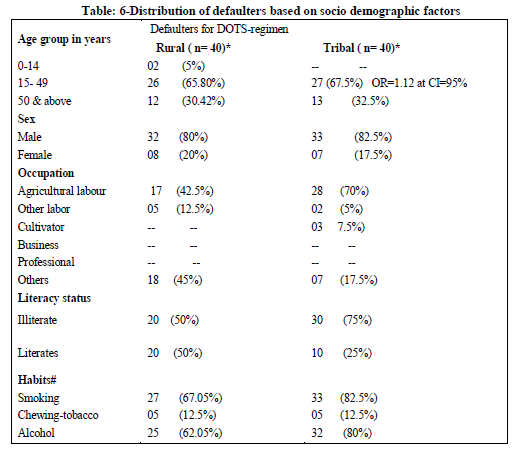
In rural area: * Among 40 defaulters, 9 cases were died and 5 cases were failure at 6th month follow-up.
In tribal area: *Among 40 defaulters, 6 cases were died and 5 cases were failure at 6th month follow-up. # Multiple responses
DISCUSSION
In the present study males were more in both the areas indicating that prevalence of TB is more in males in India. Around 2/3rd of the study population belong to the productive age group 15-49yrs. Most of the study subjects were agricultural labourers and are the bread winners for the families Chronic diseases like Tuberculosis warrant treatment for long periods for which patients have to lose their wages hampering the economic status of the family. Along with these, the cases were living in overcrowded katcha houses and in joint families leaving their family members at risk of contracting the infection. Treatment outcome was found to be better in rural areas when compared to tribal area and also the defaulters rate was more in tribal area. Both in rural and tribal areas maximum TB deaths were defaulters of treatment.
Treatment outcomes was found to be better in rural areas (44.82%) when compared to tribal area (39.25%).Defaulters rate was found to be more in tribal area (27.10%) when compared to rural area (14.94%.All failure cases in tribal area and 5 out of 9 failure cases in rural area were defaulters. This shows that the reason for treatment failure is defaulters. So it is understood that along with treatment health education should also be provided to the patients. Among 16 TB deaths in rural 9 were found to be defaulters and in rural area out of 7TB deaths 6 were defaulters. The reason for a significant proportion of the patients not adhered to treatment could be due to lack of knowledge about the importance of treatment under supervision. It was also found that all the defaulters were illiterates. In a study done in Pakistan10 it was found that around 71% of the Non-adherent patients were illiterates. This directly correlates literacy levels to the Non-adherence of treatment.
Regular adherence to treatment was only 23% and 32% in tribal and rural areas respectively. The most common factors for non-adherence is fear of adverse effects (around40%) followed by lack of personal interest followed by work load. Migration and false beliefs were other reasons for non-adherence which were comparatively more in tribal area. It is therefore clear that to achieve the target of RNTCP, proper counseling of patients regarding various aspects of the disease is a must to ensure compliance.
Treatment interruption was more in the age group of 15-49 years. This is the productive age group who are usually the bread earners for their families, so once they become asymptomatic they tend to resume their regular activities and thereby neglect the treatment.
The treatment interruption among agricultural labourers was more in tribal area (65.85%) when compared to rural area (47.87%). Approximately 70% of the non-adherent patients were found to be alcoholics indicating alcoholism as one of the factor of non-adherence to treatment.
Defaulters were more in productive age group when compared to other age group. In the tribal area 42% of male patients were defaulters when compared with female patients (24%).75% of Defaulters in tribal area were found to be illiterates.
In conclusion, the present RNTCP should develop Information, Education, Communication package for the target group of patients.
CONCLUSIONS
Majority of the study subjects were males and belong to productive age group and are found to be illiterates belonging to low socioeconomic strata. Being male and belonging to productive age group will not only affect health of the patient but also affect the family`s economic status. Lower cure rates and high defaulters are found to be more in tribal area when compared to rural area. So, locally available traditional healers, school teachers and tribal literate youth may be utilized for IEC regarding completion of treatment as per the DOTS strategy.
Treatment outcome was found to be better in rural areas when compared to tribal area .Defaulters rate was more in tribal area when compared to rural area. With this it can be concluded that lack of communication and accessibility is the major problem in the treatment of tuberculosis.
Majority of the people who died with Tuberculosis were defaulters in both the study areas. This shows that constant motivation of the patient is required for the treatment.
Reasons for treatment interruption included both patient and program factors. In rural areas the most common factors for non-adherence is adverse effects ,lack of personal interest followed by work load .In tribal area the most common factors for non- adherence is adverse effects, work load followed by lack of personal interest. Migration and false beliefs were other reasons for non-adherence which were comparatively more in tribal area.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the great help received from the scholars whose articles cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. Authors are grateful to IJCRR editorial board members and IJCRR team of reviewers who have helped to bring quality to this manuscript.
References:
- Murray, Christopher J.L., Lopez, Alan D.: The global burden of disease: a comprehensive assessment of mortality and disability from diseases, injuries and risk factors in 1990 and projected to 2020: summary WHO Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; W 74 96GL-1/1996.
- Tuberculosis programme review- India, 1992: World Health Organization, Geneva. 1992; National Tuberculosis Institute, Summaries of NTI studies, 1997, 101.
- Annual status report 2006, TB control: A.P scenario performance andProgress, page No.12http://tbcindia.nic.in/pdfs/RNTCP%20Annual%20Report%202006%20-%20AP.pdf
- L.S. Chauhan,S.P Agrwal et al.: Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme, Tuberculosis Control in India.
http://www.tbcindia.nic.in/pdfs/Tuberculosis%20Control%20in%20India-Final.pdf
- R.N.T.C.P. Andhra Pradesh annual status report 2006, message of Joint Director (TB) and State TB Officer (AP)
- TRIBAL ACTION PLAN (Proposed for the World Bank assisted RNTCP II Project ) Central TB Division, Directorate General of Health Services Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Nirman Bhavan, New Delhi – 110011, Dated: 10 May 2005
- R.N.T.C.P. Andhra Pradesh annual status report 2006, treatment out come-2005 (GEO, APBC 02) page No.41.
- R.N.T.C.P. Andhra Pradesh annual status report 2006, treatment out come-2005 (GEO, APKN 06) page No.42.
- Khatri G.R, Frieden T.R. The status and prospectus of tuberculosis control in India. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2000; 4: 193-200
- Ibrahim Khan. Assessing adherence and its determinants among TB patients. Chapter4.http://www.bieson.ub.unibielefeld.de/volltexte/2003/332/pdf/06kapitel4.pdf
- Pandit N, Chaudhary SK. A study of treatment compliance in directly observed therapy for tuberculosis. Ind J Community Medicine. 2006;31:241.
- Gopi PG, Vasantha M, Muniyandi M, Chandrasekaran V, Balasubramanian R, Narayanan PR. Risk factors for non-adherence to directly observed treatment (DOT) in a rural tuberculosis unit, South India. Indian J Tuberc. 2007 Apr; 54(2):66-70, PMID: 17575677.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License