IJCRR - 5(11), June, 2013
Pages: 56-63
Date of Publication: 18-Jun-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY OF BLOOD CULTURE ISOLATES AND THEIR ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL OF JAIPUR, RAJASTHAN
Author: Ashina single, Sweta Gupta, Dinesh Jain, Pushpa Durlabhji
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Blood culture is a gold standard for accurate detection of etiological agents of infectious diseases and can assist in choice of appropriate antimicrobial therapy. So, the present study was undertaken to identify the blood culture isolates and to study the antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of blood culture isolates. Methods: Of 500 blood specimens processed from various wards and intensive care units of Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and hospitals, Jaipur, bacteria were identified and isolated. Antibiogram was performed on all positive samples. Results: 19.6% blood culture positive cases out of which 62.2% Gram positive bacteria and 37.8% Gram negative bacteria . Among Gram positive organisms, Staph aureus was found to be the predominant isolate (47.54%) followed by Coagulase negative staphylococci (CONS) (24.5%) ,Streptococcus species (19.6%) and Enterococcus species (8.19%).Methicillin resistance was found in 34.4% strains of Staph aureus.Among Gram negative organisms, most common isolates were Salmonella typhi and Acinetobacter species(32%) followed by Escherichia coli (13.5%), Klebsiella species (8%),Pseudomonas species (8%) and Citrobacter species (5%).1.02% of Candida albicans was also isolated.Conclusion: The present study showed that most of the blood culture isolates, whether Gram positive or Gram negative were multidrug resistant. The rise in antibiotic resistance in blood culture isolates emphasizes the importance of rational and judicious use of antibiotics according to the antibiotic resistance pattern of that institution.
Keywords: Blood Culture, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, Gram Positive Cocci, Gram Negative Bacilli.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Blood born infections are the leading cause of morbidity and mortality throughout the world and one of most common origin healthcare related infections. [1] Microbes present in bloodstream whether constantly or irregularly can worsen the condition of each major organ of the body. Around 200,000 cases of bacteraemia and fungemia were found annually in USA with mortality rates varying from 20-50%.[2] The incidence of bloodstream infections in patients has been reported to correlate with the increasing use of central venous catheters, other predisposing factors including prolonged intensive care unit (ICU) stay, poor hand washing practices of medical staff. [3] The bacterial detection in a patient’s blood has enormous diagnostic and prognostic meaning for clinicians for taking decision of management. Blood cultures report give a crucial information for the assessment of different diseases like pyrexia of unknown origin, systemic and localised infection including meningitis, untreated bacterial pneumonia , septic arthritis, infective endocarditis, unexplained leucocytosis or leucopenia, sepsis etc. [4]
A wide range of bacteria has been described in febrile patients including gram negative bacteria such as E.coli , Psedomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella species,and Gram positive such as Coagulase negative staphylococci (CONS), Staph aureus, streptococcus and enterococcus species. [5] Recognition of antibiotic sensitivity pattern in regular period is compulsory for the clinicians to be alert of the emerging microbes that create a risk to the society, to give safe and effective empirical antibiotics, approve balanced clinical practices. [6] Now so many, isolated bacteria are resistant to potential antibiotics and their linked disorders require early and aggressive management with effective antimicrobial agents. Logical and proper use of these agents requires knowledge of common pathogens and drug resistance patterns. [7] Inadequate information is available about frequency of isolation and resistance to antimicrobial agents in Jaipur Rajasthan. So,the present study has been carried out in the department of microbiology in MGMC& H, representing rural and urban population of Jaipur.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
This study was carried out in the department of Microbiology, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College Hospital, Jaipur (Rajasthan). The test group selected was the population of patients with suspicion of bacteremia / septicaemia / PUO (pyrexia unknown origin) of various OPDs, IPDs, ICUs in the hospital regardless of their age, sex, occupation, religion and ethnicity.
1. Sample Collection:
The samples were collected in the hospital by technician / nursing staff under the appropriate aseptic precautions. 10 to 20 ml of blood was drawn by venipuncture in case of adults and 1 to 5 ml of blood in infants and small children.
2. Sample Culture:
The sample collected was inoculated into two culture bottles each containing 50 ml of brain heart infusion broth. After 48 hrs of incubation at 37º C subculture was made onto McConkey agar and blood agar. The subculture was repeated on seventh day until the final result is negative. The isolates obtained were further identified as per the standard laboratory technique based on CLSI guidelines. [8]
3. Organism isolation and identification
Isolates were identified by gram staining and conventional biochemical tests i.e. Oxidase test, Catalase Test, Indole Test, Methyl-Red (MR) Test ,Vogues-Proskauer (VP) Test, O-F test, Citrate Test, Urease Test, Triple-Sugar-Iron (TSI) Test, Decarboxylase test, Slide Coagulase Test,Tube Coagulase Test.[9]
4. Susceptibility testing
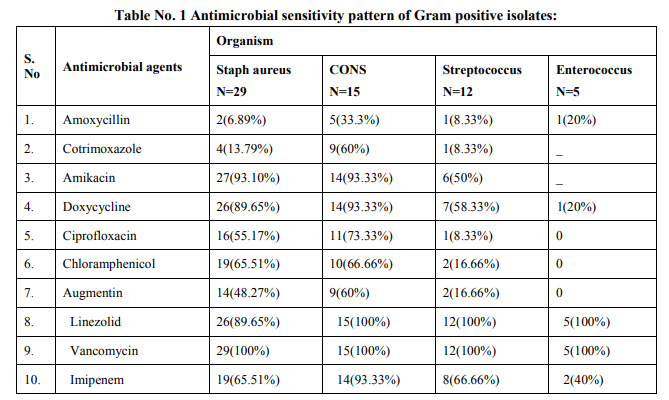
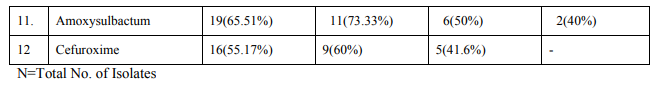
Antibiogram was performed on Muller–Hinton (MH) agar plates with commercially available discs (Hi-media, Mumbai) by Modified Kirby Bauer disc diffusion method and were interpreted as per CLSI (Formerly NCCLS) recommendations. [8] The routine antimicrobial susceptibility tests were put for following antibiotics: For Gram Positive Cocci: Amoxycillin, Linezolid, Cotrimoxazole, Doxycycline, Vancomycin, Ciprofloxacin, Imipenem, Amikacin, Gentamicin, Augmentin, Chloramphenicol, Cefuroxime. For Gram Negative Bacilli: Doxycycline, Augmentin, Ciprofloxacin, Ceftriaxone, Cefuroxime, Co trimoxazole, Chloramphenicol, Amikacin, Ticarcillin, Imipenem, Piperacillin, tazobactum, Amoxycillin, Colistin, Polymyxin B, Tigecycline.
RESULTS
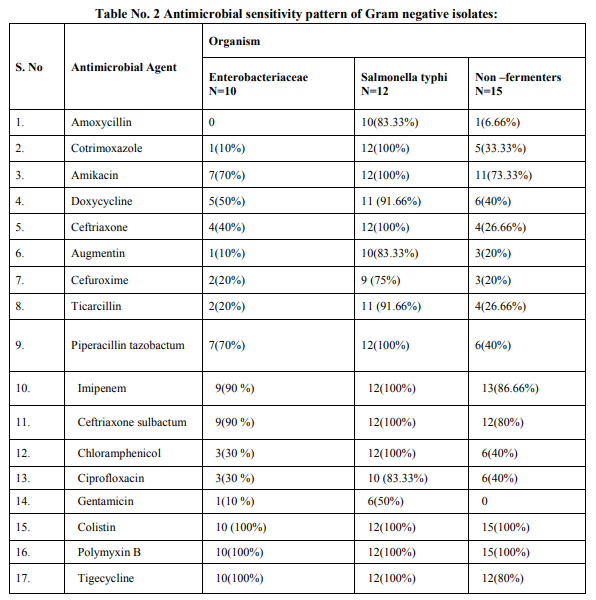
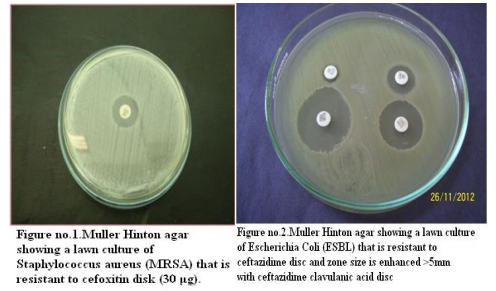
Total 500 samples were taken in this study. The present study showed that there were 19.6% (98/500) blood culture positive cases. Incidence of growth positive cases was found to be more among male patients 64 (65.3%) than in female patients 34 (34.6%).This observation shows that percentage of culture positive cases was found more (27.5%) in chidren and elderly than (23.4%) in infants and adults. Out of total culture positive cases, maximum no were from Intensive care units (53%) followed by indoor patient department (37.7%) and outdoor patient department ( 9%). Out of blood culture positive cases 62.2% were Gram positive bacteria and 37.8% were Gram negative bacteria .Among Gram positive organisms, Staph aureus was found to be the predominant isolate (47.54%) followed by Coagulase negative staphylococci CONS (24.5%) ,Streptococcus species (19.6%) and Enterococcus species (8.19%).Methicillin resistance was found in 34.4% strains of Staph aureus. Among Gram negative organisms, most common isolates were Salmonella typhi and Acinetobacter species(32%) followed by Escherichia coli (13.5%), Klebsiella species (8%),Pseudomonas species (8%) and Citrobacter species (5%).1.02% of Candida albicans was also isolated.
Prabhu et al , Gram positive cocci (64%) and Gram negative bacilli (36%). Bichitrananda S et al ,Gram positive cocci (73%) and Gram negative bacilli (26.8%).[17,13,14] However, in some other studies, rate of isolation of was different as reported by Mehta M et al (80.96%) were Gram negative bacteria and (18%) were Gram positive bacteria , Anubmani et al (46%) Gram positive and (56%) Gram negative bacteria, Atul Garg et al Gram positive bacteria (32.5%) and Gram negative ( 67.5%).[18,19,11] In the present study, among Gram positive organisms, most commonly isolated bacteria was Staph aureus followed by Coagulase negative staphylococci CONS, Streptococcus and Enterococcus. This observation is in concordance with other studies conducted by Arora U et al , their study showed that Staph aureus was the predominant organism followed by CONS. [12]Similar findings reported by K Prabhu et al, Vanitha Rani et al, Karki et al, Mehta M et al. [13,16,17,18] Among Staph aureus, Methicillin resistance was found to be 34.4%. In other studies, percentage of MRSA was 29% as reported by K Prabhu et al, 30% by Anbumani et al, 15% by Barati et al. [13,19,20] Our study showed that out of Gram negative bacteria ,most common were Acinetobacter (32%) and Salmonella typhi (32%) , followed by Escherichia coli (13.5%), Klebsiella species(8%) and Pseudomonas species (8%).This is in concordance with study conducted by Bichitrananda et al in 2011. [14] In our study 1.02% of Candida albicans was isolated. In other study conducted by Vanitha Rani et al, % of Candida spp isolation is 4%.[16] In some other studies conducted by Mehta M et al , most common Gram negative bacteria was Pseudomonas species. [18] E.coli is most common in study conducted by Karki et al. [17] Klebsiella species and Pseudomonas species were most common in study conducted by Anbumani et al. [19] The reason for this difference can be immunocompromised patients, ICU settings in hospitals. In the present study, among the antibiotics used for susceptibility testing for Gram positive isolates, Vancomycin showed the highest activity (100%) against Staph aureus, CONS, Streptococcus species and Enterococcus species. This correlates with other studies conducted by Sharma M et al, Atul Garg et al, Mehta M et al and Anbumani et al.[6,11,18,19] Our study showed that among Gram positive isolates, Staph aureus was found to be most sensitive to Vancomycin (100%) followed by Amikacin (93.33%), Doxycycline (89.65%), Linezolid (89.65%) , Amoxycillin sulbactum (65.51%) and Chloramphenicol (65.51%).This is in concordance with other studies conducted by Atul Garg et al, Karki et al, Mehta M et al. [11,17,18] In our study, it was found that Staph aureus was least sensitive to amoxicillin (6.89%) and cotrimoxazole (13.79%), this observation is in concordance with other studies conducted by Atul Garg et al , Arora U et al, Karki et al. [11,12,17] In the current study among the antibiotics used for suscepitibility testing for Gram negative isolates, ceftriaxone sulbactum was most effective (90%) followed by piperacillin tazobactum (70%) and amikacin (70%) against enterobacteriaceae. The present observation has been well documented by Atul Garg et al, Arora U et al and Roy et al. [11,12,21] Our study showed that in case of non fermenters (Acinetobacter species and Pseudomonas species) , most effective antibiotics were found to be imipenem (86.66%) followed by amikacin( 73.33%).This observation is in accordance with other studies conducted by Atul Garg et al, K Prabhu et al, Mehta M et al. [11,13,18] The present study showed that in case of Salmonella typhi, most effective antibiotics were found to be ceftriaxone (100%) followed by chloramphenicol (100%) and ciprofloxacin
DISCUSSION
Bloodstream infections range from transient bacteremia to septic shock. Blood culture is a gold standard for accurate detection of etiological agents of infectious diseases and can assist in choice of appropriate antimicrobial therapy. Moreover, early identification of bloodstream infections could avoid spreading of microbes into major organs such as brain, heart or kidneys. Early commencement of a sensitive antibiotic is decisive in management of patients with bloodstream infections. The initiation of such therapy is based on knowledge of the likely pathogens and their usual antimicrobial susceptibility pattern. In our study, percentage of blood culture positive cases was found to be 19.6% which correlates with the studies done by different scientists in various cities of India such as D S Murthy et al (2003 Hyderabad) (18.7%), Atul Garg et al (2004 Varanasi) ( 20.5%) , Arora U et al (2006 Amritsar) (20.02%).[10,11,12] Some other studies showed higher parsentage then our study such as Sharma M et al 2008 Rohtak (24.4%), K Prabhu et al 2010 Mangalore (44%),Bichitrananda S et al 2012 Bhuvneshwar (26.3%).[6,13,14] The isolation rate of blood culture positive cases in our study is 19.6% which is lower than other studies. One important reason for the lower isolation rate in present study could be because most of the patients have already received antibiotics before they come to the tertiary care hospital and other reason is that in most of the cases self medication is very common as the medicines are available at the counter. In the present study, percentage of blood culture positive cases among children and elderly was higher ( 27.5%) than that among adults ( 23.4%) which was in concordance with other study done by Sharma M et al in 2008. [6] In our study, there is male preponderance that is 65.3% were males and 34.6% were females which was also observed in another studies conducted at Nigeria by Meremikwu et al (55.1%) males and (44.9%) females , Vanitha Rani et al (60.2%) males and (39.7%) females ,Karki et al (63.3%) males and (36.7%) females. [15,16,17] The reason for this difference is because of gender bias. Females are hesitant enough to highlight their health related issues and they are given lesser importance. Our study reported that the percentage of isolation of blood culture positive cases is higher in ICU Intensive care units (53%) followed by indoor patient department (38%) and outdoor patient department (9%).This is in concordance with studies conducted by Arora U et al in 2006,Bichitrananda S et al in 2011. [12,14] Our study showed that the rate of isolation of Gram positive bacteria is higher (62.2%) than Gram negative bacteria( 37.8%).This observation is in accordance with other studies conducted by Karki et al in Nepal , Gram positive bacteria (66.2%) and gram negative bacteria ( 33.8%) . K (83.33%). This observation has been reported by Atul Garg et al, Vanitha Rani et al. [11,16]
CONCLUSION
So it is concluded that bloodstream infections are an important cause of morbidity and mortality and among the most common healthcare associated infections. The present study showed that most of the blood culture isolates, whether Gram positive or Gram negative were multidrug resistant. The rise in antibiotic resistance in blood culture isolates emphasizes the importance of rational and judicious use of antibiotics according to the antibiotic resistance pattern of that institution. Our study seems helpful in providing useful guidelines for choosing an effective antibiotic in cases of septicemia . It is also important for clinicians to be updated with current data concerning the efficacy of commonly prescribed agents and the selection of antimicrobials to be used for empiric therapy . Specific antibiotic utilization strategies like antibiotic restriction , combination therapy may help to decrease or prevent the emergence of resistance . Antibiotic usage according to the standard antimicrobial susceptibility testing may reduce the incidence of bloodstream infections.
References:
1. Diekma DJ, Beekman SE, Chapin KC. Epidemiology and outcome of nosocomial and community on set blood stream infection. J Clin Microbiol 2003;41:3655-60.
2. Karlowsky JA, Jones ME, Draghi DC, Thornsberry C, Sahm DF, Volturo GA. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibilities of bacteria isolated from blood cultures of hospitalized patients in the United States in 2002. Annals of clinical microbiology and antimicrobials 2004;3:7.
3. Lorente C, Castillo YD,and Rello J.Prevention of infection in the intensive care unit: current advances and opportunities for the future. Current Opinion in Critical Care 2002, 8:461–464
4. Yagupsky P, Nolte FS. Quantitative aspects of septicaemia. Clin Microbiol Rev 1990;3:269-79.
5. Wisplinghoff H,Bischoff T, Tallent SM,Seifert H,Wenzel R P and Edmond M B. Nosocomial Bloodstream Infections in US Hospitals: Analysis of 24,179 Cases from a Prospective Nationwide Surveillance Study. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2004; 39:309– 17
6. Sharma M, God N, Chaudhary U, Aggarwal R, Arora DR. Bacteraemia in children. Indian J Pediatr 2002; 69: 1029 – 32
7. Graham C. Bacteremia and antibiotic resistance of its pathogens reported in England and wales between 1990 and 1998: Trend analysis. Br Med J 2000; 320: 213 – 216.
8. Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests. NCCLS documents M 100 – SIS, 940 West Valley Road. Wayne, PA, USA, 2005; 19087.
9. Forbes BA. Bailey Scott’s diagnostic microbiology, 10th ed. St. Louis, Missouri, Mosby. 1998: 283–304.
10. Murty D S, Gyaneshwari M. Blood cultures in paediatric patients: A study of clinical impact. Indian J Med Microbiol 2007;25:220-4
11. Garg A., Anupurba S., Garg, J. and Sen, M. R. (2007). Bacteriological profile and antimicrobial resistance of blood culture isolates from a University hospital. Journal of the Indian Academy of Clinical Medicine 8(2), 139-143.
12. Arora U Devi P. Bacterial profile of blood stream infections and antibiotic resistance pattern of isolates. J K Sci 2007; 9:186-190.
13. Kavitha Prabhu, Sevitha Bhat, Sunil Rao Bacteriologic profile and antibiogram of blood culture isolates in a pediatric care unit Journal of laboratory Physicians Year : 2010, Volume : 2, Issue : 2, Page : 85-88.
14. Bichitrananda Swain and Sarita otta Bloodstream infections in a teaching hospital,Annals of Biological Research,2012,3(4):192 1928.
15. Meremikwu MM, Nwachukwu C E, Asuquo A E, Okebe J U and Utsalo S J. Bacterial isolates from blood cultures of children with suspected septicaemia in Calabar, Nigeria. BMC Infectious Diseases 2005, 5:110
16. Vanitha rani n, kannan gopal, venkata narendra m, vishwakanth d, v r d nagesh, yogitha m, venkata sunil m, thennarasu palani a retrospective study on blood stream infections and antibiotic susceptibility patterns in a tertiary care teaching hospital International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 4, Issue 1, 2012.
17. Karki S, Rai GK, Manandhar R. Bacteriological analysis and antibiotic sensitivity pattern of blood culture isolates in Kanti Children hospital. J Nepal Paediatric Soc 2010; 30(2):94-97.
18. Mehta MP. Dutta, V Gupta. Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of blood isolates from a teaching hospital in North India. Jpn J Infect Dis 2005;58:174-176.
19. Anbumani N, Kalyani J, Mallika M. Original research distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria isolated from blood cultures of hospitalized patients in a tertiary care hospital. Indian Journal for the practicing doctor 2008;5(2):2008-05 - 2008- 06
20. Barati M, Taher M T, Abasi R, Zadeh M M, Barati M, Shamshiri A R. Bacteriological profile and antimicrobial resistance of blood culture isolates. Iranian Journal of Clinical Infectious Diseases 2009;1(4):87-95.
21. Roy I, Jain A, Kumar M, Agarwal SK. Bacteriology of neonatal septicaemia in a tertiary care hospital of Northern India. Indian J Med Microbiol 2002;20 :156-9.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License