IJCRR - 5(12), June, 2013
Pages: 01-11
Date of Publication: 28-Jun-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A CURRENT REVIEW ON ASSESSMENT OF GENETIC ANALYSIS SYSTEM FOR MEDICINAL PLANTS WITH MICROSATELLITES
Author: Nitin Kumar Verma, Ashwani Kumar, R. K. Deshwal, Vikas Tyagi, Priyanka Rana
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Microsatellites or Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) have been preferred molecular markers ever since their advent in the late eighties. SSR are tandem repeat units of 1 to 6 base pair that are found in many prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. Despite growing rivalry from new sequencing and genotyping techniques, the use of these mobile and efficient markers continues to increase, boosted by consecutive technical advances. Random determined expansions look to be elite against for at least part of microsatellite loci, probably because of their effect on organization of chromatin, gene regulation, recombination, replication of DNA, cell-division cycle, mismatch repair system, etc. The illustration methods used previously for finding new microsatellite loci in sand files remain difficult and time consuming; insilico approach, which includes retrieval and investigation of microsatellites from large amounts of sequence data from sequence data based using microsatellite tools can yield many new candidate markers. To make the most of the latest technical developments and outline the need for a well-established strategy including standardized high-throughput bench protocols and specific bioinformatics tools, from primer design to allele calling. In this review also cover the role of microsatellites in identification and isolation of genotypes, characterization and analysis of genetic diversity, and their interactions in SSR variation.
Keywords: Genetic Diversity, Molecular Marker, Simple Sequence Repeats, Phylogenetic Relationship
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Molecular markers are used in molecular biology and biotechnology experiments where they use to identify a particular sequence of DNA. As the DNA sequences are very highly specific, they can be identified with the help of the known molecular markers which can find out a particular sequence of DNA from a group of unknown (1). Microsatellite based genetic markers, which are distributed across genomes of most of the eukaryotes, fulfill these criteria. Microsatellites also known as Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs) are short stretches of DNA which consist of an array of simple tandemly repeated mono, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta or hexanucleotide repeats such as (A)n, (CA)n, (GA)n, (GTA)n, (ATT)n, (GATA)n, (ATTTT)n, (ACGTCG)n. They are ubiquitous in prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes and are randomly distributed, both in protein coding and non-coding regions. A unique oligonucleotide on each side of the repeat region is chosen for the production of a primer pair for each of the microsatellite loci. PCR products of different lengths can be amplified using primers flanking the variable microsatellite region. Allelic variations among individuals are based mostly on differences in the number of tandem repeats in a microsatellite array providing a ready source of polymorphism (2). Thus, the only way in which alleles can be distinguished is by measuring the total length of the microsatellite allele. Cost effectiveness of the assay is achieved by combining two or more loci for simultaneous analysis through multiplex PCR. SSRs are being used extensively in studies involving Forensics, Population Genetic structure analysis, establishment of Kinship, Conservation Genetics, Linkage Mapping, Marker Assisted Breeding etc (6) .
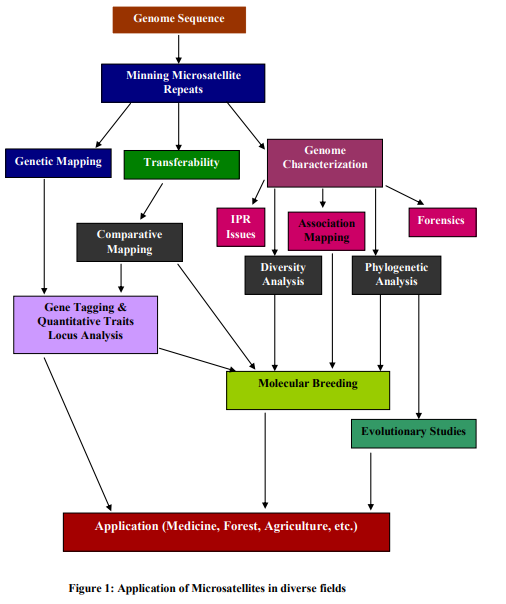
Characterization of Microsatellites
Cephalotaxus oliveri is a scarce medicinal conifer endemic to the south central region of China and Vietnam. In order to study the mating system, population genetics and the genetic effects of habitat fragmentation on Cephalotaxus oliveri, 15 polymorphic and 12 monomorphic microsatellite loci were developed for Cephalotaxus oliveri by using the Fast Isolation by AFLP of Sequences Containing repeats (FIASCO) protocol. The polymorphisms were assessed in 96 individuals from three natural populations (32 individuals per population). The number of alleles per locus ranged from two to 33, the observed and expected heterozygosity per locus ranged from 0.000 to 1.000 and from 0.000 to 0.923, respectively (27). Microsatellite markers were developed for the medicinal plant Isodon rubescens to investigate genetic variability of the species and, in future studies, to assess its relation to the content of pharmacologically active chemicals produced by the plant. Eleven primer pairs were identified and tested in multiple populations of Isodon rubescens and related species (I. henryi, I. enanderianus, I. lophanthoides) from the People's Republic of China. The primers amplified dinucleotide repeats and had between two and 12 alleles per locus in a given population (11) .Microsatellite primers were developed for a Chinese traditional herb, Panax notoginseng, to investigate its genetic diversity and cultivar breeding. Twelve polymorphic microsatellite were assessed in two populations and an assemblage containing individuals from the whole distribution area (24) . Microsatellite markers were developed for the medicinal plant Tripterygium (Celastraceae) to assess its population structure and to facilitate source tracking of plant materials used for medicinal extracts. Ten microsatellite markers were isolated and characterized in Tripterygium wilfordii using an enriched genomic library(28) . We developed a new set of microsatellite markers for studying the genome of the janaguba tree, Himatanthus drasticus (Mart.) Plumel, which is used in folk medicine in northeastern Brazil. Microsatellite loci were isolated from an enriched Himatanthus drasticus genomic library. Nine primer pairs successfully amplified polymorphic microsatellite regions, with an average of 8.5 alleles per locus (2) . Microsatellite primers were developed for a Chinese traditional herb, Panax notoginseng, to investigate its genetic diversity and cultivar breeding. The number of alleles per locus ranged from 3 to 12, with a mean of 5.8; the observed and expected heterozygosity values ranged from 0.0411 to 0.8472 and from 0.0804 to 0.7653, respectively. These new microsatellite markers will be useful for investigating the genetic diversity of this cultivated Panax notoginseng as well as assist in cultivar breeding (23) . Catharanthus roseus is a plant of great medicinal importance, yet inadequate knowledge of its genome structure and the unavailability of genomic resources have been major impediments in the development of improved varieties. For simple sequence repeat (SSR) isolation, a genomic library enriched for (GA)n repeats was constructed from Catharanthus roseus 'Nirmal' (CrN1). A segregating F (2) mapping population consisting of 111 F (2) individuals was generated. For generating the linkage map, a set of 423 codominant markers (378 newly developed and 45 published earlier) were screened for polymorphism between the parental genotypes, of which 134 were identified to be polymorphic (33) . To investigate the profile of gene expression in Salvia miltiorrhiza and elucidate its functional gene, 454 GS FLX platform and Titanium regent were used to produce a substantial expressed sequence tags (ESTs) dataset from the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza (22) . Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. Et Zucc.) Maxim, a traditional Chinese medicinal plant species, has been used extensively as genuine medicinal materials. The raw reads are cleaned and assembled into a total of 76,459 consensus sequences comprising of 17,231 contigs and 59,228 singlets. Trinucleotide SSR is the dominant repeat type (55.2%) followed by dinucleotide (30.4%), tetranuleotide (7.3%), hexanucleotide (4.9%), and pentanucleotide (2.2%) SSR. The dominant repeat motif is AAG/CTT (23.6%) followed by AG/CT (19.3%), ACC/GGT (11.1%), AT/AT (7.5%), and AAC/GTT (5.9%) (53) . Lychnophora pinaster Mart. (Asteraceae) is a Brazilian medicinal plant, size-selected genomic library comprising 280,000 colonies and representing approximately 18% of the chickpea genome, was screened for (GA)n, (GAA)n and (TAA)n microsatellite-containing clones, of which 389 were sequenced. A total of 174 primer pairs gave interpretable banding patterns, 137 (79%) of which revealed at least two alleles on native polyacrylamide gels.Segregation of 46 markers (39%) deviated significantly (P > or = 0.05) from the expected 1:1 ratio (8). Recombinant DNA libraries were constructed for seven chromosome types isolated from two translocation lines of field bean (Vicia faba L.) with reconstructed karyotypes. The insert size ranged between 50 and 2200 bp and the mean length estimated in individual libraries varied between 310 and 487 bp (20) . Identification and Isolation of Microsatellite Clivia is a genus of great horticultural importance and has been widely cultivated as ornamental plants in all over the world. The number of alleles ranged from two to six, observed heterozygosity ranged from 0.04 to 1.00 and expected heterozygosity ranged from 0.04 to 0.83. These microsatellite marker loci provide tools for future studies of Clivia species and cultivars (5) . Medicinal plant species has a valuable economic importance because of its usage as pharmaceuticals, nutritional, as well as its use in popular medication. SDS-based DNA isolation method was used to extract DNA from 11 species of different aromatic and medicinal plants collected from Saudi Arabia. The extracted genomic DNA was found suitable for restriction digestion and PCR amplification (1). The stems of Dendrobium thyrsiflorum RCHB.F. ex ANDRÉ can be processed into an important class of Traditional Chinese Medicine named "Huangcao Shihu," which has diverse curative effects, such as nourishing yin and clearing away unhealthy heat, benefiting the stomach, and promoting the production of body fluid, 14 Dendrobium thyrsiflorum-specific microsatellite markers were developed in this study (48) . Simple sequence repeat (SSR) was used to investigate the genetic diversity and structure of Dendrobium officinale. A total of 15 primer pairs with stable and repeatable polymorphism were screened out from 60 SSR primer pairs developed by the method of microsatellite enrichment by magnetic beads. Fifteen primer pairs were used in Dendrobium cross-species amplification and totally 13 primer pairs were proved to have the transferability in Dendrobium officinale related species (44). In Salvia miltiorrhiza, 159 simple sequence repeats (SSR) were detected, which amounted to 3.79% of the non-redundant starting sequence population. The results showed that 72 primer pairs were successfully amplified in Salvia miltiorrhiza samples to yield and 279 loci with an average of 3.88 loci per primer pair (4) . Herba Cistanches is a common traditional Chinese medicine, Four Cistanche species were found as Herba Cistanches in China herbal markets, including Cistanches deserticola, Cistanches tubulosa, Cistanches salsa and Cistanches sinensis. Standard chemical fingerprints were generated from each of four Cistanche species, which could be identification markers (31). Flow-sorted plant chromosomes are being increasingly used in plant genome analysis and mapping and report on optimization of procedures for primed in situ DNA labeling (PRINS) and cycling-PRINS (C-PRINS) for fluorescent labeling of repetitive DNA sequences on sorted plant chromosomes suitable for their identification. Chromosomes of barley, wheat, and field bean were sorted onto microscope slides, dried, and subjected to PRINS or CPRINS with primers for GAA microsatellites (barley and wheat) or FokI repeat (field bean) (18) . Analysis of genetic diversity Microsatellite markers of an important medicinal plant, Eurycoma longifolia, were developed for DNA profiling and genetic diversity studies. Eighteen polymorphic microsatellite loci were developed for Eurycoma longifolia. The number of alleles detected per locus ranged from four to 16, while the observed heterozygosity ranged from 0.097 to 0.938. The 18 microsatellite markers of Eurycoma longifolia are highly polymorphic and informative (37) . Microsatellite primers were developed for Gynostemma pentaphyllum, a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, to investigate its population genetic diversity. Using the Microsatellite Sequence Enrichment protocol, 14 polymorphic primers sets were identified in four Chinese Gynostemma pentaphyllum populations. The primers amplified di- and trinucleotide repeats with 1-6 alleles per locus, and the observed heterozygosities ranged from 0.000 to 1.000 per population (21) . The different species of the genus Satureja are known as "Marze Kohi" in Iran, herbal drugs of these plants have long been used in traditional medicine. A total of 515 polymorphic DNA fragments were amplified, with a mean of 103 bands per assay (15) . Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. is a well-known traditional Chinese herb. The set of ESTs represents a significant proportion of the Salvia miltiorrhiza transcriptome, and gives preliminary insights into the gene complement of Salvia miltiorrhiza (47) . Tribulus terrestris is medicinal importance in curing urino-genital disorders. Six assays each of AFLP and SAMPL markers and 21 each of ISSR and RAPD markers were utilized. AFLP yielded 500 scorable amplified products, of which 82.9% were polymorphic. SAMPL primers amplified 488 bands, 462 being polymorphic (94.7) (32) . Sixty-one clinical and forty-nine environmental isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii from Australia and the United States were analyzed by random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD), using 12 to 22-mer primers in pairs, and/or PCR fingerprinting with a single primer derived from the microsatellite core sequence of the wild-type phage M13 (5' GAGGGTGGCGGTTCT 3') (34). To analyze the genetic relationship of 9 Marsdenia species from Yunnan. The range of the GS (genetic similarity) value was 0.6675-0.8210. In 9 Marsdenia species, Marsdenia auricularis is a relative of Marsdenia tenacissima. Marsdenia balansae and Marsdenia officinalis have the closest genetic relationship. It is supported by ISSR that the Marsdenia auricularis which is sib species of Marsdenia tenacissima, and the folk medicine of Marsdenia are worthy deep investigation and study (1) . Paris polyphylla var. chinensis is a perennial herb with medicinal properties and found in China. The observed and expected heterozygosities ranged from 0.000 to 0.467, with a mean of 0.247, and from 0.383 to 0.662 with a mean of 0.537, respectively. Six loci (Pp1, Pp3, Pp6, Pp7, Pp9, and Pp12) were found to significantly deviate from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (17) . An effort was made to determine the impact of geographic range on genetic richness and chemical constituents of Valeriana jatamansi Jones, an herb indigenous to the northwestern Himalaya. Overall genetic diversity among the populations was 45 %, with a cumulative range of 35-92 % similarity for most of the high-altitude plants and a comparatively narrow range, 50-88 %, for the population below the altitude of 1,800 m (36) . Microsatellite markers and morphological analyses were used to explore patterns of genetic and morphological diversity in wild populations of Bromelia antiacantha (49). The taxonomic identity of Capsicum species is found to be difficult as it displays variations at morphochemical characters. The six Capsicum species, namely, Capsicum annuum, Capsicum baccatum, Capsicum chinense, Capsicum eximium, Capsicum frutescens, and Capsicum luteum were investigated for phenotypic diversity based on flower color and for genetic differences by molecular makers. Capsicum luteum was found to be rather closer to Capsicum baccatum complex, both phenotypically and genetically (38). Seven polymorphic and transferable nuclear microsatellites were used to investigate the population structure of genetic diversity of Schisandra chinensis and Schisandra sphenanthera for facilitating their conservation and sustainable utilization (45). A genetic linkage map for Bupleurum chinense DC. has not been developed. In this study, with the theory of pseudo-testcross, 96 F1 plants from an intraspecific cross of Bupleurum chinense were used as mapping populations. This map will be provide a basis for studies on gene mapping, map based cloning and marker-assisted selection of important traits in Bupleurum chinense (50). A method was developed based on multiple approaches wherein DNA and chemical analysis was carried out toward differentiation of important species of Sida complex that is being used for commercial preparation. Based on similarity index, S. acuta and Sida rhombifolia found to be most similar (51%). High number of species-specific bands played pivotal role to delineate species at genetic level (39) .
Terminalia trees are being over-exploited because of their medicinal and economical importance leading to loss of valuable genetic resources. The three species are genetically distinct was revealed by all the three marker systems as unique DNA fingerprints were obtained (30). In the identification of Liriope spicata var. prolifera and its affinis species, which are difficult to be differentiated with routine method, based on ISSR molecular marker technology and explore their relationship. In this study screened out 9 effective primers and achieved ISSR electrophoretic spectrum and phylogenetic tree of 15 samples (25) . Njavara is a medicinal rice strain, endemic to Kerala, South India, bestowed with medicinal qualities. Genetic variations and some of the physicochemical properties were studied using standard molecular protocols and compared with those of nonmedicinal rice varieties: Jyothi and IR 64. Genetic similarity coefficient studies showed two well-defined clusters separating Njavara from Jyothi and IR 64. Njavara, Jyothi, and IR 64 have similar amylose equivalent (AE), which was confirmed by microsatellite markers (3) . Paris polyphylla Smith var. yunnanensis (Franch.) Hand.-Mazz. is an important Chinese medicinal herb. Because of overharvesting, the wild populations of this herb have greatly declined and become fragmentized. Although the neighbour-joining cluster analysis seemed to suggest that there was conspicuous genetic differentiation between the natural and cultivated populations, the AMOVA showed that only 4.84% of the total variance existed between groups of natural and cultivated populations, while 67.51% of the variance occurred within populations (10) . RAPD and ISSR markers were used to assess the germplasm genetic diversity among 10 individuals of Rehmannia glutinosa, including 8 cultivars and 2 virus-free lines micropropagated by tip tissue culture.
The 17RAPD primers and 10 ISSR primers generated 177RAPDfragments and 110 fragments, respectively (54). The chemical and genetic methods used in authentication of ginseng, especially the recent advances in microsatellite genotyping. Analysis of well-characterized marker compounds is now the most popular method for identifying the herbal materials and quality control of TCM, eg, ginsenoside profiling for authentication of Panax species (13) . Microsatellites, very short tandemly repeated DNA sequences, are being extensively used in evolutionary genetics and molecular breeding of crop plants, because of their high degree of allelic variability, which is presumably caused by a high rate of mutation that changes microsatellite array length. Compared to animals, higher mutation rates in chickpea are likely to be due to the presence of long (TAA)n microsatellite repeat arrays and the larger number of DNA replications that meristematic initials of the plants undergo before reaching the reproductive phase (40). The analysis of five microsatellite loci in 500 Melaleuca alternifolia individuals produced 98 alleles that were useful for population genetic studies. Considerable levels of observed heterozygosity were recorded (HO = 0.724), with approximately 90% of the variability being detected within populations (12). The genetic variability in agronomically important chickpea accessions (Cicer arietinum L.) as detected by single-locus RFLP probes, RAPD and isoenzyme markers, is rather low. Recently, highly polymorphic microsatellites became the markers of choice for linkage mapping and population studies. Most but not all primers generated distinct fingerprint-like banding patterns after agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining of the amplification products (35) .
CONCLUSIONS
The literature reviewed the fact, that throughput and cost-effectiveness of next-generation sequencing should allow researchers to be more selective in their choice of SSR loci. In particular, sequencing depth should provide sufficient data on sequence variation to focus on conserved regions flanking polymorphic SSR motifs for designing primers, considerably simplifying the whole process of marker testing and considerable progresses have been made in SSR development and genotyping, including in associated bioinformatics. As a consequence, SSR markers are not used to their full power, as shown by our survey of a sample of the recent literature. The use of next generation sequencing techniques instead of cloning and conventional sequencing to obtain sequence data and identify SSRs in such species is just beginning and appears extremely promising. It provides the optimal conditions for subsequent multiplex development by detecting many potential SSRs. The researchers to take a number of precautions and to better evaluate candidate loci, which eventually benefits to the whole genotyping process. The utilization of microsatellites has been demonstrated by a large number of studies applying this marker and by the variety of areas that apply microsatellites for several purposes. Furthermore, new technologies have enabled the development of markers for previously neglected species through the generation of new sequences and a more refined search in databases. With all the difficulties Itemized, we wish to emphasize that for certain phylogenetic problems microsatellites remain the most promising approach and it seems well worth the effort of improving methods for their analysis. The novelty of microsatellite method is that the expected rate of differentiation can be estimated by studying microsatellite mutations. This review showed numerous lines of evidence available, which suggest that SSR genomic distribution; characterization is non-random across coding and noncoding regions, because the evolutionary process leading to length variability at the SSR loci does not follow a simple mutation model, nor does it follow a strict single-stepwise model. Since a significant part of SSR structures are functionally important for gene transcription, translation, chromatin organization, recombination, DNA replication, DNA MMR system, cell cycle, etc.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are thankful to the Executive Director, Shri Ram College, Muzaffarnagar (UP), India for providing the necessary facilities and tools to carry out the project work.
References:
1. Alatar AA, Mahmoud MA, Al-Sohaibani SA, Abd-Elsalam KA.Simple and rapid protocol for the isolation of PCR-amplifiable DNA from medicinal plants.citatioGenet Mol Res. 2012 Feb 13; 11(1): 348-54.
2. Baldauf C, Ciampi MB, Vigna BB, Mori GM, Guedes JP, De Souza AP, Dos Santos FA.Characterization of microsatellite loci in Himatanthus drasticus (Apocynaceae), a medicinal plant from the Brazilian savanna.Am J Bot. 2011 Sep; 98(9): e244-6.
3. Deepa G, Venkatachalam L, Bhagyalakshmi N, Shashidhar HE, Singh V, Naidu KA Physicochemical and genetic analysis of an endemic rice variety, Njavara (Oryza sativa L.), in comparison to two popular South Indian cultivars, Jyothi (PTB 39) and IR 64 J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Dec 23; 57(24): 11476-83.
4. Deng KJ, Zhang Y, Xiong BQ, Peng JH, Zhang T, Zhao XN, Ren ZL. Identification, characterization and utilization of simple sequence repeat markers derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza expressed sequence tags. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2009 Oct; 44(10): 1165-72.
5. Gao W, Zhao H, Liu Y, Li MR, Nurmamat E, Li LF, Ren YY, Xiao HX. Isolation and Identification of Fourtn Meeicrosatellite Markers in Clivia miniata and Clivia nobilis (Amaryllidaceae).Int J Mol Sci 2012; 13(8): 9609-14.
6. Guan Z, Zhang L, Song M, Li H, Zhang Z. Genetic relationship on several medicinal plants in Marsdenia from Yunnan in ISSR marker. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 Jun; 37(11): 1550-2.
7. Geistlinger J, Weising K, Winter P, Kahl G. Locus-specific microsatellite markers for the fungal chickpea pathogen Didymella rabiei (anamorph) Ascochyta rabiei. Mol Ecol. 2000 Nov; 9(11): 1939-41.
8. Haber LH, Cavallari MM, Santos FR, Marques MO, Gimenes MA, Zucchi MI. Development and characterization of microsatellite markers for Lychnophora pinaster: a study for the conservation of a native medicinal plant. Mol Ecol Resour. 2009 May; 9(3): 811-4.
9. Hadian J, Azizi A, Tabatabaei MF, Naghavi MR, Jamzad Z, Friedt W.Analysis of the genetic diversity and affinities of different Iranian Satureja species based on SAMPL markers.Planta Med. 2010 Nov; 76(16): 1927-33.
10. He J, Wang H, Li DZ,Chen SF Genetic diversity of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis, a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, detected by ISSR markers Janta Med. 2007 Oct; 73(12): 1316-21.
11. Harris ES, Klooster MR.Development of microsatellite markers for the medicinal plant Isodon rubescens (Lamiaceae) and related species.Am J Bot. 2011 Oct; 98(10): 293-5. 12. Hüttel B, Winter P, Weising K, Choumane W, Weigand F, Kahl G Sequence-tagged microsatellite site markers for chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Genome. 1999 Apr; 42(2):210-7.
13. Hon CC, Chow YC, Zeng FY, Leung FC. Genetic authentication of ginseng and other traditional Chinese medicine. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2003 Sep; 24(9): 841-6.
14. Hufford KM, Kochert G, Hamrick JL. Microsatellite primers and amplification of aborted embryos in Platypodium elegans J. Vogel (Fabaceae, Papilionoideae).Mol Ecol. 2000 Aug; 9(8):1174-6.
15. Heubl G.New aspects of DNA-based authentication of Chinese medicinal plants by molecular biological techniques.Planta Med. 2010 Dec; 76(17): 1963-74.
16. Joshi RK, Kar B, Nayaand Schisandra sphenanthera revealed by nuclear microsatellites.S21.Exploiting EST databases for the mining and characterization of short sequence repeat (SSR) markers in Catharanthus roseus L. Bioinformation. 2011 Feb 7; 5(9): 378-81.
17. Koblízková A, Dolezel J, Macas J. Subtraction with 3' modified oligonucleotides eliminates amplification artifacts in DNA libraries enriched for microsatellites. Biotechniques. 1998 Jul; 25(1): 32-4.
18. Kubaláková M, Lysák MA, Vrána J, Simkoá H, Cíhalíková J, Dolezel J. Rapid identification and determination of purity of flow-sorted plant chromosomes using CPRINS. Cytometry. 2000 Oct 1; 41(2): 102-8.
19. .Koblízková A, Dolezel J, Macas J. Chromosomal localization and distribution of simple sequence repeats and the Arabidopsistype telomere sequence in the genome of Cicer arietinum L Chromosome Res. 1998 Feb; 6(2): 97-104.
20. Koblízková A, Dolezel J, Macas J. Construction of chromosome-specific DNA libraries covering the whole genome of field bean (Vicia faba L.).Chromosome Res. 1996 Nov; 4(7): 531-9.
21. Liao H, Zhao Y, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang X, Lu F, Song Z.Microsatellite markers in the traditional Chinese medicinal herb (Cucurbitaceae).Am J Bot. 2011 Mar; 98(3): e61-320.
22. Li Y, Sun C, Luo HM, Li XW, Niu YY, Chen SL. Transcriptome characterization for Salvia miltiorrhiza using 454 GS FLX. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2010 Apr; 45(4): 524-9.
23. Liu H, Xia T, Zuo YJ, Chen ZJ, Zhou SL.Development and characterization of microsatellite markers for Panax notoginseng (Araliaceae), a Chinese traditional herb.Am J Bot. 2011 Aug; 98(8): e218-20.
24. Liu H, Xia T, Zuo YJ, Chen ZJ, Zhou SLDevelopment and characterization of microsatellite markers for Panax notoginseng (Araliaceae), a Chinese traditional herb.Am J Bot. 2011 Oct; 98(10): e274-6.
25. Liu X, Liu Z, Yang M, Chen KL. Study on diversity of Liriope spicata var. prolifera and its affinis species with ISSR method .Zhong Yao Cai. 2010 Jul; 33(7): 1052-5.
26. Luo H, Li Y, Sun C, Wu Q, Song J, Sun Y, Steinmetz A, Chen S.Comparison of 454- ESTs from Huperzia serrata and Phlegmariurus carinatus reveals putative genes involved in lycopodium alkaloid biosynthesis and developmental regulation.BMC Plant Biol. 2010 Sep 21; 10(5):10- 209.
27. Miao Y, Lang X, Li S, Su J, Wang Y. Characterization of 15 Polymorphic Microsatellite Loci for Cephalotaxus oliveri (Cephalotaxaceae), a Conifer of Medicinal Importance. Int J Mol Sci 2012; 13(9): 11165-72.
28. Novy A, Jones KC Characterization of polymorphic microsatellites for Tripterygium (Celastraceae), a monospecific genus of medicinal importance.Am J Bot. 2011 Oct; 98(10): 280-1.
29. Rossetto M, Slade RW, Baverstock PR, Henry RJ, Lee LS. Microsatellite variation and assessment of genetic structure in tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia-Myrtaceae). Mol Ecol. 1999 Apr; 8(4): 633-43.
30. Sarwat M, Das S, Srivastava PS.Estimation of genetic diversity and evaluation of relatedness through molecular markers among medicinally important trees: Terminalia arjuna, T. chebula .Mol Biol Rep. 2011 Nov; 38(8): 5025-36.
31. Shi HM, Wang J, Wang MY, Tu PF, Li XB. Identification of Cistanche species by chemical and inter-simple sequence repeat fingerprinting. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 Jan; 32(1): 142-6.
32. Sarwat M, Das S, Srivastava PS. Analysis of genetic diversity through AFLP, SAMPL, ISSR and RAPD markers in Tribulus terrestris, a medicinal herb Plant Cell Rep. 2008 Mar; 27(3): 519-28.
33. Shokeen B, Choudhary S, Sethy NK, Bhatia S.Development of SSR and gene-targeted markers for construction of a framework linkage map of Catharanthus roseus.Ann Bot. 2011 Aug; 108(2): 321-36.
34. Sorrell TC, Chen SC, Ruma P, Meyer W, Pfeiffer TJ, Ellis DH, Brownlee AG. Concordance of clinical and environmental isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii by random amplification of polymorphic DNA analysis and PCR fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1996 May; 34(5): 1253-60.
35. Sorrell TC, Chen SC, Ruma P, Meyer W, Pfeiffer TJ, Ellis DH, Brownlee AG.Sorrell TC, Chen SC, Ruma P, Meyer W, Pfeiffer TJ, Ellis DH, Brownlee AG. The potential of microsatellites for hybridization- and polymerase chain reaction-based DNA fingerprinting of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and related species. Electrophoresis. 1995 Sep; 16(9): 1755-61.
36. Sundaresan V, Sahni G, Verma RS, Padalia RC, Mehrotra S, Thul ST.Impact of geographic range on genetic and chemical diversity of Indian valerian (Valeriana jatamansi) from northwestern Himalaya Biochem Genet. 2012 Oct 5; 11 (79-10): 797- 808.
37. Tnah LH, Lee CT, Lee SL, Ng KK, Ng CH, Hwang SS.Microsatellite markers of an important medicinal plant, Eurycoma longifolia (Simaroubaceae), for DNA profiling.Am J Bot. 2011 May; 98(5): e130- 2.
38. Thul ST, Darokar MP, Shasany AK, Khanuja SP Molecular profiling for genetic variability in Capsicum species based on ISSR and RAPD markers.Mol Biotechnol. 2012 Jun; 51(2): 137-47.
39. Thul ST, Srivastava AK, Singh SC, Shanker KGenetic and chemical diversity of high mucilaginous plants of Sida complex by ISSR markers and chemical fingerprinting. Mol Biotechnol. 2011 Sep; 49(1): 77-81.
40. Udupa SM, Baum M. High mutation rate and mutational bias at (TAA)n microsatellite loci in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Mol Genet Genomics. 2001 Aug; 265(6): 1097-103.
41. Udupa SM, Robertson LD, Weigand F, Baum M, Kahl G. Allelic variation at (TAA)n microsatellite loci in a world collection of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) germplasm. Mol Gen Genet. 1999 Mar; 261(2): 354-63.
42. Vardevanian PO, Minasbekian LA, Parsadanian MA DNA homology in various strains of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 2000; (1): 27-30. Russian.
43. Winter P, Pfaff T, Udupa SM, Hüttel B, Sharma PC, Sahi S, Arreguin-Espinoza R, Weigand F, Muehlbauer FJ, Kahl G. Characterization and mapping of sequencetagged microsatellite sites in the chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genome. Mol Gen Genet. 1999 Aug; 262(1): 90-101.
44. Xie ML, Hou BW, Han L, Ma YH, Ding XY Development of microsatellites of Dendrobium officinale and its application in purity identification of germplasm. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2010 May; 45(5): 667-72.
45. Y, Wen X, Huang H.Genetica..Genetic diversity and population structure of two important medicinal plant species Schisandra chinensis 2011 Apr; 139(4): 497-503.
46. Yu K, Park SJ, Poysa V, Gepts P. Integration of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers into a molecular linkage map of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Hered. 2000 NovDec; 91(6): 429-34.
47. Yan Y, Wang Z, Tian W, Dong Z, Spencer DF.Generation and analysis of expressed sequence tags from the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza. Sci China Life Sci.2010 Feb; 53(2): 273-85.
48. Yuan YH, Hou BW, Xu HJ, Luo J, Ding XYIdentification of the geographic origin of Dendrobium thyrsiflorum on Chinese herbal medicine market using trinucleotide microsatellite markers Biol Pharm Bull. 2011; 34(12): 1794-800.
49. Zanella CM, Bruxel M, Paggi GM, Goetze M, Buttow MV, Cidade FW, Bered Genetic structure and phenotypic variation in wild populations of the medicinal tetraploid species Bromelia antiacantha (Bromeliaceae).Am J Bot. 2011 Sep; 98(9): 1511-9.
50. Zhan QQ, Sui C, Wei JH, Fan SC, Zhang J. Construction of genetic linkage map of Bupleurum chinense DC. using ISSR and SSR markers.Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2010 Apr; 45(4): 517-23.
51. Zheng JY, Wang H, Chen XX, Wang P, Gao P, Li XNMicrosatellite markers for assessing genetic diversity of the medicinal plant Paris polyphylla var. chinensis (Trilliaceae.,.Genet Mol Res. 2012 Aug 6; 11(3): 1975-80.
52. Zhang ZR, Yang J, Sun Y, Gao TG, Li DZ, Xue CY.A set of novel microsatellite markers developed for the traditional Tibetan medicinal plant Halenia elliptica (Gentianaceae).Am J Bot. 2011 Jul; 98(7): e173-5.
53. Zeng S, Xiao G, Guo J, Fei Z, Xu Y, Roe BA, Wang Y. Development of a EST dataset and characterization of EST-SSRs in a traditional Chinese medicinal plant, Epimediumsagittatum (Sieb. Et Zucc.) Maxim. BMC Genomics. 2010 Feb 8; 11: 94
. 54. Zhou YQ, Jing JZ, Li ZY, Zhang BH, Jia JF. Assessment of genetic diversity of Rehmannia glutinosa germplasm detected by RAPDs and ISSRs. Yi Chuan. 2004 Nov; 26(6): 922-8.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License