IJCRR - 9(12), June, 2017
Pages: 01-10
Date of Publication: 24-Jun-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Impact of Heavy Metals and Other Factors on Soil Acarines in Four Different Edaphic Habitats in and Around a Metropolitan Township
Author: Manabendra Nath Moitra
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Objectives: The objective was to examine the nature, the extent and the variation of the impact of edaphic factors and heavy metals (Pb, Zn, Cu) on soil acarine populations at different disturbed habitats and at a forest site in and around a metropolitan township.
Method: Four differently used edaphic habitats \? a solid waste disposal site, a roadside area, sides of a sewage canal and a natural forest in and around Kolkata were selected for the study. Sampling was conducted for three years with 30 days interval.
Results: Soil moisture and organic carbon exhibited statistically significant and positive correlation with the mite population in all the sites (p< 0.05), while soil temperature and heavy metals showed weak or strong negative effect in most instances. Solid waste disposal site appeared worst affected.
Conclusion: Edaphic factors and accumulation of heavy metals appeared to render more or less similar impact on acarine populations at the disturbed site irrespective of the nature of the habitats; at the forest site, the nature and the extent however differed.
Keywords: Soil mite, Edaphic factors, Heavy metals, Polluted sites
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Among soil mesofauna, Acari is one of the major microarthropod groups and is often found to constitute the largest fraction of them (Bhattacharya, 1979; Choudhuri and Pande, 1981; Sanyal, 1982). Their importance owing to their high numerical abundance and diversity in the context of edaphic environment is well established (Crossley, 1977; Heneghan et al., 1998). Population abundance of mites in soil vary in relation to various environmental factors like temperature, moisture, organic matters, nutrient availability etc. (Choudhuri and Pande, 1981; Sanyal, 1982; Ghatak and Roy, 1991; Tousignant and Coderre, 1992; Rutigliano et al., 2013; Bokhorst et al., 2014). The ecological study of soil microarthopods including mites in polluted or ecologically disturbed areas has drawn the attention of many researchers in different parts of the world (Russek, and Marshall, 2000; Zaitsev and van Straalen, 2001; Iloba and Ekrakene, 2008; Sarkar et al., 2015; Manu et al., 2017). In India however, a few studies on different groups of soil microarthropods in degraded and polluted areas have been attempted (Hazra et al., 1982; Hazra and Choudhuri, 1990; Bhattacharya and Chakraborti, 1994; Ghosh et al., 2007), but specific studies relating edaphic factors and abundance of acarines in degraded or polluted sites is limited when the magnificent variability of observations in their ecology is considered. The present work was therefore taken up to deal with this aspect and to add up to the information base necessary for future assessment of the environmental conditions and biomonitoring as well.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Four differently used edaphic habitats – a solid waste disposal site, a roadside area, sides of a sewage canal and a natural forest in and around Kolkata were selected for the study. At each of the sites, five sub-plots of 1 m2 area were marked for the collection. Three cores of samples up to 15 cm depth were collected from each of the sub-plots.
1. Dhapa (Site-I): This is a dumping ground of city wastes, located by the side of Eastern Metropolitan Bypass and is spread over an area of 35 hectares. Vegetation was sparse in the selected site. Jacaranda mimosaefolia (Bignoniacae), Calotropis procera (Asclepiadaceae), Datura metel (Solanaceae) and Lantana camara (Verbinaceae) etc. were found in the area.
2. Sides of VIP-Barasat road (Site-II): VIP-Barasat road is one of the main arterial roads of North Kolkata connecting Ultadanga and Barasat and experiences heavy vehicular movement daily. The present site therefore has been considered as degraded. Euphorbia hirta (Euphorbiaceae), Colocasia esculenta, Datura metel (Solanaceae), Amaranthus sp. (Amaranthaceae), Acacia auriculiformis (Mimoseae), Michelia champaka, Euphorbia sp. (Euphorbiaceae), Saccharum spontaneum (Poaceae), Calotropis sp. (Asclepiadaceae) were among the common vegetation at the site.
3. Tollygunj Nalah (Site-III): Tollygunj Nalah or Tolly nullah is a remnant of ‘Adi Ganga’. Nowadays this nulah receives a large amount of sewage daily from the adjoining human settlements as well as the small industries that have mushroomed around it. The sampling site selected for the present study was located in between Garia metro station and Garia rail station on the embankment of the nulah. Poinciana regina (Leguminosae), Musa sp. (Musaceae), Tamarindus sp. (Leguminosae), Ricinus communis (Euphorbiaceae) and Saccharum sp. (Poaceae) abounded the sampling site.
4. Chintamani Abhyaranya, Narendrapur (Site-IV): This abhayaranya is located near Narendrapur Ramkrishna Mission in south Kolkata. Dalbergia sp. (Papilionateae), Saraca indica (Annonaceae), Terminalia arjuna (Combretaceae), Adina sp. (Rubiaceae) Tamarindus sp. (Leguminosae), Ricinus communis (Euphorbiaceae), Saccharum sp. (Poaceae), and Dryopteris sp. (Polypodiaceae) constituted the dominant vegetation at the site.
Sampling:
A cylindrical steel holder, an iron rod and a stainless steel core with 5 cm internal diameter and 5 cm depth were used for sampling (Dhillon and Gibson, 1962). Sampling was conducted during three consecutive years (2007-2009) with a monthly interval. Three cores of samples from five sub-plots (of 1m2 area) of each of the sites were collected.
Tullgren funnel apparatus modified by Macfadyen (1953) was used for the extraction of soil fauna from the samples in the present work.
Microarthropod groups were separated using needles and fine camel hair brush. They were preserved in tubes with 80% alcohol. Sorting and counting of the microarthropods was done using a wide field stereoscopic microscope with 70x magnification.
Physicochemical parameters:
Physicochemical factors investigated in the present study included soil moisture, soil temperature, organic carbon, pH and heavy metals - copper, lead and zinc.
Soil temperature was recorded at the sites during collection of samples using a soil thermometer. For other edaphic factors, soil samples were tasted in laboratory.
Soil temperature: Soil temperature was recorded from 3 cm depth of soil profile by inserting a mercury thermometer.
Soil moisture: Soil moisture was estimated by following the method suggested by Dowdeswell (1959).
Organic Carbon: Rapid titration method (Walkley and Black, 1934) was followed to estimate the organic carbon content of soil.
Hydrogen ion concentration (pH): The soil pH value was measured from soil suspension using a digital pH meter (Beckman).
Estimation of Heavy metals: Concentrations of three heavy metals– lead, zinc and copper in soil were estimated by atomic absorption spectroscopy using method based on ISO 11047 (1998) (ISO 11047: 1998: Determination of cadmium, chromium, cobalt, copper, lead, manganese, nickel and zinc: Flame and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometric methods). Soil Analyst 700 atomic absorption spectrometer (Perkin Elmer make) was used for the purpose.
Statistical Analysis:
A natural log transformation of the data was made to meet the requirements of normality data sets whenever necessary in the application of parametric statistical methods that included linear correlation analysis, multiple regression analysis and analysis of variance (ANOVA) (Gerard and Berthet 1966). For statistical analysis, software Minitab, version 5.1.2600 service pack 2 was used.
RESULTS
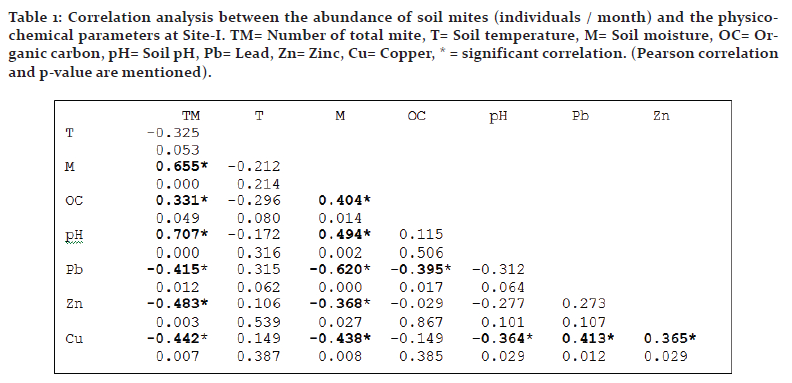
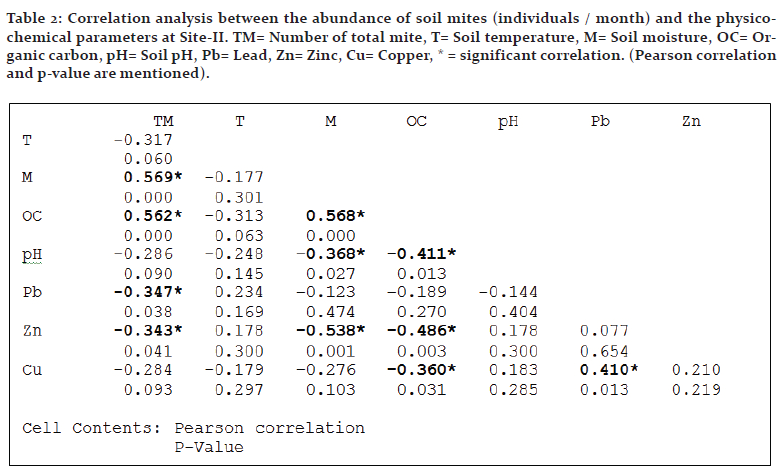
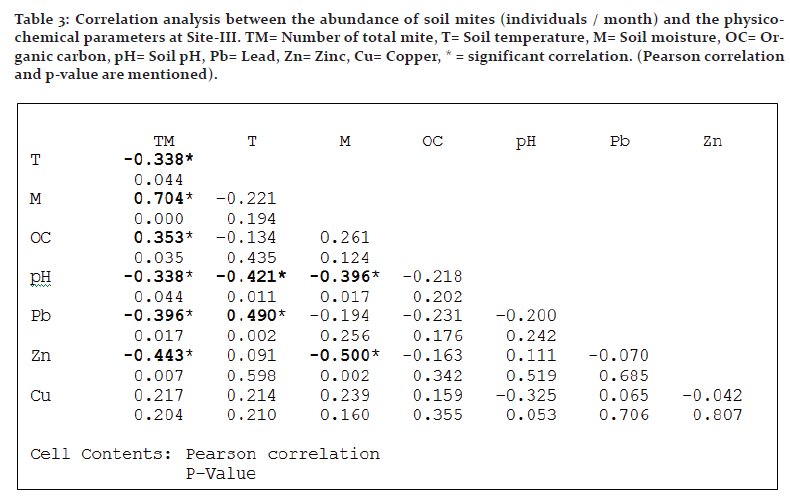
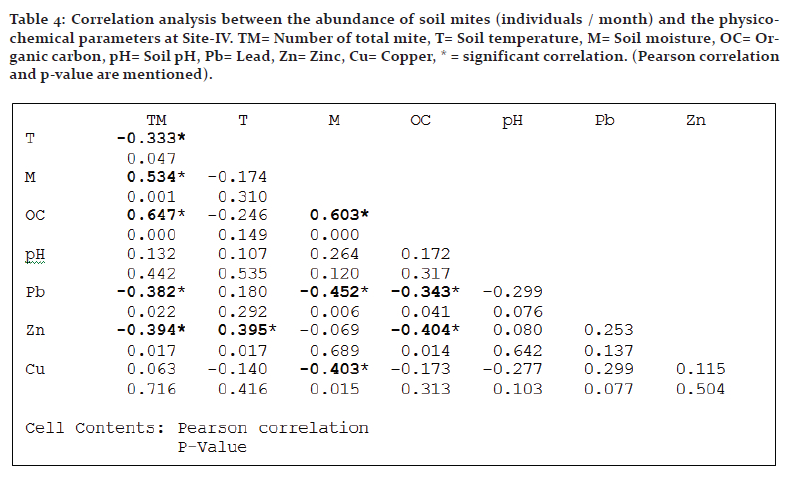
Soil moisture and organic carbon exhibited statistically significant and positive correlation with the mite population in all the sites, while soil temperature and heavy metals showed weak or strong negative effect in most instances. Interrelations between edaphic factors were also studied along with mite population which indicated negative impact of moisture on metal content in many instances (Tables 1-4).
Site-wise observation on correlation between mite population and physicochemical factors:
Site-I: Soil temperature showed no significant correlation with the abundance, while moisture and organic carbon exhibited strong positive correlation (p<0.05). pH was also positively correlated with the abundance (p<0.01). Heavy metals (lead, zinc and copper) showed significant negative impact (p<0.05) (Table 1).
Site-II: Temperature exhibited no significant relationship with population. Soil moisture and organic carbon had positive correlation (p<0.01). Lead and zinc exhibited significant negative effect on abundance (p<0.05). pH and copper showed no significant correlation with the same (Table 2).
Site-III: Temperature exhibited strong negative correlation (p<0.05). Soil moisture (p<0.01) and organic carbon (p<0.05) exhibited significant positive effect on the abundance, whereas for pH, lead and zinc, negative correlations (p<0.05) were observed. Copper showed no significant correlation with the abundance (Table 3).
Site-IV: Soil temperature showed significant negative correlation (p<0.05) with the population abundance. Lead and zinc also exhibited significant negative impact (p<0.05). Soil moisture (p<0.05) and organic carbon (p<0.01) showed positive correlation with the abundance, while pH and copper showed no significant correlation with the same (Table 4).
Regression Analysis (Regression Lines and Multiple Regression):
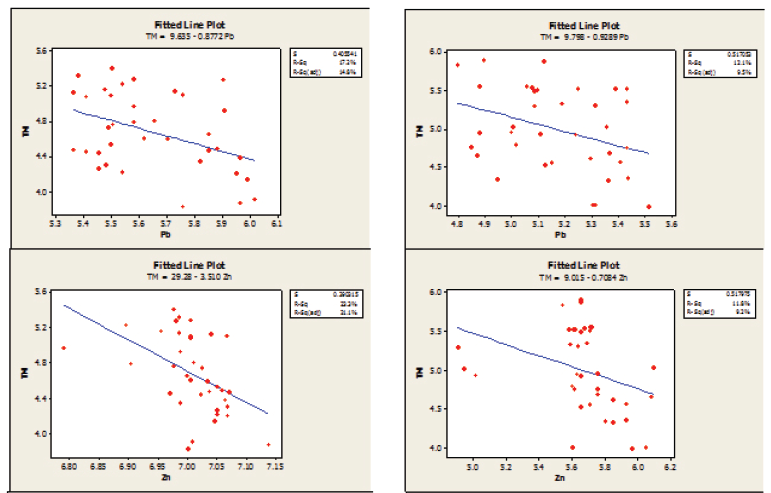
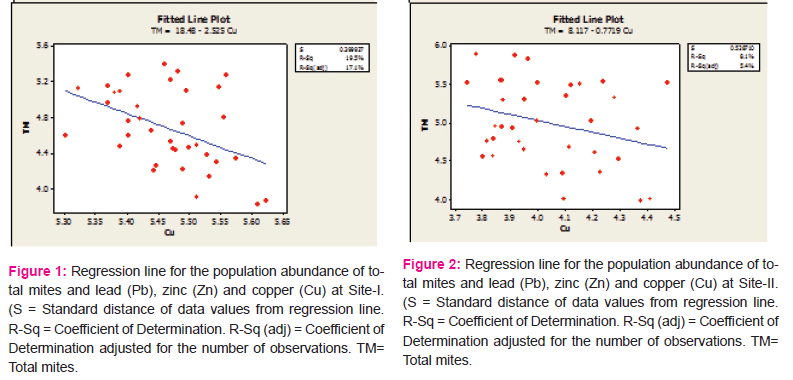
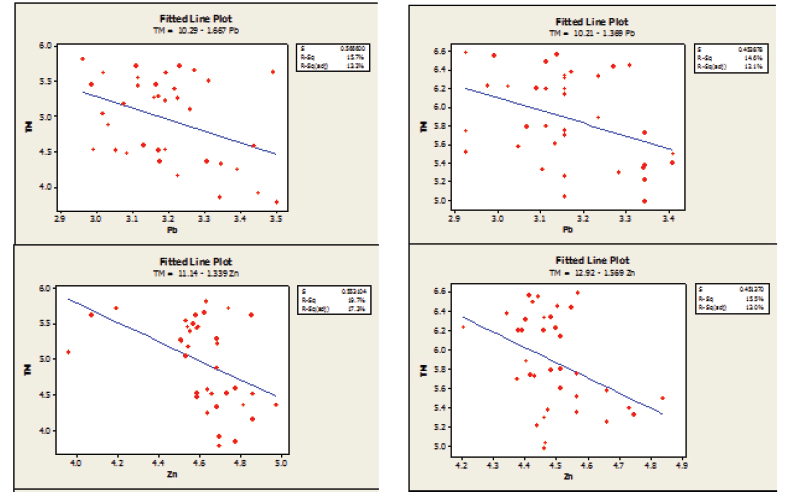
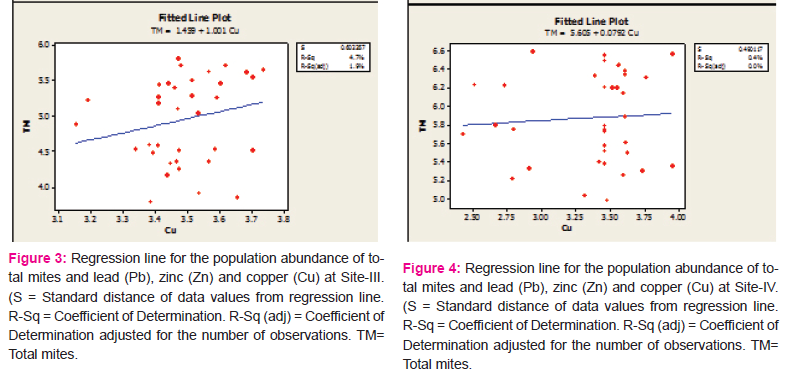
Equations of regression lines depicting interrelationships between edaphic factors and population abundance of mites were worked out and lines were drawn to see the extent of impact of the factors separately (Figs. 1-4). Besides multiple regression analysis were also performed to investigate the collective impact of the factors (Table 5).
Site-wise observations on Regression Lines and Multiple Regression Analysis:
Site-I: The regression lines had negative slope for temperature, lead, zinc and copper and for the rest, the slope was positive. The adjusted R2 (Coefficient of determination) ranged from 8.3% (organic carbon) to 48.5% (pH) (Fig. 1).
Multiple regression equation taking abundance of mites as response and seven physicochemical factors were prepared. R2 value (Coefficient of determination) indicated that the predictors might explain up to 70.9% of variance of the response (mite population). The R2 adjusted for the number of predictors in the model was 63.6% (Table 5).
Site-II: The slopes of regression lines were negative for temperature, pH, lead, zinc and copper and positive for the rests. The adjusted R2 showed a range from 5.4% (copper) to 30.4% (moisture) (Fig. 2).
In multiple regression analysis, R2 value indicated. It showed that the predictors might explain up to 43.3% variance of the abundance of mites, while, 36.6% was the adjusted R2 (Table 5).
Site-III: Positive slopes of regression lines were noticed for soil moisture, organic carbon and copper. Individual factors could explain 1.9% (copper) to 48.5% (soil moisture) of variation of population as the adjusted R2 suggested (Fig. 3).
In multiple regression analysis, R2 value shows that the predictors may explain up to 66.7% of variance of the response while the adjusted R2 was 58.4% (Table 5).
Site-IV: The slopes of regression lines were negative for temperature, lead, and zinc and positive for the rests. Selected factors, taken separately, could explain from 0.4% (copper) to 40.1% (organic carbon) of variance of abundance data as the adjusted R2 showed (Fig. 4). R2 value in the multiple regression analysis indicated that the predictors explained upto 59.5% variance of the response while the adjusted R2 became 49.3% (Table 5).
DISCUSSION
Negative impact of temperature on mite population is a common observation in West Bengal and earlier reported by workers like Sengupta and Sanyal (1991), Sanyal (1996), Sanyal et al. (1999), Roy et al. (2004). In other parts of India, Singh and Yadava (1998) and Chitrapati and Singh (2006) recorded positive interaction in Manipur while negative correlation was observed by Tripathi et al. (2007) at Thar Desert, Rajasthan. Significant positive correlation with temperature however was reported by Choudhuri and Pande (1981) in Darjeeling Himalayas, while some workers reported the same in other parts of West Bengal (Sanyal, 1981b, 1982; Sanyal and Bhaduri, 1982; Sanyal, 1991a). Of them however, significant positive correlation was reported only by Sanyal (1981b). Negative correlation in Darjeeling was recorded by Choudhuri and Pande (1979, 1981) and Ghosh and Roy (2004).
Significant positive correlation between the soil moisture and the mite populations in the present study was in agreement with several studies conducted earlier (Choudhuri and Pande, 1979; Joy and Bhattacharya1981; Sanyal, 1981a, 1981b, 1982; Sanyal and Bhaduri, 1982; Banerjee, 1988; Sheela and Haq, 1991; Sanyal et al., 1999). Choudhuri and Pande (1979, 1981) and Ghosh and Roy (2004) however reported significant negative correlation with moisture in the Darjeeling Himalayas. Besides, Sarkar (1991), Sengupta and Sanyal (1991), Sanyal and Sarkar (1993) and Roy et al., (2004) also recorded similar observations in other parts of West Bengal. Singh and Yadava (1998) and Chitrapati and Singh (2006) recorded positive interaction in Manipur and Tripathi et al. (2007) observed the same at Thar Desert, Rajasthan.
Impact of organic carbon on mite populations was significantly positive at all sites. This is in conformity with the earlier observations made in this region (Choudhuri and Pande, 1979, 1981, 1982; Ghosh and Roy, 2004) and other places in West Bengal (Banerjee, 1974b; Bhattacharya and Raychaudhuri, 1979; Joy and Bhattacharya, 1981; Sanyal, 1981a, 1981b, 1982, 1991b; Sanyal et al., 1999; Roy et al., 2004). Chitrapati and Singh (2006) recorded positive correlation in Manipur and the same was observed at Thar Desert, Rajasthan by Tripathi et al. (2007). Negative impact of carbon on acarines however was reported by Chattopadhyay and Hazra (2000) at a few sites in Kolkata when studying the effect of sewage effluents on arthropods.
pH exhibited a varying relationship with mites in the present work. At Site-I the effect was strongly positive, at Site-III significant negative interaction was observed for total mites, correlation was weak at other sites. Different mode of interactions between the mite populations and soil pH has also been reported from various other studies. Bhattacharya and Raychaudhuri (1979), Sanyal (1981b), Sanyal and Sarkar (1993), Sanyal et al., (1999), Roy et al. (2004) and Tripathi et al., (2007) observed negative correlation, while Joy and Bhattacharya (1981), Sanyal (1981a) and Sarkar (1991) reported either weak or significant positive impact of pH. Choudhuri and Pande (1979, 1981, 1982), and Ghosh and Roy (2004) reported negative correlation with pH at different sites in the Darjeeling Himalayas, West Bengal.
Negative impact of heavy metals on the diversity and the abundance of soil organisms including mite is a common observation as it is evidenced from various studies (Dindal et al., 1975; Hazra and Choudhuri, 1990; Posthuma and van Straalen, 1993; Gergocs and Hufnagel, 2009; Tyokumbur, 2016; Skubala et al., 2016; Manu et al., 2017). There are however some different observations too (Denneman and Van Straalen, 1991; Gackowski et al., 1997; Skubala and Kafel, 2004). Lead and zinc rendered significant negative impact in almost all the instances in the present study while copper exhibited only weak correlation in many cases. Hazra and Choudhuri (1990) reported detrimental effect of lead and copper on mites in West Bengal. Negative effect of lead and copper on the acarine populations was reported by Chattopadhyay and Hazra (2000) at various sites at Kolkata. Hågvar and Abrahamsen (1990) showed that although increasing lead concentration decreased species richness, there were only slight changes in total abundance because the density of several species had grown. High Cu concentration has adverse effects on abundance, growth, and activity of soil fungi which are an essential trophic resource for soil microarthropods including various taxa of mites (Siepel and De Ruiter-Dijkman, 1993; Kuperman and Carreiro, 1997; Gadd et al., 2001) and the negative impact of copper on mites may be functional in this way.
Zaitsev and van Straalen (2001) observed that the mite community as a whole was tolerant to the contamination of heavy metals like lead, zinc and copper by a metallurgical plant. Skubala and Kafel (2004) observed that despite the high Zn concentrations, there was no significant decrease in density compared to the control and thus it could be concluded that Zn does not have a significant effect on this group. Similar result was obtained by Hågvar and Abrahamsen (1990). Skubala et al. (2016) observed positive correlation between the Zn content of oribatid mites and their microhabitat which indicate that the group is prone to bioaccumulation of this metal. Other edaphic factors like moisture, pH etc. are also important and should be taken into consideration while investigating the effects of heavy metals on mite population (Steiner, 1995).
For all the edaphic factors cited above, there should be an optimum range favourable for soil organisms including mites, below or above of which the factor may render detrimental effect on the organisms. Different species have their respective physiological needs and range of tolerance for those factors. The qualitative or quantitative characters of the factors at a given site however, may not always develop as per the biological need. Different studies with same components (either organisms or environmental factors or both remaining same) at different time and place may produce different outcome for the above uncertainty. Further, the factors may or may not remain interlinked and may produce combined effect with greater impact of some more important factors.
CONSLUSION
In the control site, i.e., the forest floor, the mode and the extent of impact of the selected factors differed conspicuously from rest of the sites. The acarine community of the sites with polluted or disturbed habitats however appeared to be affected in a more or less similar pattern in spite of their differentiable mode of perturbations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author conveys his sincere gratitude to the then director of Zoological Survey of India and Dr. Asok Kanti Sanyal, Scientist-F, ZSI for providing laboratory support and literature. The author is also thankful to the staff of the Acarology section of ZSI, New Alipore, Kolkata. Further, the author acknowledges the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The author is also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.

References:
- Bhattacharya T. Climate, soil and soil inhabiting arthropods of Shantiniketan and adjoining areas. Journal of Research, Visva-Bharati 1979; 3(2): 12-23.
- Bhattacharya T, Chakraborti P. Community structure of soil Oribatida of a young Rubber plantation and an adjacent waste land in Tripura (India). In : Advances in Ecology and Environmental Science. PC Mishra, N Behera, BK Senapati, BC Guru (eds). 1994; pp. 65-77.
- Bhattacharya T, Raychoudhuri DN. Monthly variation in the density of soil microarthropods in relation to some climatic and edaphic factors. Entemon 1979; 4(4): 313-18.
- Bokhorst S, Wardle DA, Nilsson MC, Gundale MJ. Impact of understory mosses and dwarf shrubs on soil microarthropods in a boreal forest Chronosequence. Plant and Soil 2014; 379(1-2): 121-133.
- Chattopadhyay A, Hazra AK. Effect of heavy metal contaminated sewage effluents on the soil arthropods in and around Calcutta. Rec. zool. Serv. India 2000; Occasional paper No. 186: 1-107.
- Chitrapati C, Singh TB. The role of abiotic factors in the distributional patterns of acarina and collembola in the sub-tropical forest ecosystem of Manipur. Indian. J. Environ. and Ecoplan 2006; 12(1): 39-45.
- Choudhuri DK, Pande T. High altitude soil animal and their relation with soil factors, with special reference to mites. Rev. Ecol. Biot. Sol. 1979; 16(2): 219-226.
- Choudhuri DK, Pande T. Studies on the population and distribution of high altitude soil acarines in relation to different soil factors. In: Contributions to acarology in India. GP Channa Basavanna (ed). Acarological soc. India, Univ. of Agric. Sci., Bangalore, India, 1981; pp. 147-154.
- Choudhuri DK, Pande T. An ecological study of acarines from soil of Himalayan ecosystem. Geobios News Report 1982; 1: 24-26.
- Crossley DA(Jr). The roles of terrestrial saprophagous arthropods in forest soils: current status of concepts. In: Proceedings in Life Sciences The Role of Arthropods in Forest Ecosystems. WJ Mattson (ed). Springer-Verlag, New York, 1977; pp. 49-56.
- Denneman CAJ, Van Straalen NM. The toxicity of lead and copper in reproduction tests using the oribatid mite Platynothrus peltifer. Pedobiologia 1991; 35: 305- 311.
- Dhillon BS, Gibson NHE. A study of the Acarina and Collembola of Agriculture soils 1. Numbers and distribution in grassland. Pedobiologia 1962; 1: 189-209.
- Dindal DL, Schwart D, Norton RA. Effect of sewage effluent disposal on community structure of soil invertebrates. In: Progress in Soil Zoology. J Vanek (ed). Prague, 1975; pp. 419-427.
- Dowdeswell WH. In: Practical Animal Ecology. Methuen Educational Ltd., London, 1959; pp. 320.
- Gackowski G, Seniczak S, Klimek A, Zalewski W. Soil mites (Acari) of young Scots pine forests in the region polluted by a copper smelting works at G1ogo´w (in Polish). Zeszyty Naukowe ATR, Bydgoszcz, Ochrona S´ rodowiska, 1997; 208: 27-35.
- Gadd GM., Ramsay L, Crawford JW, Ritz K. Nutritional influence on fungal colony growth and biomass distribution in response to toxic metals. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001; 204: 311–316.
- Gerard G, Berthet P. A statistical study of microdistribution of Oribatei (Acari). II. The transformation of the data. Oikos 1966; 17: 142-149.
- Gergócs V, Hufnagel L. Application of oribatid mites as indicators (review). Applied Ecology and Environmental Research 2009; 7(1): 79-98.
- Ghatak TK, Roy S. The role of soil moisture and organic matter on the distribution of acari fauna in the forest floor of Hooghly district, West Bengal. In: Contribution to Acarilogical Researches in India. AB Mukherjee, AK. Som Choudhury, PK Sarkar (eds). Kalyani 1991. pp. 143-158.
- Ghosh SN, Chattopadhyay A, Bhattacharya DK. Studies on road side soil inhabiting ants (Hymenoptera:Formicidae) of Kolkata with special reference to the effects of lead emitted through automobile exhaust. Occassional Paper No. 257. Records of The Zoological Survey of India 2007; Occassional Paper No. 257: 149.
- Ghosh TC, Roy S. Distribution and diversity of acarina community three tea gardens at different altitudes of Darjeeling Himalayas. Proc. Zool. Soc. Calcutta 2004; 57: 87-93.
- Hågvar S, Abrahamsen G. Microarthropods and Enchytraeidae (Oligochaeta) in naturally lead-contaminated soils: a gradient study. Environmental Entomology 1990; 19: 1263-1277.
- Hazra AK, Choudhuri DK. Ecology of subterranean macro and microarthropod fauna in different degraded and polluted soil environment in West Bengal, India. Rec. zool. Surv. India 1990; Occasional Paper No. 120: 1-195.
- Hazra AK, Mukhopadhya P, Guha DK. Sanyal AK. Effects of industrial effluents on population structure of soil microarthropods at Durgapur Steel Plant area: A preliminary report. Proc. Symp. Ecol. Anim. Popul., Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata 1982; 3: 93-98.
- Heneghan L, Coleman DC, Zoub X, Crossley DA(Jr), Hainesc BL. Soil microarthropod community structure and litter decomposition dynamics: A study of tropical and temperate sites. Applied Soil Ecology 1998; 9: 33-38.
- Iloba BN, Ekrakene T. Soil Microarthropods Associated with Mechanic Workshop Soil in Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria. Research Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences 2008; 4(1): 40-45.
- Joy S, Bhattacharya T. Cryptostigmatid population of the soil of a banana plantation in relation to some edaphic factors. In: Progress in soil biology and ecology in India. GK Veeresh (ed). Univ. Agri. Sci. Bangalore, India, 1981; UAS Tech. Series No. 37: 100-106.
- Kuperman RG, Carreiro MM. Soil heavy metal concentrations, microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a contaminated grassland ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1997; 29: 179– 190.
- MacFadyen A. Notes on methods for the extraction of small soil arthropods. J. Animal Ecol. 1953; 22: 65- 77.
- Manu M, Onete M, Florescu L, Bodescu F, Iordache, V. Influence of heavy metal pollution on soil mite communities (Acari) in Romanian grasslands, North-Western Journal of Zoology 2017; e161104
- Posthuma L, van Straalen NM. Heavy metal adaption in terrestrial invertebrates, a review of occurence, genetics, physiology and ecological consequences. Com. Biochem. Physiol. 1993; 106 c(l): 11-38.
- Roy A, Sanyal AK, Santra SC. Biomonitoring of soil quality in agroecosystem with mites as indicator – A preliminary study. Rec. zool. Surv. India. 2004; Occ. Paper No. 218: 1-40.
- Russek J, Marshall VG. Impacts of airborne pollutants on soil fauna. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 2000; 31: 395-423.
- Rutigliano FA, Migliorini M, Maggi O, Ascoli D, Fanciulli PP. and Persiani, AM. Dynamics of fungi and fungivorous microarthropods in a Mediterranean maquis soil affected by experimental ?re. European Journal of Soil Biology 2013; 56(2013): 33-43.
- Sanyal AK. Ecology of soil oribatid mites in an uncultivated field of gangetic delta of West Bengal in relation to soil pH and salinity. In: Progress in soil Biology and Ecology in India. GK Veeresh (ed). 1981a; UAS Tech. series No. 37: 107- 112.
- Sanyal AK. Qualitative and quantitative composition of Oribatei in gangetic delta of West Bengal in relation to edaphic factors. Bull. Zool. Surv. India, 1981b; 4(3): 295-307.
- Sanyal AK. Soil oribatid mites and their relation with soil factors in West Bengal, J. Soil Biol, Ecol. 1982; 2(1): 8-17.
- Sanyal AK. Influence of agricultural practices on the population of soil mites in West Bengal, India. In: Advances in Management and conservation of soil fauna. 1991; GK Veeresh, D Rajagopal, CA Virakthamath (eds). pp. 333-340.
- Sanyal AK. Soil arthropod population in two contrasting sites at Nadia, West Bengal. Environ. Ecol. 1996; 14: 346-350.
- Sanyal AK, Bhaduri AK. Diversity in Soil Mites (Acari) of West Bengal. In: Proceedings of National Seminar on Environmental Biology, AK. Aditya, P Haldar (eds). 1998; pp. 173-179.
- Sanyal AK, Kundu BG, Roy S. Ecology of soil oribatid mites in relation to some edaphic factors in Gangetic Delta of West Bengal. Rec. zool. Surv. India 1999; Occ. Paper No. 177: 1-61.
- Sanyal AK, Sarkar BJ. Ecology of soil oribatid mites at three contrasting sites at Botanical Garden, Howrah, West Bengal. Environment and Ecology 1993; 11(2): 427-34.
- Sarkar S. Studies on microarthropod community in one undisturbed habitat at Tripura with special reference to oribatid mites. In: Advances in Management and Conservation of soil fauna. GK Veeresh, D Rajagopal, CA Virakthamath (eds). Oxford and IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi. 1991; pp 777-788.
- Sarkar SK, Chakraborty K, Moitra MN. On regional variability of major soil microarthropod groups at four different edaphic systems in the northern alluvial plains of Bengal, India. Asian Journal of Biological and Life Sciences 2015; 4(1): 65-70.
- Sengupta D, Sanyal AK. Studies on soil microarthropod fauna of a paddy field in West Bengal, India. In: Advances in Management and conservation of soil fauna. GK Veeresh, D Rajagopal, CA Virakthamath (eds). Bangalore, India. 1991; pp. 789-796.
- Siepel H, de Ruiter-Dijkman EM. Feeding guilds of oribatid mites based on their carbohydrase activities. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 1993; 25: 1491-1497.
- Singh TB, Yadava PS. Seasonal Fluctuation of oribatid mites in a Subtropical Forest Ecosystem of Manipur, North Eastern India. Intl. J. of Ecol. and Env. Sci. 1998; 24: 123 – 129.
- Skubala P, Kafel A. Oribatid mite comunities and metal bioaccumulation in oribatid species (Acari, Oribatida) along the heavy metal gradient in forest ecosystems. Environmental Pollution 2004; 132(1): 51-60.
- Skubala P, Rola K, Osyczka, P. Oribatid communities and heavy metal bioaccumulation in selected species associated with lichens in a heavily contaminated habitat. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. Int. 2016; 8861-88761.
- Steiner WA. Influence of air pollution on moss-dwelling animals: 3. Terrestrial fauna, with emphasis on Oribatida and Collembola. Acarologia 1995; 36(2): 149-176.
- Tousignant S, Coderre D. Niche partitioning by soil mites in a recent hardwood plantation in Southern Quebec, Canada. Pedobiologia 1992; 36: 287-294.
- Tripathi G, Kumari R, Sharma BM. Mesofaunal biodiversity and its importance in Thar desert. Journal of Environmental Biology 2007; 28(2): 503-515.
- Tyokumbur ET. Evaluation of effects of heavy metals on abundance and diversity of soil mites in a tropical landfill. International Journal of Pure and Applied Zoology 2016.
- Walkley A, Black IA. An examination of the Begtjareff method for determining soil organic matters and a proposed modification of chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934; 37: 29-38.
- Zaitsev AS, van Straalen NM. Species diversity and metal accumulation in oribatid mites (Acari, Oribatida) of forests affected by a metallurgical plant. Pedobiologia, 2001; 45(5): 467-479.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License