IJCRR - 5(13), July, 2013
Pages: 58-63
Date of Publication: 17-Jul-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
PREVALENCE OF DIABETIC FOOT AND THE ASSOCIATED RISK FACTORS AT PRIMARY HEALTH CARE LEVEL IN SOUTHWESTERN SAUDI ARABIA
Author: Hassan M. Al-Musa
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: An understanding of the causes of diabetic foot enables early recognition of patients at high risk. The objective of the present work was to study frequency and determinants of diabetic foot among diabetics attending the urban primary health care centers (PHCCs) in Abha City, Southwestern Saudi Arabia. Methods: In this cross sectional study researcher included all diabetic patients attending the seven urban PHCCs in Abha city were studied. Data were collected during 15th November, 2011 to 30th March, 2012. Data were obtained from the chronic diseases files, socio demographic variables ¸type and duration of diabetes, diabetic foot and concomitant conditions were investigated and analyzed. Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS ver.18) was used for analysis. Results: The present study included 2308 diabetic patients (1252 males and 1056 females). A minimal prevalence of 1.2% of diabetic foot was found. In multivariate binary logistic regression analysis the following potential risk factors were identified; age more than 60 years, obesity and number of visits for the PHCC of less than four in the previous year. Conclusions: The study emphasizes the importance of regular visits to the PHCCs among diabetic patients. Regular screening for foot complications is recommended in all patients. Treating physicians should be encouraged to exert more attention and care to foot examination, especially for the obese and elderly diabetics.
Keywords: Diabetic, Obesity, PHCC, Early, Saudi Arabia
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Any foot pathology that results directly from or its long term complications called as diabetic foot.1 Diabetes is recognized as the most common cause of non-traumatic lower limb amputation in the western world, with individuals over 20 times more likely to undergo an amputation compared to the rest of the population. 2According to the World Health organization diabetic Foot can be defined as “The foot of diabetic patients that has the potential risk of pathologic consequences including infection, ulceration and or destruction of deep tissues associated with neurologic abnormalities, various degrees of peripheral vascular disease and / or metabolic complications of diabetes in the lower limb.” Data from the pilot study in Ireland indicate that a sizeable number of people with diabetes attending an urban general practice in the west of Ireland have vascular insufficiency and abnormal measures of neural function in their feet. These findings are of concern given the associations between lowerlimb vascular insufficiency, neuropathy and increased risk of ulceration.3 The term „diabetic foot? (DF) includes any pathology that results directly from diabetes or its long-term complications.4 Globally, foot problems account for more hospital admissions than any of the other long-term complications among patients with diabetes. An understanding of the causes of these problems enables early recognition of patients at high risk. It has been shown that up to 50% of amputations and foot ulcers in diabetes can be prevented by effective identification and education. Foot problems occur in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes and it has been estimated that the lifetime risk of a patient developing a foot ulcer is 25%.5 In Saudi Arabia, DF was prevalent in 13.5% of the diabetic patients referred to the nephrology clinic and 7.7% of the patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis.6 The mortality rate is higher in the patients with DF, and represents approximately twice the number of diabetic patients without DF.7 Identifying diabetic patients who are at high risk of developing DF may constitute a cost effective strategy in controlling progression to end stage complications. The Aseer region is located in the southwest of Saudi Arabia. It extends from the high mountains of Sarawat to the Red Sea, and lies few kilometers from the northern border of the neighboring Yemen. Abha city is the capital of Aseer. The latest Saudi Arabia?s September 2004 population census reported that Abha city has a total population of 220,000.8 This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (REC) from the College of Medicine, King Khalid University (KKU), Abha, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Type of study:
It is a retrospective, cross sectional type of study. Duration of study: 15th November, 2011 to 30th March, 2012 (Proposed) Consent: The data was obtained from the chronic diseases files. After the written consent taken from the administration of the hospital. In this study researcher follows the principles of WMA Declaration of Helsinki - Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects, principal investigator and all other co- staff members will follow all those ethical principals i.e. protect the life, health, dignity, integrity, right to self-determination, privacy, and confidentiality of personal information of research subjects. Type of sampling: In this study, researcher adopted the convenience type of nonprobability sampling. Inclusion criteria: All the diabetic patients, visited to the primary health care unit in Abha were included in the study. Exclusion criteria: Females who were pregnant or nursing or females of childbearing potential; Life expectancy < 6 months due to concomitant illnesses; Exposure to any investigational drug or procedure within 1 month prior to study entry or enrolled in a concurrent study that may confound results of this study. Active infectious disease and/or known to have tested positive for HBV, HCV, CMV and/or syphilis and History of cancer (other than non-melanoma skin cancer or insitu cervical cancer) in the last two years. Sample Size: As researcher adopted the nonprobability convenience samplings and the sample size is 2308 diabetic patients. List of variables: Socio-demographic variables i.e. age, gender, family history, concomitant conditions, complications and compliances i.e. Hypertension Hyperlipidemia, Smoking, Obesity, type of diabetes, duration of diabetes. Data collection: Researcher collected the data from the chronic diseases files those who visited and fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criterion, to the primary health care center in Abha. . A well qualified team of doctors and nurses examined the patients and helped the researcher regarding the data availability and data compilation in PHCC Abha, KSA. Data Analysis: Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) ver. 18 9 was used for entering and analyzing the data. Data were coded for entering purpose List of PHCC in Abha: Al-Manahal Primary Health Care Center, Al-Numais Primary Health Care Center, Al-Mansak Primary Health Care Center, Al-Aziziah Primary Health Care Center, Al –Qabil, Wasat Abha Primary Health Care Center, and Haiyal Moazzifin Primary Health Care Center Statistical Analyses: Descriptive statistics i.e. mean, standard deviation, maxima, minima, range, percentages of Socio- demographic variables were calculated to determine the information about the respondents and risk factors. To check the significance differences among the variables i.e. associated risk factors statistical tests were applied chi-square tests for discrete data i.e. proportion of type I and II diabetes among male and female while t-test for continuous data i.e. comparison of age groups of diabetic males and females. Adjusted odds ratios along with confidence interval were calculated to explore the potential risk factors for diabetic foot. Level of significance: Researcher fixed the level of significance at 95% means any p-value less than 0.05 considered significant.
RESULTS
The present study included 2308 diabetic patients (1252 males and 1056 females). Sociodemographic profile: Table 1 shows the profile of the study sample. The age ranged from 11 to 92 years with an average of 57.65+ 15.06 years and a median of 56 years. Diabetic males were significantly (t= 1.982, P= 0.001) older (58.22 + 15.2 years) than diabetic females (56.9 + 13.2 years). Male diabetics were significantly more educated than females (χ2 =140.3, P=0.001). Types, duration and family history of diabetes: The proportion of type 1 diabetes among male diabetics (15.7%) was significantly (χ2 =8.12, P=0.005) higher than that among female diabetics (11.6%). The duration of diabetes among males (9.24 + 7.44 years) was significantly (t= 3.704, P= 0.001) longer than females (8.17 + 6.26 years). On the other hand the proportion of positive family history of diabetes among females (42%) was significantly higher (χ2 =17.66, P=0.001) compared to males (33.5%). Concomitant conditions: The prevalence of obesity and hyperlipidemia were significantly (P=0.001) higher among females (58.6% and 26.7%, respectively) compared to male diabetics (36.3% and 19.3%, respectively). On the other hand the prevalence of smoking among males (14.4%) was significantly higher (P=0.001) compared to females (1.1%). The prevalence of hypertension was not significantly different (χ2 =0.352, P=0.553) among males (24.1%) and females (25.2%).
Prevalence of Diabetic foot:
The present study included 27 cases diagnosed as diabetic foot giving a minimal prevalence of 1.2%. There was no significant deference (χ2 =0.409, P=0.522) between males (1.1%) and females (1.3%) regarding the prevalence of diabetic foot.
Determinants of diabetic foot:
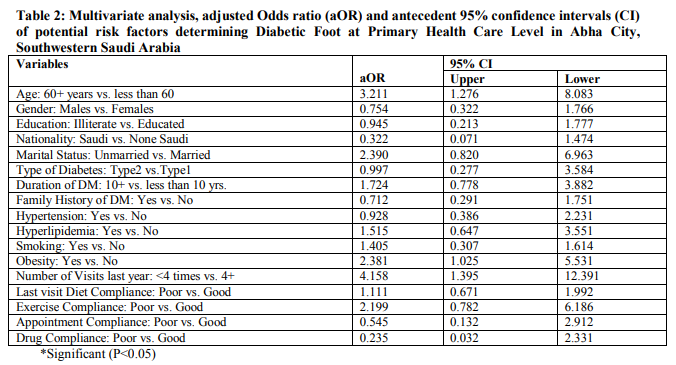
Multivariate binary logistic regression analysis was used to identify potential risk factors associated with diabetic foot (Table 2). After adjusting for other potential risk factors, the study showed that diabetics aged more than 60 years having more than three times the risk to develop diabetic foot compared to diabetics aged less than 60 years old. Similarly, the following significant risk factors were identified; obesity and number of less than four visits for the PHCC during last year. On the other hand, gender, educational level, nationality, marital status, type and duration of diabetes, family history of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking diet, and exercise compliance were found to be of no significant value in developing diabetic foot.
DISCUSSION
The present study reported a minimum prevalence rate of 1.2% of diabetic foot among diabetics at PHC level in Abha. In Saudi Arabia, DF was prevalent in 13.5% of the diabetic patients referred to the nephrology clinic and 7.7% of the patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis.10 In Netherlands an annual incidence rate of DF of 1.2% was reported among diabetics at PHC level.11In Germany, approximately 2–6% of all diabetics developed poor healing and frequently chronic lesions on the feet which were associated with a high risk of minor or major amputation.12 In UK in a cohort of 1192 people with diabetes receiving care in community settings an incidence of DF of 1.9% was found. 13 . This low prevalence in this study indicated that diabetic patients of this study were very cautious about their feet reason being the continuous health education by centre staff enabling then and took all the preventive measures to overcome the foot problems. The present study identified the following potential risk factors; age more than 60 years, obesity and number of less than four visits for the PHCC during last year.A case control study in Riyadh, found that the presence of DF was significantly associated with: male gender, age older than 40 years, illiteracy, type 2 diabetes, longer duration of the disease, earlier age of the onset of diabetes, higher ESR.14 In a crosssectional study in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) investigating the risk factors of DF, the main risk factors for complications of DF were: male gender, poor level of education, UAE nationality, long disease duration, type 2 diabetes mellitus, presence of hypertension, and poor glycemic control.15 Diabetic patients should be given general advice on foot hygiene, nail care and the purchase of footwear. Their risk status should be reviewed annually. Patients with any risk factor should be reviewed more frequently and educated about preventive foot care. These simple steps have been shown to significantly reduce the incidence of foot ulceration. Much of the screening and primary health education of patients with diabetes is undertaken in primary care. A community foot care team might include a general practitioner, and practice nurse. Education for at-risk patients is often provided in this setting. The introduction of multidisciplinary team work in the community has been shown to result insignificant reduction in the number of amputations.16 In conclusion, this study could be considered as a preliminary study of the risk factors of DF in southwestern Saudi Arabia. It emphasizes the importance of regular visits to the PHCCs among diabetic patients. 1.1% of the males and 1.3% of the females? respondent experience the diabetic foot, which reflects the low prevalence but to further reduce this prevalence regular screening for foot complications is recommended in all diabetic patients. To decrease the potential risk factors observed in this study i.e. age over than 60-years, obesity and less than 4 visits to PHCC, Treating physicians should be encouraged to exert more attention and care to foot examination, especially for the obese and elderly diabetics. An important part of preventing diabetic foot is having foot and footwear checks done annually by any healthcare provider who comes in contact with the patient, particularly for those patients with long duration of diabetes who use insulin and those who smoke. Daily foot checks should also be taught to patients and their caregivers 17 Strength and future aspects of the study: This study will help the future researcher to further investigate about the potential risk factors of the DF. In the light of this study, doctors and hospital administration will take the preventive measures to overcome or reduce such risk factors. This study to be followed in the future by a large scale prospective study all over Aseer region, including all the possible risk factors derived from the current study and other studies
References:
1. Boulton A. The diabetic foot: from art to science. The 18th Camillo Golgi lecture, Diabetologia (2004) 47:1343–1353.
2. J. Rodrigues ,N. Mitta ,Diabetic Foot and Gangrene, Gangrene - Current Concepts and Management Options, Dr. Alexander Vitin. (2011).
3. Nather A, Bee CS, Huak CY et al. Epidemiology of diabetic foot problems and predictive factors for limb loss. J Diabetes Complications (2008) 22: 77-82
4. Boulton A. The diabetic foot.MEDICINE 2010, 38(12): 644-648.
5. Singh N, Armstrong DG, Lipsky BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA (2005); 293: 217-28.
6. Qari FA. Profile of Diabetic Patients with End-stage Renal Failure Requiring Dialysis Treatment at the King Abdulaziz University Hospital, Jeddah. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl (2002); 13: 199-202.
7. Hunt D. Diabetes: foot ulcers and amputations. ClinEvid 2009; 1: 1-16.
8. Preliminary results of 2004 census. Central Department of Statistics. Riyadh (KSA): Ministry of Economy and Planning; (2005).
9. SPSS Inc. Released 2009. PASW Statistics for Windows, Version 18.0. Chicago: SPSS Inc.
10. Jbour AS, Jarrah NS, et al. Prevalence and predictors of diabetic foot syndrome in type 2 diabetes mellitus in Jordan. Saudi Med J (2003); 24: 761-764.
11. Mulle I, Bartlink M, Grau W, Hoogen H, Gerwen W and Rutten G. Foot ulceration and lower limb ambutation in type 2 diabetic patients in Dutch primary health care. Diabetic Care (2002);25:570-574.
12. Pscherera S, Dippelb F, Lauterbachc S, Kostevd K. Amputation rate and risk factors in type 2 patients with diabetic foot syndrome under real-life conditions in Germany. Primary Care Diabetes 2012; 6: 241–246.
13. Crawford F, McCowan C, Dimitrov BD, Woodburn J, Wylie GH, Booth E, Leese GP, Bekker HL, Kleijnen J, Fahey T. The risk of foot ulceration in people with diabetes screened in community settings: findings from a cohort study.QJM. 2011; 104(5):403- 10.
14. Abolfotouh MA, Alfaifi SA, Al-Gannas AS.Risk factors of diabetic foot in central Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 2011;32(7):708- 13.
15. Al-Maskari F, El-Sadig M. Prevalence of risk factors for diabetic foot complications. BMC FamPract (2007) 10; 8: 59.
16. Krishnan S, Nash F, Baker N, Fowler D, Rayman G. Reduction in diabetic amputations over 11 years in a defined UK population: benefits of multidisciplinary team work and continuous prospective audit. Diabetes Care (2008); 31: 99-101.
17. Larsson J, Apelqvist J. Towards less amputations in diabetic patients: incidence, causes, cost, treatment and prevention-a review. Acta Orthop Scand. 1995; 66(2):181- 192
Table 1: Description of the Study Sample of Diabetics at Primary Health Care Level in Abha City, Southwestern Saudi Arabia

|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License