IJCRR - 5(14), July, 2013
Pages: 88-95
Date of Publication: 29-Jul-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON METHODS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF ENTERIC FEVER
Author: Renu Mathew, Jobin.S.R.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Enteric fever continues to be a global health problem and isolation of organism from blood is the gold standard for the diagnosis. Objectives: Aim of this study was to find out the usefulness of three different methods such as blood culture, clot culture and Widal test for diagnosis of enteric fever. Materials and Methods: Total number of blood samples collected was 290 from patients with pyrexia for blood culture, clot culture and Widal test. Results: Among the 290 cases studied, 117 patients were positive for enteric fever with either positive Widal test and or with culture positivity. Culture was positive in 40 patients (34%). Out of 117 positive cases of enteric fever, 89 (76%) had typhoid fever and 28 (24%) patients had paratyphoid fever. This was on the basis of significant Widal titers and isolation of Salmonella from blood or clot. Significant Widal titers were seen in 96 patients. Discussion: The sensitivity and specificity of clot culture were 95% and 100% respectively and both blood culture and clot culture had shown the same rate of isolation. Advantage of clot culture is that it can be done with the sample taken for Widal test. The sensitivity and specificity of the Widal test were 47.5% and 69.2% respectively and Widal test done on convalescent-phase serum gave more reliable results. Conclusion: Blood culture and clot culture had more importance when compared to Widal test for the diagnosis of enteric fever.
Keywords: Blood culture, Clot culture, Enteric fever, Salmonella typhi, Widal test
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Enteric fever continues to be a global health problem, with an estimated 21.6 million people (incidence of 3.6 per 1,000 population) and kills an estimated 200,000 people every year.The disease is endemic in many developing countries, particularly in Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, South and Central America and Africa, with annual incidence rate estimated to be greater than 900 per 100,000 populations in India. 1 Enteric fever includes typhoid fever and paratyphoid fevers caused by Salmonella typhi and S. paratyphi A, B and C. Isolation of organism from blood is the gold standard for diagnosis of enteric fever. Other methods like bone marrow culture, clot culture, antigen detection, Widal test and stool culture can also be done for the diagnosis. Delayed and inaccurate diagnosis and treatment results in increased costs and higher rates of serious complications and deaths. Early detection and antimicrobial susceptibility surveillance must be applied to prevent the complications as well as the emergence of multidrug resistance strains.2
In view of the above facts, the present study was undertaken to compare the usefulness of different methods for the diagnosis of enteric fever.
AIM
A cross sectional study to find out the usefulness of three different methods such as blood culture, clot culture and Widal test for diagnosis of enteric fever.
OBJECTIVES
1. To isolate and identify the agents causing enteric fever (Salmonella typhi, Salmonella paratyphi A, B and C) using clot culture and conventional blood culture method.
2. To detect the presence of antibodies against Salmonella antigens in serum using Widal test.
3. To compare the results of clot culture method and Widal test with conventional blood culture method which is the gold standard for diagnosis of enteric fever.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The present study was carried out at Saveetha Medical College, which is a tertiary care hospital in Thandalam, Kanchipuram district. Study period was from October 2011 to January 2012.
INCLUSION CRITERIA
Patient with clinically suspected Enteric fever (pyrexia of more than five days) from all age groups.
Exclusion criteria
- Patients with respiratory tract infections (tuberculosis, pneumonia).
- Patients with urinary tract infections
- Patients with malaria
- Immuno-compromised patients (AIDS)
Total number of samples collected was 290. Venous blood (5-10 ml from adult and 2-5 ml from paediatric patients for blood culture, clot culture and Widal test) was collected aseptically from patients with pyrexia attending the Paediatric and Medicine departments at Saveetha Medical College and hospital. Consent form and proforma were duly filled up. After clotting of blood in the sterile tube, the specimens were centrifuged for 5 minutes at 3000 rpm (rotation per minute) and serum was aseptically removed for Widal test. The clot was used for clot culture.3 The specimens were transported within two hours to the laboratory. 4 For whole blood culture, 2-10 ml blood was added to the brain heart infusion broth without centrifugation.5
Conventional blood culture method (Gold standard):
Blood contains substances that inhibit the growth of the bacilli and hence it is essential that the broth be taken in sufficient quantity to provide at least fourfold dilution of blood. The addition of liquid (sodium polyanethol sulphonate) counteracts the bactericidal action of blood.
From adult patients with pyrexia, 5-10 ml blood was collected and inoculated in to 50- 100 ml Brain Heart Infusion medium. (In pediatric age group, 2-5 ml blood was collected and inoculated in to 20-50 ml Brain Heart Infusion broth)
- The culture was incubated at 370 c for 24 hours.
- At interval of 1, 3, 7 day, subculture was done on Blood agar and Mac Conkey agar.
- Non-lactose colonies from the Mac Conkey agar plates were identified by Gram staining, oxidase test and conventional biochemical tests (such as indole, citrate, urease, triple sugar iron, mannitol motility and slide agglutination test with high titre sera.5,6
CLOT CULTURE METHOD
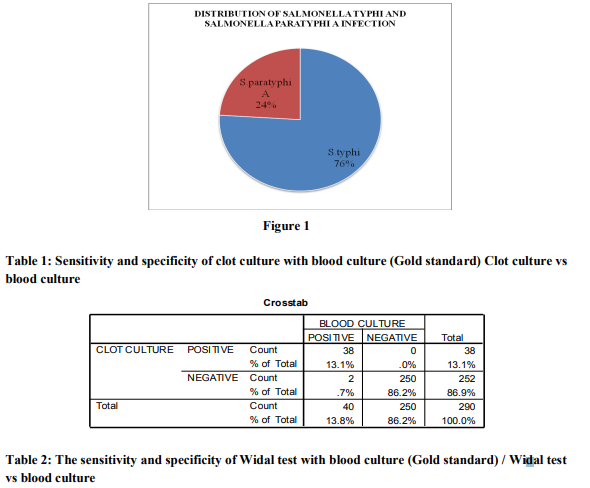
Clot cultures yield a higher rate of isolation than blood culture as the bactericidal action of the serum is obviated. Clot culture can be done with the sample taken for Widal test. A total of 5 ml blood is enough for both isolation of agent causing enteric fever as well as antibody detection. For blood clot culture, a modification of method described by Escamilla et al 7 was used. ? Five ml of blood was collected from patients with pyrexia and allowed the blood to clot. ? After the blood clotted in the sterile tube, the specimens were centrifuged for 5 minutes at 3000 rpm (rotation per minute) and the serum was aseptically removed for Widal test. ? The clot was used for blood clot culture. ? The clot was broken up with a sterile glass rod and added to bottle of 50 ml bile broth. ? Streptokinase (100 units per ml) was added into the broth to facilitate lysis of the clot.6 ? Culture was incubated at 370C for 24 hours. ? At interval of 1, 3, 7 day subculture were done on Blood and Mac Conkey agar. ? Non-lactose colonies from the Mac Conkey agar plates were identified by Gram’s staining, oxidase test, conventional biochemical tests and slide agglutination test using high titre sera. WIDAL TEST Widal test is a tube agglutination test which detects the presence of agglutinins (H and O) in patient’s serum with typhoid and paratyphoid fever. The antigen used in the test is the H and O antigen of Salmonella typhi and the H antigen of Salmonella paratyphi A and B. Commercial antigen from Tulip Diagnostics was used. ? Appropriate number of sets (as required; one set for each antigen suspension) of 8 test tubes were taken and labeled them 1 to 8. ? 1.9 ml of physiological saline was pipetted into tube No.1 of all sets. ? 1 ml of physiological saline was added to each of the remaining tubes (2 to 8). ? 0.1 ml of serum sample to be tested was added to tube No.1 of all sets and mixed well. ? 1 ml of the diluted serum sample from tube No.2 was transferred to No.3 and mixed well. Serial dilution till tube No.7 in each set was continued. ? 1.0 ml of the diluted serum from tube No.7 of each set discarded. ? The dilutions of the serum sample achieved from tube No.1 to 7 respectively in each set was as follows 1:20, 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, 1:640, 1:1280.Tube No.8 in all sets, served as a saline control. ? To all the tubes (1 to 8) of each set one drop of the respective well mixed antigen suspension from the reagent vials was added and mixed well. ? Covered and incubated at 370C overnight (approximately 18 hours). ? The reading was taken after incubation. ? Significant titer was taken as 1:80 and above for TO and 1:160 and above for TH. 4,8 RESULTS A total number of 290 blood samples were collected from patients with clinically suspected enteric fever and subjected to blood culture, clot culture and Widal test. Duration of fever was ranging from 5 to 14 days. Among the 290 cases studied, 117 patients were positive for enteric fever with either positive Widal test and or with culture positivity. Culture was positive in 40 patients (34%). Out of 117 positive cases of enteric fever, 89 (76%) had typhoid fever and 28 (24%) patients had paratyphoid fever. This was on the basis of significant Widal titers and isolation of Salmonella from blood or clot. Significant Widal titers were seen in 96 patients. Out of 117 patients 77 (66%) were inpatients and 40 (34%) were outpatients. Among 117 positive cases, 66 (56%) patients were males and 51 (44%) were females. Out of 117 positive cases, 30 (26%) were belonging to the age group of < 20 years, 52 (44%) between 21-40 years, 32 (27%) between 41-60 and 3 (3%) from above 60 years of age group. Maximum number of patients 52 (44%) were from 21-40 years of age group. Distribution of Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi A infection is shown in Fig- 1
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
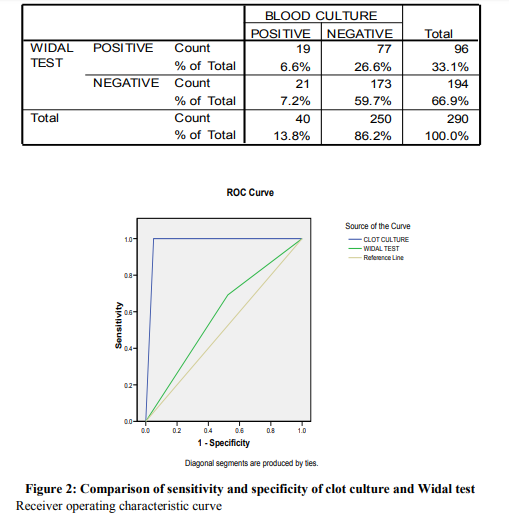
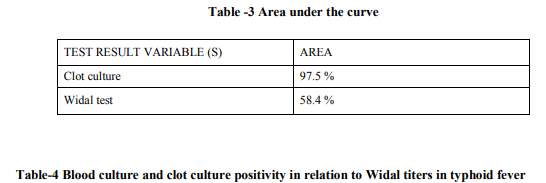
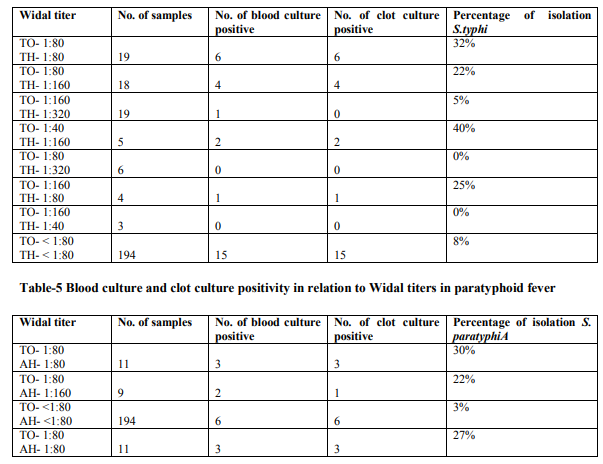
The results of clot culture, Widal test were compared with blood culture (Gold standard). Sensitivity and specificity were calculated based on the compared results, which is depicted in Table 1 and 2. Table- 1: The sensitivity and specificity of clot culture were 95% and 100%. Positive and negative predictive values were 100% and 99.2% respectively. Chi-square test value was 273.313, P<0.001 and df 1. Table – 2 : There was significant difference (Chi-square value=4.343, P<0.05 and df=1) between the Widal test and blood culture method for the detection of enteric fever. But the sensitivity and specificity of the Widal test were 47.5% and 69.2% respectively. The positive predictive and negative predictive values were 19.79% and 89.17%. Comparison of sensitivity and specificity of clot culture and Widal test is shown in Figure 2 and Table 3. Fig 2 (Graph 1) Table -3 Table-4 Table-5 The higher rate of isolation was found to be with low Widal titer as shown in Table 4 and 5. Out of 40 Salmonella isolates, 29 isolates were Salmonella typhi and 11 were Salmonella paratyphi A.
DISCUSSION
Typhoid fever remains as an important cause of morbidity even at present. In the present study, 290 blood samples were taken from patients with clinically suspected enteric fever and blood culture, clot culture and Widal test were done for the diagnosis. Among the 290 cases studied, 117 patients were positive for enteric fever with Widal test, blood and clot culture. Culture was positive in 40 patients of which 29 isolates were Salmonella typhi and 11 were Salmonella paratyphi A. Culture positivity was 34%. Significant Widal titers were seen in 96 cases (82%). In our study, out of 117 positive cases, maximum number 52 (44%) was from the age group between 21 to 40. A similar study done by Karkey A et al had reported the maximum positivity from adult age groups. 9 The sensitivity and specificity of clot culture was 95% and 100% respectively in our study. A similar study by Simanjuntak CH et al, Indonesia compared the sensitivities of whole blood and clot culture in 155 patients with typhoid or paratyphoid fever. Salmonella typhi or Salmonella paratyphi A were isolated from 98.7% of blood culture and 94.8% of clot culture. Whole blood culture and clot culture were of nearly equal sensitivity. The results of the above study correlated well with ours. 10 Mantur B G et al had a similar study where the clot culture was found to be much more sensitive for Salmonella than whole blood culture. Bacterial growth was significantly faster in culture of blood clots compared to whole blood.11 Isolation rate of Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi A was 76% and 24% in our study. In a similar study done by Krishnan P et al in Chennai, 70% of isolates were Salmonella typhi and 30% were Salmonella paratyphi A, which was in accordance with our study.12 Among 290 sera 194 blood samples shown <1:80 antibody titer for both antigens, 15 were culture positive for Salmonella typhi in both blood and clot culture method. Out of 194 samples that had shown <1:80 antibody titer for both O and AH antigens, 6 blood samples were positive for Salmonella paratyphi A. In our study, the sensitivity was 47.5% and specificity was 69.2% for Widal test. Similar study done by Taiwo SS et al, has reported the sensitivity as 90% and specificity as 88.5% which was more when compared with the present study. 13 Widal test done on acute phase serum of patients suspected to have typhoid fever had shown limited diagnostic value because of its low sensitivity. Widal test done on convalescentphase serum gave more reliable results with higher specificity and sensitivity. Paired sera testing would be more advantageous than a single Widal test.
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
- In this study, 89 (76%) had typhoid fever and 28 (24%) patients had paratyphoid fever on the basis of significant Widal titers and isolation of Salmonella.
- The sensitivity and specificity of clot culture were 95% and 100% respectively with an advantage that it can be done with the sample taken for Widal test.
- Both blood culture and clot culture had shown the same rate of isolation, confirming the significance of blood culture as the gold standard for diagnosing enteric fever.
- The sensitivity and specificity of the Widal test were 47.5% and 69.2% respectively and Widal test done on convalescent-phase serum gave more reliable results.
- In conclusion, Blood culture and clot culture had more importance when compared to Widal test for the diagnosis of enteric fever.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We acknowledge Dr. Shameem Banu, Professor and Head and Dr. Kalyani. M, Professor of Department of Microbiology for their valuable support in carrying out this study.
References:
1. Eric Mintz. Enteric fever – Epidemiology and Reports from the Field: Global situation and WHO recommendations. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference Asia-Pacific symposium on typhoid fever and other Salmonellosis. Dhaka, Bangladesh 1-2 March 2013.
2. Mandell, Douglas and Bennett’s (2000), Principles and practice of infectious diseases, 6th edition, chapter 220, Salmonella species, including Salmonella typhi, page no – 2636 -2650.
3. Koneman’s (2006), Colour Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, Sixth edition, page no 251-257.
4. Olopoenia LA, King AL. Widal agglutination test - 100 years later: still plagued by controversy. Postgrad Med J 2000; 76(892): 80-4.
5. Paniker CK. Enterobacteriaceae-III Salmonella. In: Ananthanarayan R, Paniker CK, editors. Textbook of Microbiology. 8th ed. Chennai, India: Orient Longman Private limited; 2010. p. 289-290.
6. Chakraborty P (2007), A text book of Microbiology, chapter 77, Pyrexia of unknown origin, page no: 676-677.
7. Escamilla J, Ugrate HF, Kilpatrick ME. Evaluation of blood clot cultures for isolation of S. typhi, S. paratyphi A and Brucella melitensis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1986; 24(3):388-90.
8. Old DC. Salmonella. In: Collee JG, Fraser AG, Marmion BP, Simmons A, editors. Mackie And McCartney Practical Medical Microbiology. 14th ed. London: Churchill Livingstone; 1996. p. 385-404.
9. Karkey A, Arjyal A, Anders KL, Boni MF, Dongol S, Koirala S, My PV, Nga TV,Clements AC, Holt KE, Duy PT, Day JN, Campbell JI, Dougan G, Dolecek C, Farrar J, Basnyat B, Baker S. The burden and characteristics of enteric fever at a healthcare facility in a densely populated area of Kathmandu. PLoS One. 2010 Nov 15; 5(11):e13988.
10. Simanjuntak CH, Hoffman SL, Darmowigoto R, Lesmana M, Soeprawoto, Edman DC, Streptokinase clot culture compared with whole blood culture for isolation of Salmonella typhi and S. paratyphi A from patients with enteric fever. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988; 82(2):340-1.
11. Mantur BG, Bidari LH, Akki AS, Mulimani MS, Tikare NV, Diagnostic yield of blood clot culture in the accurate diagnosis of enteric fever and human brucellosis. Clin Lab. 2007;53(1-2):57-61.
12. Krishnan P, Stalin M, Balasubramanian S. Changing trends in antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica serovar typhi and salmonella enterica serovar paratyphi A in Chennai. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2009 Oct-Dec; 52(4):505-8.
13. Taiwo SS, Fadiora SO, Oparinde DP, Olowe OA, Widal agglutination titers in the diagnosis of typhoid fever .West Afr J Med. 2007 Apr-June; 26(2):97-101.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License