IJCRR - 5(14), July, 2013
Pages: 16-23
Date of Publication: 29-Jul-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
INDUCTION PROTOCOLS FOR NEURONAL TRANSFORMATION OF GLOBOSE BASAL STEM CELLS
Author: Avinash Thakur, Duraimurugan Muniswami, George Tharion, Indirani Kanakasabapathy
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective(s): Consistent efforts with increasing optimistic outcome are being made to identify a candidate (neuron- progenitor cell) for a reliable therapeutic intervention of CNS injury. In this venture, recent years witnessed an increasing bang on the olfactory epithelium for suitable neuripotent stem cells. In this research work we aim at exploring the cultural characteristics and standardizing induction media for neuronal transformation of the potential multipotent Globose basal stem cells (GBC) residing in the basal compartment of the olfactory epithelium of rat olfactory mucosa. Methodology: GBC were isolated in pure form from olfactory mucosa of albino wistar rats using GBC-III monoclonal antibody and fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). Two different induction protocols were defined for the transformation of GBC into functional neurons. Results: GBC transformed into neurons and astrocytes in both the induction media. The neurons and astrocytes hence formed were immunohistologically characterized. Conclusion: This research work conclusively elucidates the cultural characteristics of a novel multipotent candidate (GBC) which can be induced into functional neurons using specific external niche and can prove to be beneficial for further research in neuro-regenerative therapies.
Keywords: Globose basal cell, olfactory mucosa, multipotent, induction, neuron, astrocytes
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
For many decades neuroscientific researchers have been in the search of an ideal cell with the properties of absolute totipotency and regenerability in vitro and in vivo. Science has come very close to the quest, but still many unanswered questions remain. In this research work we aim at analyzing the neuronal potency of a group of very specialized stem cells present in the olfactory epithelium called the Globose basal cells (GBC) and evaluate their ability for continued renewal and transformation into neurons in culture environment using two different induction protocols with modifications of the existing protocols proposed by Greco et al 1 and Xiufang Guo et al 2. This would allow us to manipulate these cells to a therapeutic grade and assay their value for CNS injury treatment in humans using rat GBC or human GBC. GBC are small, round, morphologically non-descript and cyto-keratin negative cells that sit between the horizontal basal cells (HBC) below and the immature olfactory receptor neurons above, that proliferate at a high rate in the normal OE, are limited to the OE and are poorly characterized at the level of their molecular phenotype.
Neurogenesis is a process by which new neurons are generated from a precursor cell. This process requires the proliferation, differentiation and migration of neurogenic stem cells into neurons. It was believed for many decades that in mammals neurogenesis occurred only during embryonic life, but recent work in this field has made it evident that neuronal regeneration occurs even after birth in specific tissues like the hippocampus, dentate gyrus, subventricular zone and olfactory epithelium 3. The formation of neurospheres in olfactory epithelium and other tissues like spinal cord 4, eye 5, ear 6 and hippocampus 7 has been extremely important in determining the role of stem and progenitor cells in trans-differentiation into neuronal elements. In marked contrast to other parts of the nervous system, there is substantial anatomical and functional recovery of the olfactory epithelium and its projection into the CNS even in the face of overwhelming injury. For example, in the case of epithelial lesions caused by a single exposure to methyl bromide (MeBr), the olfactory epithelium is restored to a status that is indistinguishable from unlesioned epithelium within 6–8 weeks after damage 8. In the past few decades, variety of fetal, embryonic and adult stem and progenitor cells have been tried with conflicting outcome for cell therapy of central nervous system injury and diseases9. Transplantation of adult animal and human olfactory epithelium (OE) cells has been used in the past for experimental and clinical correction of spinal injuries10. Embryonic stem cells have enormous ability to regenerate into different types of cells in the body; but they also share the possibilities of immune rejection, adverse effects of immunosuppressive therapy and many ethical issues which exclude them as an ideal candidate for clinical work. Olfactory mucosa is readily accessible, easily biopsied for autologous cell transplantation and regenerates completely without any loss of function. These properties make the olfactory epithelial stem cells as the ideal candidate for use in clinical research and therapy. The adult OE is a unique and a complex tissue containing heterogeneous population of epithelial cells. Apart from the support cells and neruoreceptor cells, this complex is said to retain a kind of progenitor cells that are competent to make neurons (neural stem cells) and non- neural support cells 11,12,13. This study has been undertaken to understand the culture requirements, proliferative and differentiative properties of Globose Basal Cells since there is shortage of data regarding these properties of GBCs because of non-conclusive trials in the past to prove their multipotency. This research work conclusively establishes that GBC are the group of neural stem cells capable of such neuronal differentiation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
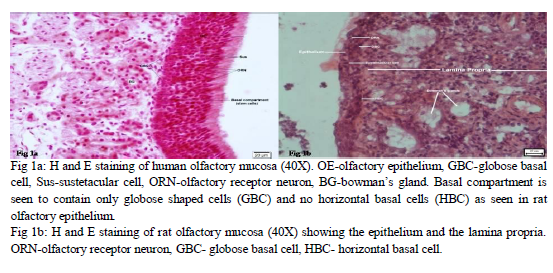
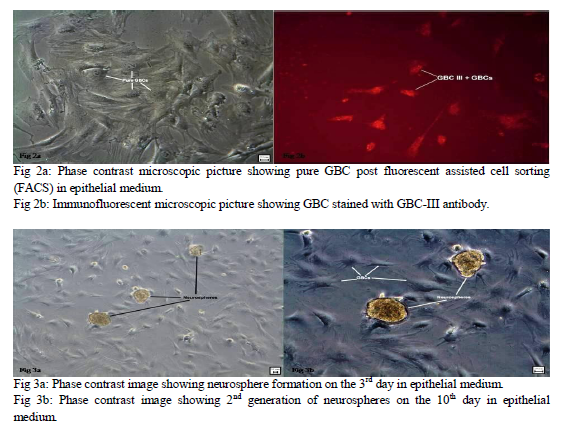
Six Albino wistar rats were used at different occasions and their nasal septum was completed excised along three surgical lines: the arc of the perpendicular plate, the cribriform plate and the ceiling of the oral cavity to obtain the olfactory mucosa and the respiratory mucosa was discarded. Olfactory mucosa of humans and rat was stained with haematoxylin and eosin and also with toulidine blue to do comparative study of the histological characteristics of the OE and its basal compartments (fig.1a, b). The OE was separated from the mucosa under Leica EZ2HD dissecting microscope by enzymatic treatment with 0.5 ml of Dispase-II for 45 minutes. The epithelial cells were separated from each other with the use of an enzymatic cocktail containing collagenase – 1 mg/ml, hyaluronidase – 1.5 mg/ml, trypsin inhibitor – 0.1 mg/ml and cultured in the epithelial medium composed of Dulbeco’s modified Eagle medium / F12 (1: 1) – 47.5 ml, 2% fetal bovine serum – 1.0 ml, N2 supplement – 0.5 ml, epidermal growth factor (25 ng / ml) – 12.5 µl and L-glutamine – 0.5 ml for generation of neurospheres. GBC were isolated in pure form (fig.2a) from the epithelial cells by tagging them with a highly specific monoclonal antibody GBC-III (fig.2b) and sorting them with fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS). GBC-III is a mouse monoclonal IgM antibody which recognizes a 40 kDa surface antigen which is a laminin receptor surface protein. It is highly specific as a marker for GBCs, unlike the earlier antibodies used like GBC-I which were nonspecific markers for GBCs and showed positive reaction even with HBCs, Sus and duct cells14. GBC-III was received with courtesy from TUFTS University (USA) in powdered form. It was reconstituted into the recommended volume of 250 µl. It was used in a concentration of 1:100 for immunostaining.
Two different induction media were used to trans- differentiate GBC into neurons and glial cells. Induction medium I was composed of Ham’s F12 media, fetal bovine serum – 2%, B-27 supplement– 1%, retinoic Acid (RA) – 20 mM and bFGF (beta fibroblast growth factor) - 12.5 ng/ml. GBC were cultured in this medium for 12 days and morphological changes were recorded regularly. GBC were also plated for 21 days on induction medium II which was composed of neurobasal medium, B-27 supplement - 2%, L-Glutamine - 0.5 mM, Penicillin - 100 µl, Streptomycin - 100 µl and Amphotericin - 200 µl.
Differentiated neurons and astrocytes were characterized immunologically using numerous primary antibodies for neuron specific markers like microtubule associated protein-2 (MAP-2), beta III tubulin, neuronal nuclei (NeuN), neurofilament H, M and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP for astrocytes). Cover slips coated with poly D-lysine were plated with the differentiated neuronal cells from both the induction media. 4% paraformaldehyde was used as the fixative. Glass slides were prepared and kept moist for mounting the cover slips. After blocking with 2% goat serum and 0.1% triton X the slides were treated with the primary antibodies and incubated overnight at 40C. Slides were then treated with the respective secondary antibodies and incubated at 370C for 1 hour. The slides were then examined under immunofluorescent microscope.
RESULTS
Striking similarities were found during the staining of human and rat olfactory mucosa. The ciliated, pseudostratified OE was made of the similar three basic cell types, namely; olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs), basal cells and sustentacular cells. ORNs and sustentacular cells were similar in morphology and their location in the OE. The basal compartment of the rat OE consisted of two types of cells, namely; HBC located closer to the basal lamina and GBCs located in a layer above the HBCs (fig. 1b). The basal compartment of human OE consisted of only one type of cells which were globose in shape which are also called GBC (fig. 1a). This has been described earlier in the literature and it has been suggested that these human GBCs act and possess the properties of both the cell types present in rodents 15. The lamina propria was much thicker comparatively in the human OM with higher density of bowman’s glands.
Neurosphere formation began in the olfactory epithelial medium by the end of 3 days (fig. 3a). These neurospheres were passaged on the 6th day to obtain the 2nd generation of neurospheres (fig. 3b). Multiple neurospheres were formed by the end of 2 weeks. The self renewal potential of olfactory stem cells was evident from the formation of multiple generations of neurospheres. During this period of 2 weeks, many of the neurospheres had started to proliferate. Hence an effective method of generating neurospheres from olfactory epithelial cells was established. EGF and N-2 supplement seem to play a significant role in providing an optimum external niche for formation of multiple generations of neurospheres from epithelial stem cells. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a potential stem cell mitogen allowing cell proliferation through activating signaling pathway and inducing the production of beta fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) from the progenitor cells. It was also established that neurosphere generation depended on the initial plating density. An ideal cell density to be plated on the culture plates is required to avoid excessive or minimal growth of cells and neurosphere formation. Cell density of 10 X 105 was found to be ideal for optimal growth of epithelial stem cells and for formation of multiple generations of neurospheres. 99% pure GBC were isolated using GBC-III antibody and FACS.
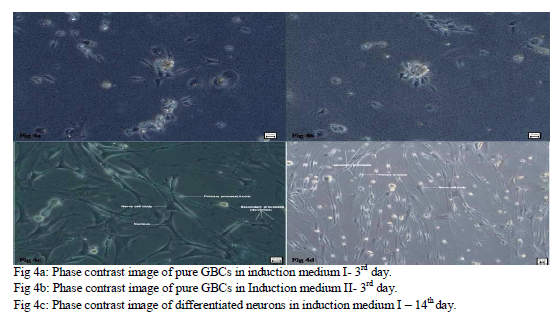
Two different induction media; medium I and medium II were used to differentiate GBCs into neurons (fig.4a, b). These media were composed to meet the culture and differential needs of the growing GBCs and assist them to easily and effectively transform into neuronal cell types. Retinoic acid was used in medium I and hence all the work while handling the medium was done under dark conditions. B-27 supplement was also used to assist the cell differentiation and growth. bFGF was added to the medium II to assist in cell growth. Antibiotics were added to the media to avoid contamination with bacterial agents. 2nd passage GBC was plated in medium-I for 14 days and in medium-II for 21 days. Medium-I was left unchanged whereas medium-II was changed every 3 days using all sterile precautions. GBC plated onto the two different induction media for different number of days transformed into mature neurons and other glial cells by the end of the induction protocol in both the media (fig.4c, d). These neurons demonstrated a single, long primary process and multiple numbers of smaller secondary processes. GBC also transformed into astrocytes in both the induction media.
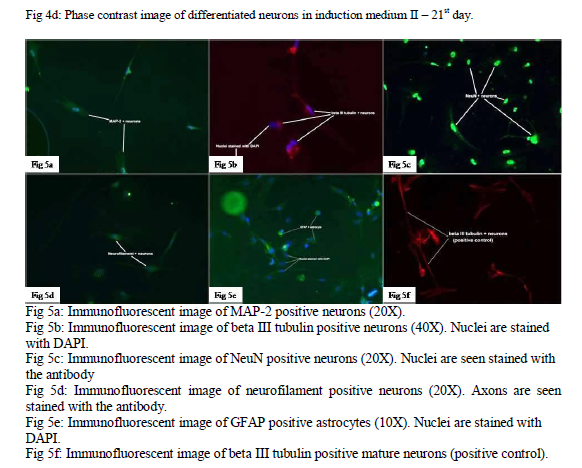
The differentiated neurons were positive for all the neuron specific markers (fig. 5a, b, c, d), hence proving the viability and functionality of the differentiated neurons. The differentiated cells were also positive for GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein), hence proving the transformation of GBCs and the viability of these astrocytes (fig. 5e). Mature neurons of rat were also stained with neural markers as positive control (fig. 5f). Electrophysiological characterisation of the differentiated neurons was tried using a whole cell voltage clamp. The cell membranes of the neurons were extremely fragile and it was not possible to obtain a high resistance seal on them. Hence voltage gated channels present on these neurons could not be identified. Further studies on characterizing the ion gated channels in the differentiated neurons would be extremely helpful in the future to determine the functionality and excitability of these neurons.
DISCUSSION
Neurogenesis begins in the early embryonic period (4th week) and continues 10 to 12 years after birth 16. The nervous system development is completed only during the adolescent period when myelination of the neurons of major tracts is completed 17. Neurogenesis in adults has been a topic of discussion in the field of neuroscience for decades with varying opinions from different researchers in this field. Early researchers believed the nervous system to be fixed and incapable of proliferation and regeneration based on the their opinions that neurons and non-neuronal cells in the nervous system could not divide actively by mitosis and they lacked the potential to transform from simple to more complex forms of neuronal morphologies. Another reason for such belief was inability in the past to demonstrate progenitor stem cells residing in the nervous system niche by specific markers. Cells in the nervous system could be demonstrated only by negative staining which was very non-specific13,18,19. Two important factors play a significant role in neurogenesis in adults. First being the microenvironment in which the stem cells responsible for neurogenesis reside and the other being the germ cell lineage of these stem cells. Hence it is important to provide these external and internal factors to the stem cells to promote their induction into neuronal cells. This research work studies one such population of stem cells residing in the olfactory epithelium which have the niche required to get accepted in the CNS environment and they are derived from the same germ line as the neuronal cells. This gives a hint that these might be the ideal neural progenitor cells which can be easily harvested and used for autologous transplantations.
The most recent development in this field of research has been the demonstration of neurogenesis in the olfactory system including the olfactory bulbs and more importantly in the olfactory mucosa. This finding proved very beneficial for working on the neural stem cells because of the easy accessibility of the olfactory mucosa. Numerous researchers have proved that there is ongoing neurogenesis throughout life in the basal compartment of the olfactory epithelium but they have not been able to define concretely, the lineage of cells responsible for this neuropotency. The dilemma still remains that whether HBC or GBC are the main colony of cells responsible for this ongoing neurogenesis. This research work on GBC has been able to prove with certain solidarity that it’s the GBC that behave as neural progenitor cells in the basal compartment of the OE. We study and standardize the microenvironment required for these cells to transform into neuronal cells.
CONCLUSIONS
This research work has been able to clarify with solidarity the prevailing ambiguity of the olfactory stem cells and has derived some definite conclusions about the cellular characteristics and cultural requirements of GBC for their neuronal transformation. It has now conclusively been made evident that Globose basal cells are the colony of neural stem cells residing in the basal compartment of the olfactory epithelium responsible for the ongoing neurogenesis in the OE throughout adult life and GBC require an ideal external microenvironment containing both internal and external factors for their proliferation, neurosphere formation and differentiation.
References:
- Fricker RA, Carpenter MK, Winkler C, Greco C, Gates MA, Björklund A. Site-specific migration and neuronal differentiation of human neural progenitor cells after transplantation in the adult rat brain. J Neurosci. 1999;19(14):5990-6005.
- Guo X, Johe K, Molnar P, Davis H, Hickman J. Characterization of a human fetal spinal cord stem cell line, NSI-566RSC, and its induction to functional motoneurons. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2010;4(3):181-93.
- G. J. Brewer. Regeneration and proliferation of embryonic and adult rat hippocampal neurons in culture. Exp. Neurol. 1999; 159, No. 1, 237-247.
- Rossi SL, Nistor G, Wyatt T, Yin HZ, Poole AJ, Weiss JH, Gardener MJ, Dijkstra S, Fischer DF, Keirstead HS. Histological and functional benefit following transplantation of motor neuron progenitors to the injured rat spinal cord. PLoS One. 2010;29;5(7):e11852.
- Ahmad S, Osei-Bempong C, Dana R, Jurkunas U. The culture and transplantation of human limbal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2010;225(1):15-9.
- Guo QC, Zhang Y, Wang YF, Tang HF, Wu PY, Liu ZY, Li ZQ. Distribution and differentiation of marrow stem cells transplanted by different ways in ischemic myocardium and other organs in rabbits. Clin Transplant. 2010; 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2010.01375.x .
- Shetty AK, Turner DA. In vitro survival and differentiation of neurons derived from epidermal growth factor-responsive postnatal hippocampal stem cells: inducing effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurobiol. 15. 1998;35(4):395-425.
- Schwob, J.E., Youngentob, S.L. and Mezza, R.C Reconstitution of the rat olfactory epithelium after methyl bromide-induced lesion. J. Comp. Neurol. 1995; 359, 15–37.
- V. Viktorov and G. T. Sukhikh, Vestn. Rossiisk. Akad. Medico-biological aspects of using stem cells. Med. Nauk. 2002; No. 4, 24-30.
- S. C. Barnett and J. S. Riddell. Olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs) and the treatment of CNS injury: advantages and possible caveats. J. Anat. 2004; 204, No. 1, 57-67.
- Ramon-Cueto, F. Valverde. Olfactory bulb ensheathing glia: a unique cell type with axonal growth-promoting properties. Glia. 1995; 14 163– 173.
- Jang W, Lambropoulos J, Woo JK, Peluso CE, Schwob JE. Maintaining epitheliopoietic potency when culturing olfactory progenitors. Exp Neurol. 2008;214(1):25-36.
- M. Caggiano, J.S. Kauer, D.D. Hunter. Globose basal cells are neuronal progenitors in the olfactory epithelium: a lineage analysis using a replication-incompetent retrovirus. Neuron. 1994; 13 339– 352.
- Jang W, Kim KP, Schwob JE. Nonintegrin laminin receptor precursor protein is expressed on olfactory stem and progenitor cells. J Comp Neurol. 2007;502(3):367-81.
- C.G. Hahn, L.Y. Han, N.E. Rawson, N. Mirza, K. Borgmann-Winter, R.H. Lenox, S.E. Arnold. In vivo and in vitro neurogenesis in human olfactory epithelium. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005;483, 154– 163.
- T. Paus et al. Structural maturation of neural pathways in children and adolescents: In vivo study. Science. 1999; 283, 1908.
- Flechsig, Paul. Developmental (myelogenetic) localisation of the cerebral cortex in the human subject. The Lancet. 1901; 1028.
- A.L. Calof, J.S. Mumm, P.C. Rim, J. Shou. The neuronal stem cell of the olfactory epithelium. J. Neurobiol. 1998; 36 190– 205.
- L.A. Carter, J.L. MacDonald, A.J. Roskams. Olfactory horizontal basal cells demonstrate a conserved multipotent progenitor phenotype. J. Neurosci. 2004;24 5670–5683.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License