IJCRR - 9(11), June, 2017
Pages: 53-58
Date of Publication: 12-Jun-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
The Vitamin D Status in 6-14 Year Old Children Attending Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital in South India
Author: Bindusha S., Riaz I., Sujith K. R., Lalitha Kailas
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Vitamin D insufficiency among healthy children and adolescents is reported to be highly prevalent in the different parts of world.
Objective: To assess the Vitamin D status in children in the age group of 6-14 years attending a tertiary care teaching institute of South India and to analyze the factors which can contribute to Vitamin D deficiency in these children.
Methods: Cross-sectional study. 6 \? 14 year old children attending the outpatient department were included in the study. Children with co \? morbid conditions that affect Vitamin D metabolism and those children on chronic drug treatment and on Vitamin D supplementation were excluded from the study.
Results: Average age of study population was 8.93\? 2.02. In the study 48 (52.2%) children among a total of 92 had a normal Vitamin D status while the rest 44 children (47.9%) had insufficient Vitamin D status (25 hydroxy vitamin D < 30 ng/ml). Among these children 21 (22.8%) had sub-optimal vitamin D levels, 19 (20.7%) were deficient, 3 (3.3%) had severe and 1 (1.1%) had very severe deficiency of Vitamin D. The average Vitamin D level among the study population was 31\?14.13 ng/ml. There was significant statistical association between Vitamin D deficiency and stunting (p=0.003). No statistically significant association was found between outdoor activity, clothing and skin colour with Vitamin D deficiency in this study.
Conclusions: Vitamin D insufficiency was documented in 47.9% of 6 \? 14 year old children and there is a significant association between stunting and Vitamin D deficiency.
Keywords: Vitamin D status, Hypovitaminosis D, VDD, Stunting, Outdoor activity
Full Text:
Introduction
Vitamin D Deficiency is on a rise as a major public health problem in India. Majority of the population in India resides in areas receiving ample sunlight throughout the year; still vitamin D deficiency is a problem of growing concern 1, 2, 3. Skin complexion, poor sun exposure, vegetarian food habits and lower intake of vitamin D fortified foods could be attributing to the high prevalence of VDD in India 4. However till the early 1990s, VDD was considered to be rare in India. Such belief was based on studies measuring serum calcium and alkaline phosphatase in Indian population. A study conducted in 2000 by Goswami et al among apparently healthy subjects to measure their serum 25 hydroxy D level documented that significant hypovitaminosis D was present in all groups, except those with maximal sunlight exposure2. Subsequently, studies conducted in different parts of the country have documented a widespread prevalence of VDD in all age groups including toddlers, school children, pregnant women, neonates, adult males and females residing in rural or urban areas5, 6,7,8,9.
Data on vitamin D deficiency among children and adolescents of Kerala is scarce. Children in the school going age group more susceptible to vitamin D deficiency disorders. This is the age group in which there is a tremendous increase in the bone growth and high vitamin D requirement. Hence this study was undertaken for estimating the Vitamin D status in children of the age group 6-14 years attending the outpatient department of tertiary care teaching hospital in Kerala.
Materials & Methods
Objectives:
- To assess the Vitamin D status in children aged 6 – 14 years
- To analyze the factors which can contribute to Vitamin D deficiency in these children
Study design
This was a tertiary hospital based, cross sectional descriptive study.
Study population
Children aged 6 to 14 years attending the Outpatient department of a tertiary care teaching hospital
Study period
One year - From October 2013 to October 2014
Inclusion criteria
Children in the age group of 6-14 years attending the local Outpatient department
Exclusion criteria
Children with co – morbid conditions that affect Vitamin D metabolism like chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, heart disease and chronic neurological diseases were excluded from the study. Children on Vitamin D supplementation and children on chronic drug treatment including multivitamins, anticonvulsants, steroids, thyroxin, antituberculous treatment and antimetabolites were also excluded from the study.
Methodology
Sanction of Institutional Ethical committee was obtained before starting the study. Parents and children were interviewed with the help of a detailed questionnaire prepared to assess the personal information of the children. The questionnaire also included their pattern of clothing, time spent for outdoor and physical activity. The nutritional status of the children was assessed with respect to height, weight and BMI. They were examined for clinical features of Vitamin D deficiency. Biochemical investigations including Serum Calcium, Serum Phosphorus, Serum Alkaline phosphatase, Serum Albumin and 25 hydroxy Vitamin D were done.
Hypovitaminosis D was defined on the basis of the measurement of serum 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D concentrations. The kit used for the study was the 25 hydroxy Vitamin D ELISA kit manufactured by Biovendor research and diagnostics Products, Hamburg, Germany (Cat No. REA 300/96), a monoclonal anti 25 hydroxy Vitamin D antibody based ELISA test. Serum 25 hydroxy vitamin D level more than 80nmol/L (>30ng/ml) by enzyme linked immunoassay was considered as optimum level9. Concentrations of 20-30 ng/ml, 10–20 ng/ml, 5–10 ng/ml and less than 5 ng/ml 25 hydroxy vitamin D were classified as Suboptimal Vitamin D, Vitamin D deficiency, Severe and Very Severe hypovitaminosis D respectively9. 30-50 ng/ml was taken as Optimal Vitamin D and 50-70 ng/ml as Upper Normal vitamin D. The data was analyzed to find out the factors which affect the Vitamin D concentration in the children.
Data is presented as mean ± SD. The chi-square test was used for the analysis of categorical variables. Fisher’s exact test was used for the analysis of categorical variables, when more than 20% cells had value less than 5. A p-value <0.05 was considered significant. Data was statistically analyzed with the use of the Statistical Package for Social Science program (SPSS version 20.0 for Windows)
Results
92 children in the age group 6 – 14 years were included in the study, out of which 51 (55.4%) were boys and 41(44.6%) were girls. 50 children (54.3%) were aged between 6 -10 years, while 42 children (45.7%) were aged between 10 – 14 years. The mean age of the study group was 8.93±2.02. 69 children, representing 75% of the study population were normally nourished, with weight more than 80% of the weight expected for their age. 18 children (19.6%) had Grade 1 and 5 children (5.4%) had Grade 2 malnutrition, according to IAP classification. 76 children (82.6%) had normal height, defined as height more than 95% of expected height for their age. 11children (12%) had 1st degree, 4 children (4.3%) had 2nd degree and 1 child (1.1%) had 3rd degree stunting according to Waterlow classification. 31(33.7%) children had normal body mass index, while 55 children (59.8%) were underweight, 5 children (5.4%) were overweight and 1 child (1.1%) was obese.
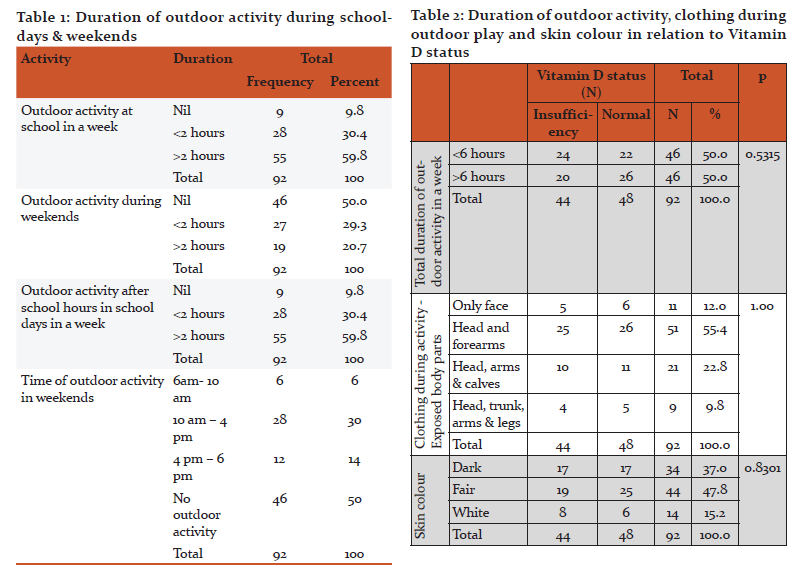
The mean duration of outdoor activity during school time was 2.85±1.38 hours in a week. 59.8% of children had more than 2 hours of outdoor activity at school in a week. 30.4% children had less than 2hrs of outdoor activity in school during weekdays. 9 children (9.8%) did not engage in any outdoor play during the school hours. 83 children (90.2%) did some outdoor activity during school hours. Among them 46 children (50%) played outdoors between 1- 2 PM during the lunch break. 37 children (40%) played outdoors between 3- 4 PM, during PT hours.
The duration of outdoor play after the school time on school days was 2.85 ± 1.3 hours in a week. 28 children (30.4%) played for less than 2 hours/ week and 64 children (49.8%) played for more than 2 hours/week during weekdays. 9 children (9.8%) did not participate in any outdoor play after the school hours. The mean duration of outdoor activity during weekends was 1.41±1.58 hours. 46 children (50%) had no outdoor activities during the weekend. The mean duration of outdoor activity during the whole week was 6.99 ± 3.50 hours. The minimum duration of outdoor activity in week was 3 hours and maximum duration of outdoor activity in week was 13 hours. 50% of children had less than 6 hours outdoor activity per week.
During weekends, only 30 % of children had sun exposure during the period of 10AM to 4PM, when there is maximum concentration of UV rays in the sunlight. 55.4% of children were exposing only head and forearms during outdoor activity.
14.1% of children had clinical features of rickets. 7 children had genu valgus and 6 children had genu varus. No other skeletal deformity was seen in the study group.
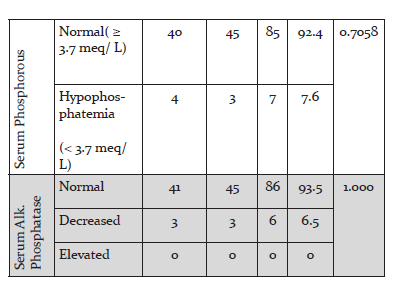
Among the study population, 9 children (9.8%) had hypocalcaemia, which is defined as serum calcium below 8.5 meq / L. 83 children (90.2%) had normal serum Calcium level. The mean Serum Calcium level was 9.63± 0.81 meq/L. 7 children (7.6%) had hypophosphatemia with serum phosphorous level less than 3.7 meq/L. 85 children had normal serum phosphorous level. The mean Serum Phosphorous level was 4.52± 0.69 meq/L. 86 children (93.5%) had serum Alkaline phosphatase level in the normal range; between 145 – 420 U/L in 1-9 yr old and 140- 560 U/L in 10-14 yr old children. 6 children(6.5%) had low alkaline phosphatase level less than 145 U/L. None of the children in the study group had elevated Serum alkaline phosphatase level.
48 children (52.2%) had 25 hydroxy Vitamin D levels more than 30 ng/ml, which is considered as optimal Vitamin D status. 44 children (47.9%) had insufficient Vitamin D levels. The mean 25 hydroxy Vitamin D level in the study population was 31.00± 14.13 ng/ml. The mean 25 hydroxy Vitamin D level was 31.87 ± 13.54 among boys and 29.98± 14.92 ng/ml among girls. The mean 25 hydroxy Vitamin D level in children in the age group 10- 14 years was 31.00 ± 14.52 ng/ml. The mean 25 hydroxy Vitamin D level in children in the age group 6- 10 years was 31.01 ± 13.93 ng/ml.
For statistical comparison, all children with Serum 25 hydroxy Vitamin D levels less than 30 ng/ml were grouped as Vitamin D insufficiency. This group was compared with the group having sufficient levels of Vitamin D (≥ 30 ng/ml). Age (p= 0.423) and gender (p= 0.559) did not have any statistically significant association with Vitamin D insufficiency.
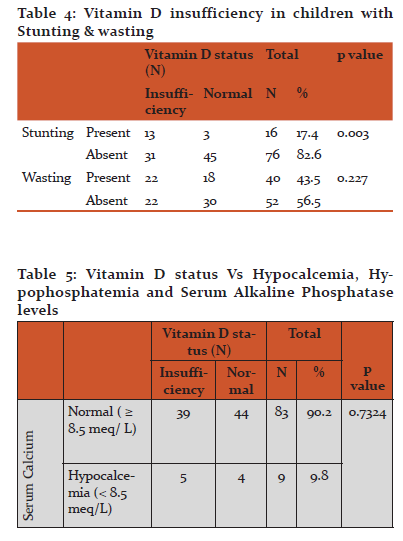
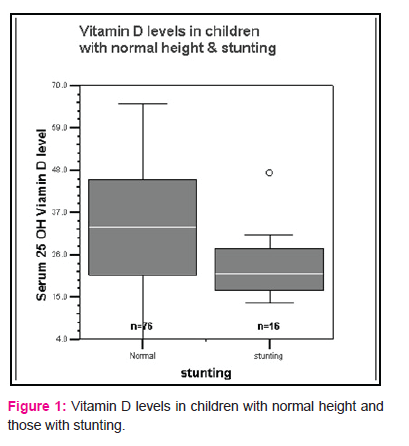
There was a statistically significant relationship between Stunting and Vitamin D insufficiency in the present study (p=0.003). No relation was found between Vitamin D insufficiency and wasting (p= 0.227), Body mass index (p=0.225) or malnutrition (p= 0.823).
No statistically significant relationship was found between duration of physical training and Vitamin D insufficiency (p= 0.446), when children with more than 2 hrs of PT class in a week was compared with children with less than 2 hours of PT in a week. No statistically significant relation was found between Vitamin D insufficiency and total duration of outdoor activities in a week, when the group with outdoor activity less than 6 hours per week was compared with the group with more than 6 hours of outdoor activity per week (p=0.404). No significant association was found between Vitamin D deficiency and skin colour (p=0.628) or clothing during outdoor activity (p=0.992). No association was found between Vitamin D insufficiency and hypocalcaemia (p= 0.894) and hypophosphatemia (p= 0.263). Elevated Serum alkaline phosphatise level was not seen any of the children in the study group.
Discussion
25 hydroxy Vitamin D levels in apparently healthy Indian population was first evaluated by Goswami R et al in the year 2000 2. Marwaha et al studied the Vitamin D status and bone mineral density of healthy school children in North India1. They found that 92.6% of children in the low socioeconomic group and 84.9% of children in the upper socioeconomic group had hypovitaminosis D according to Lips classification7. The mean serum concentration of 25(OH) D in the study on children from northern India was 11.8±7.2 ng/ml in this study 1.
Study conducted by Das G et al among school girls, reported the prevalence of Vitamin D deficiency as 73% and mean serum 25 hydroxy D level as less than 12ng/ml10. Puri.S et al studied the Vitamin D status among school girls aged 6-18 years belonging to both lower and upper socio economic status11. They documented the prevalence of biochemical hypovitaminosis D (serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D <50 nmol/l) as 90·8%. 89·6% of girls belonging to low socioeconomic status (5·2% severe, 25·4% moderate, 59% mild) and 91·9% of girls in the upper socioeconomic group (2·8% severe, 36·5% moderate, 52·6% mild) had vitamin D deficiency11. A study conducted on 6-17 years schoolgirls from both lower and upper socio economic status reported the prevalence of VDD as 93.7%. However, the prevalence of VDD in lower socioeconomic strata was higher (97.3%) as compared to upper socioeconomic strata (90.9%) 12. In a study conducted by Kapil U et al. among 6 – 18 year old children in Himachalpradesh, hypovitaminosis D was observed in 93% subjects (using cut off value as serum 25 hydroxy D < 20 ng/ml) with mean serum 25 hydroxy D level of 12.8 ± 6.5 ng/ml in 6-11 year old boys and 13.8±5.2 ng/ml in 12-18 year old boys13. Harinarayanan et al found that the prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency (25 hydroxy D < 30 ng/ml) among healthy South Indians was 83.5%, 99%, 88% and 94% in rural men, rural women, urban men and urban women respectively8.
Vitamin D insufficiency (25 hydroxy Vitamin D < 30 ng/ml) was seen in 47.9% of children in the present study. Vitamin D deficiency (25 hydroxy Vitamin D < 20 ng/ml) was seen only in 25.1% of the study group. This is much lower when compared to the previous studies from India. The mean 25 hydroxy Vitamin D level in the study population was 31.00± 14.13 ng/ml, which is higher compared to the previous studies. The lower prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and higher mean 25 hydroxy levels may be explained by the geographical difference. Most of the Indian studies are from the North India. Kerala being a south Indian state receives more vertical sunrays and more ultra violet rays, as it is closer to the equator.
There was no gender predilection with respect to vitamin D deficiency (p= 0.559) in the present study. No difference in 25 hydroxy vitamin D levels were seen in the study by Khadgawat R et al14, but boys had significantly higher serum 25(OH) D concentrations (p= 0.004)in the study by Marwaha et al1.
There was no statistically significant relationship (p=0.446) between duration of outdoor play during the school hours and Vitamin D deficiency. In the present study there was no statistical significance (p=0.404) between Vitamin D deficiency and duration of outdoor activities in a week. The minimum duration of outdoor activity in a week among our study population was 3 hours, which will amount to 25 minute per day. There was no significant (p=0.628) relationship between Vitamin D deficiency and skin colour and no relation between body surface exposed and Vitamin D status (p=0.992). Puri S et al found a significant correlation between 25 hydroxy D concentration and estimated sun exposure and between 25 hydroxy D and percentage of body surface area exposed 11. Dark skin is a risk factor for low Vitamin D in adolescents according to Gordon et al15. But skin colour was not found to be significantly related to skin colour in infants and toddlers16.
There is a significant (p=0.003) relationship between Stunting and Vitamin D deficiency in the present study. Kremer R et al also found a positive relation between 25 hydroxy vitamin D levels and height among young women17.
No significant relationship found between Vitamin D deficiency with hypocalcaemia, hypophosphatemia and elevated alkaline phosphatase in our study. The study by Kapil U et also failed to demonstrate statistical significant relation between vitamin D status and serum calcium, phosphorous and serum alkaline phosphatase levels13. Elevated serum alkaline phosphatase activity is considered as a marker of increased osteoclastic activity seen in rickets. But none of the children in the study group showed elevated serum alkaline phosphatase. This finding questions the use of serum alkaline phosphatase as a screening test for vitamin D deficiency.
Conclusions
Almost half of the children studied had insufficient Vitamin D status. Mean level of Serum 25 hydroxy Vitamin D was 31.00± 14.13 ng/ml. The prevalence of Vitamin D insufficiency in the present study is low and mean 25 hydroxy Vitamin D level is higher compared to other studies from India. This may be explained by the geographical position of Kerala, which is closer to the equator than other parts of India. Vitamin D insufficiency had direct correlation with stunting. Subclinical vitamin D deficiency may be a factor contributing to stunting in children. Future studies are needed in this direction. No statistically significant association was found between vitamin D insufficiency and outdoor activity, exposed body surface or skin colour in the present study.
Funding
The study was funded by the State Board of Medical Research, Kerala.
Acknowledgement
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest
No authors have any conflict of interest to declare.
References:
1.Marwaha RK, Tandon N, Reddy DRHK, Aggarwal R, Singh R, Sawhney RC, et al. Vitamin D and Bone mineral density of healthy school children in northern India. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005; 82:477-82.
2.Goswami R, Gupta N, Goswami D, Marwaha RK, Tandon N, Kochupillai N. Prevalence and significance of low 25-hydroxy vitamin D concentrations in healthy subjects in Delhi. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000; 72:472-5.
3. Goswami R, Kochupillai N, Gupta N, Goswami D, Singh N, Dudha AJ. Presence of 25(OH) D deficiency in a rural north Indian village despite abundant sunshine. J Assoc Physicians India. 2008; 56:755-7.
4. Hodgkin P, Kay GH, Hine PM, Lumb GA, Stanbury SW. Vitamin D deficiency in Asians at home and in Britain. Lancet. 1973; 2:167-72.
5. Arya V, Bhambri R, Godbole MM, Mithal A. Vitamin D status and its relationship with bone mineral density in healthy Asian Indians. Osteoporos Int. 2004; 15:56-61.
6. Harinarayan CV. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in postmenopausal south Indian women. Osteoporos Int. 2005; 16:397-402.
7. Marwaha RK, Sripathy G.Vitamin D and Bone mineral density of healthy school children in northern India. Indian J Med Res. 2008; 12:239-44.
8.Harinarayan CV, Ramalakshmi T, Prasad UV, Sudhakar D, Srinivasarao PV, Sarma KV, et al. High prevalence of low dietary calcium, high phytate consumption, and vitamin D deficiency in healthy south Indians. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007; 85:1062-7.
9. Lips P. Worldwide status of vitamin D nutrition. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2010; 121(1–2): 297–300.
10. G Das, S Crocombe, M McGrath, J L Berry, M Z Mughal. Hypovitaminosis D among healthy adolescent girls attending an inner city school. Arch Dis Child. 2006; 91:569–572.
11.Puri S, Marwaha RK, Agarwal N, Tandon N, Agarwal R, Grewal K et al. Vitamin D status of apparently healthy schoolgirls from two different socioeconomic strata in Delhi: relation to nutrition and lifestyle. Br J Nutr. 2008; 99:876-82.
12.Marwaha RK, Tandon N, Agarwal N, Puri S, Agarwal R, Singh S et al. Impact of two regimens of Vitamin D supplementation on calcium - Vitamin D – PTH axis of schoolgirls of Delhi. Indian Pediatr. 2010; 47(9):761-9.
13. Kapil U, Pandey RM, Goswami R, Sharma B, Sharma N, Ramakrishnan L et al. Prevalence of Vitamin D deficiency and associated risk factors among children residing at high altitude in Shimla district, Himachal Pradesh, India. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2017?21 (1):178–183.
14.Khadgawat R, Thomas T, Gahlot M, Tandon N, Tangpricha V, Khandelwal D, et al. The effect of puberty on interaction between Vitamin D status and insulin resistance in obese Asian-Indian children. International Journal of Endocrinology. 2012; Article ID173581
15. Gordon CM, De Peter KC, Feldman HA, Grace E, Emans SJ. Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency among Healthy Adolescents. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2004; 158(6):531-537.
16. Gordon CM, Feldman HA, Sinclair L et al. Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency among Healthy Infants and Toddlers. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med.2008; 162(6): 505-512.
17. Kremer R, Campbell PP, Reinhardt T, Gilsanz V. Vitamin D Status and its Relationship to Body Fat, Final Height and Peak Bone Mass in Young Women. J Clin Endocrin Metab. 2008;doi:10.1210/jc.2008-1575
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License