IJCRR - 9(11), June, 2017
Pages: 06-09
Date of Publication: 12-Jun-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Differentiation and Comparison of Left handed and Right handed writers on the basis of Strokes and Slope of letter
Author: Manju Sahu, Alpha Kujur
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Handwriting is a written speech of an individual with characteristics peculiar to himself. The handwriting of a person is a product of his mental, emotional, intellectual and physical personality. Once the handwriting is set it is unique expression of his graphic personality. The differentiation for the identification of handedness of author plays an important role to identify an individual in document cases and to study this differentiation and comparison of left handed and right handed writers on the basis of strokes and slope of letter, the present study was conducted at Bilaspur district, Chhattisgarh in which 100 samples of handwriting, 50 left-handed and 50 right-handed writer were collected. The handwriting samples were examined by hand lens, flexible arm illuminated magnifier, grid scale and the characteristics features like stroke and slope were observed in various letters. A significant difference was observed in left handed and right handed writing and was concluded that left-handed writer make strokes in right-to-left direction and the slope of letters has an inclination in backward direction where as right-handed writer make strokes in left-to-right direction and the inclination of slope was in forward direction. Thus, this differentiation and comparison helps to solve many document cases.
Keywords: Handwriting, Identification, Slope, Stroke, Left handed, Right handed
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Handwriting is an individual style of writing (1). It is an acquired skill and clearly one that is a complex perceptual-motor task, sometimes referred to as a neuromuscular task (2). Handwriting can be described as the formation of letters, characters or symbols using writing implement according to a recognizable patter which is designed to communicate with another person (3). Each writer has intrinsic forces of perception, capacity for graphic expression, and technical expression. It takes many years of practice to develop skill and proficiency of writing. Graphic maturity is reached when the motor skills of the writer are fully developed, and the writer no longer has to focus attention on the act of writing (4). At this point, the writer concentrates on content and lets his or her subconscious handle the execution of the writing act. Writing is a conscious act, through repeated use, the actual formation of each letter or word becomes almost automatic, so that the experienced writer concentrates most on his conscious thought on the subject matter rather than on the writing process itself. Thus writing comes to be made up of innumerable subconscious habitual patterns which are much a part of the individual assembly of his personal habits or mannerism (5). Handwriting is affected by state of mind, health, age and other factors. In general the more writing a person does, the greater the range of variation and he more it will change with time. It is a set of subconscious habits. It is a mechanism of muscles and nerves which is influenced by a mental picture and sometimes modifies by writers individual interest and ability to imitate (6).
Hand preference is the most prominent behavioral expression of brain asymmetry in man. The majority (approximately 90%) of the human population writes with right hand (7). Right- handed writers use their thumb to exert pressure on the writing instrument to push it horizontally in a rightward and upward direction. The middle finger pushes the writing instrument leftward both diagonally and horizontally while thumb and index finger pull the instrument down towards the baseline, which is the imaginary line to which the writing returns. Because writer movement is from left to right, the right handed writer has advantage of being able to see the writing as it is being executed. The left-handed writer must adjust his or her hand to compensate for the fact that the hands covering the line of writing assist it being executed. Many left handed writers hook their hand over the writing so they can see what they are writing. (4). This is assumed that the right handed writers make strokes from left-to-right and left handed writers make strokes from right-to-left. The right handed writing and left handed writing is also differentiated by slope character (8) (9). This slope can be examined in only cursive writing. The right handed writers makes forward slope and left handed writers makes backward slope. The identification of writer group attributes like gender, age and handedness from handwriting is an important goal in the forensic studies. The document examiner can eliminate many suspects with the help of this technique in various document cases.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
For this study, total 100 handwriting samples were collected from Bilaspur district of Chhattisgarh in which 50 were left handed and 50 were right-handed from school and college students and working individuals between the age group of 18 to 30 years for identification of handedness of writer. Examinees were asked to sit straight and copy the given printed paragraph in English to the provided white sheet of paper and given ball point pen to each and everyone with their normal speed neither too slow nor too fast on a stable flat table and chair in adequate amount of light. The collected handwriting samples were examined by hand lens, flexible arm illuminated magnifier and grid scale. To study the characteristic features like strokes and slope in the writing handwriting samples of left handed writers and right handed writers were investigated. For direction of stroke in letters having cross bar like t, f, A, E, F has a noteworthy degree of variation in their formation were observed among the left handed and right handed writer. It was assumed that the left handed writer makes the horizontal stroke in Right-to-Left direction in contrast to the right handed writer who writes in left to right direction. In this study five letters was selected like t, l, d, g, and y. The slant was observed visually.
RESULTS
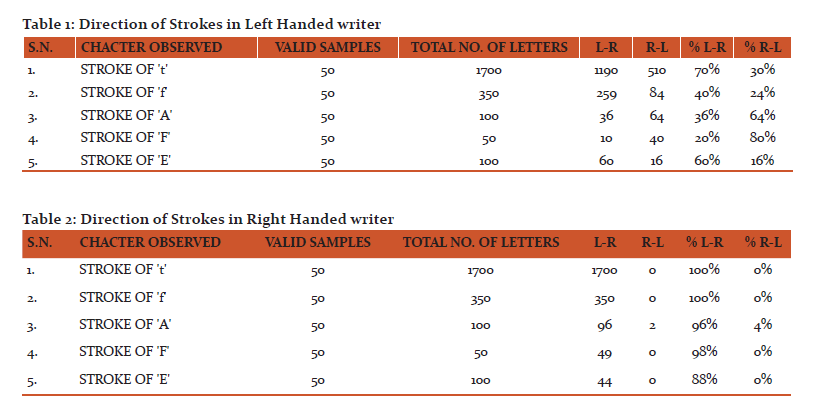
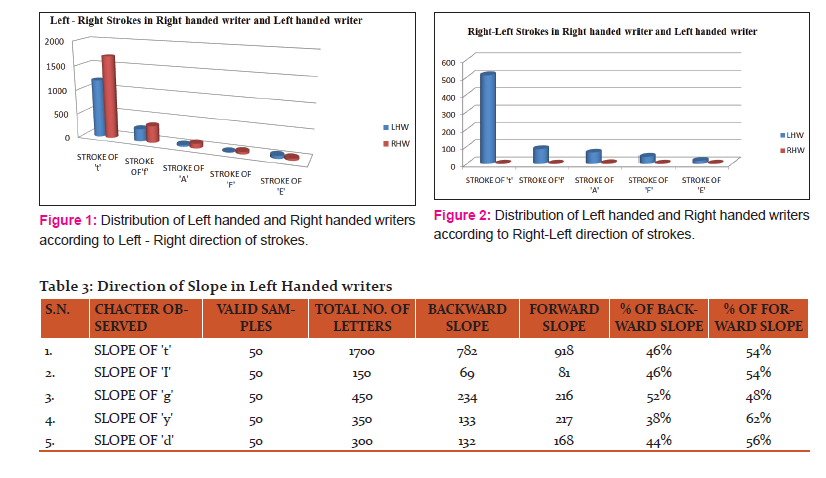
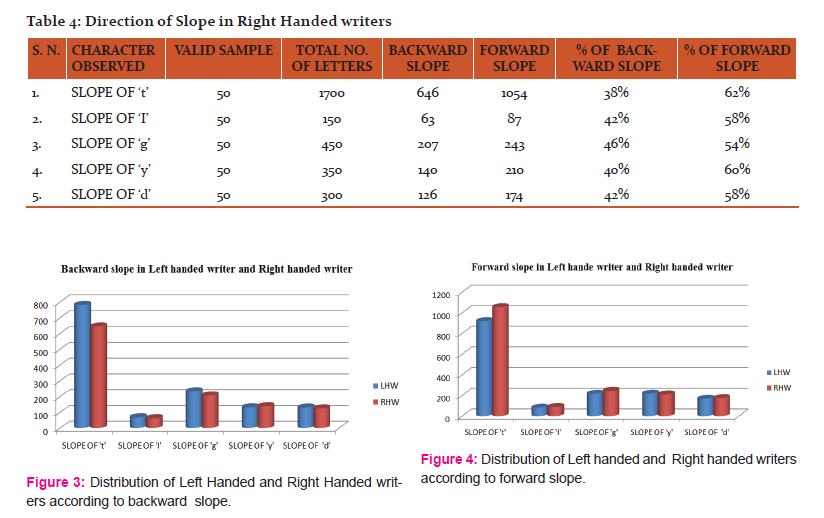
The results reported here in from Tables 1-4 along with the related Figures 1-4 highlights on the difference between left-handed writer and right-handed writer.

DISCUSSION
Writing is a complex process and it needs a lot of effort and practice to learn and to perfect it. The brain initiates the process and body parts: the fingers, hand, wrist and forearm execute it (10). The handwriting characteristics of an individual are his characteristics creations of writing units such as slopes and strokes. In addition, hand inclination is also an important behavioral expression whose differentiation and comparison can help to solve many document as well as forgery cases. The examiner believes that handwriting in question having a perverted form may or may not have been written by someone using the left hand, or the unusual opposite hand. Some appearances of opposite-hand writing are also examined in the writing of the customarily untrained writer. In addition, opposing to some observations that left-handed writers are less trained than right- handed writers, in their study, Stangohr reported “no remarkable skill difference between the two groups” (11). In the present study, results shows that the left-handed writer made strokes in right-to-left direction and the slope of letters has an inclination in backward direction where as right-handed writer made stokes in left to right direction and the inclination of slope was in forward direction as opposite to the findings of Gordon. This justifies the need to do a thorough, comprehensive and exhaustive investigation comparing all available information and exemplars (especially the opposite-hand requested exemplar, if possible).
CONCLUSION
The present study was to identify the handedness of writer i.e. the difference between left-handed writer and right-handed writer. The outcomes in the study from table alongside the figures, it has been concluded that left-handed writer made strokes in right-to-left direction and the slope of letters has an inclination in backward direction where as right-handed writer made stokes in left-to-right direction and the inclination of slope was in forward direction. Thus, this differentiation and comparison of left handed and right handed writers on the basis of slope and stroke of letters plays an important role to identify an individual in document cases.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are thankful to a large number of anonymous subjects from Bilaspur District, Chhattisgarh, India who voluntarily participated in this study and provided the handwriting samples for the present study. Authors also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Saran Vaibhav, Kumar Suneet, Gupta A. K., Ahmad Syeed., Differentiation of Handedness of Writer Based on their Strokes and Characteristic Features. Journal of Forensic Research, 2013; 4(5)
2. Huber A. Roy., Headrick M. A., Handwriting Identification: Facts and Fundamentals, CRC Press, Boca Raton New York. 1999.
3. Sharma B. R., Forensic Science in Criminal Investigation and Trials, Fourth Edition, Universal Law Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd. 2005
4. Koppenhaver M. Katherine, Forensic Document Examination, Humana Press. 2007
5. Ordway. Hilton., Scientific Examination of Questioned Documents, Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. 1982
6. Jay. Siegal, Geoffery Knupfer, Pekka Saukko., Encyclopedia of Forensic Sciences, Three volumes set. Elsevier. 2000
7. Grabowska1 Anna., Gut Malgorzata., Binder Marek., Forsberg Lars., Rymarczyk1 Krystyna., Urbanik Andrzej., Switching handedness: MRI study of hand motor control in right-handers, left-handers and converted left-handers, Acta Neurobiol Experimentals, 2012;(72) 439-451
8. J. E. Franks., T. R. Davis., Variability of stroke direction between left and right handed writer, Journal of the Forensic Science Society, 1985;(28) 353-370.
9. J. L. Smart., C. Jeffery., B. Richards., A retrospective of relationship between birth history and handedness at six years. Early Human Development, 1956; (10) 56-60
10. Sharma B. R., Handwriting Forensics, Second Edition, Universal law Publishing, 2017
11. Stangohr, Gordon R., Opposite-hand writings. Journal of Forensic Sciences, 1968, (13) 376-89
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License