IJCRR - 5(15), August, 2013
Pages: 95-101
Date of Publication: 17-Aug-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF CARDIAC REHABILITATION VS HOME EXERCISES AFTER CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING (CABG) ON HEMODYNAMICS
Author: Pratibha Manhas, Tushar J. Palekar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Exercise training has been shown to modify the sympathovagal control of heart rate toward an increase in parasympathetic tone. At the same time, the improved vagal activity is associated with reduced death risk from cardiac events (Wu S-K, Lin Y-W et al). Although a cardiac rehabilitation exercise program is standard therapy for patients after a cardiac event and especially for those who have received Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), the relationship between a cardiac rehabilitation exercise programme and acute hemodynamics and comparison with home based exercise programme has not been clearly demonstrated. Objectives: To find the effect of cardiac rehabilitation and home exercises on blood pressure, Heart rate, Respiratory Rate and Rating of perceived exertion (RPE) and compare the effects of cardiac rehabilitation and home exercises. Method: Thirty consecutive eligible patients undergone Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) referred by cardiovascular surgeons had participated in this study. After completion of baseline exercise stress test at discharge or within first week after discharge were randomly assigned to group A (Hospital based Cardiac rehabilitation) and group B (Home based cardiac rehabilitation) for 6 weeks. Materials: Perceived exertion scale, Stop watch, Blood Pressure apparatus, Pulse oxymeter Result: There were significant improvements in hemodynamics (p=0.000) both with hospital based cardiac rehabilitation and home based exercises but there were no significant differences between hospital cardiac rehabilitation and home based exercises. Conclusion: This study had concluded that both hospital based cardiac rehabilitation and home based exercises are effective in improving acute hemodynamics.
Keywords: CABG, Cardiac Rehabilitation, Home Exercises
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Cardiac Rehabilitation programmes are associated with significantly improving exercise tolerance and functional capacity, increasing psychosocial well being, alleviating activity related symptoms, reducing disability and decreasing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. This is achieved through exercise, patient education and advice, relaxation, drug therapy, and specific help for patient’s psychological sequelae.1 There is good evidence that both exercise and comprehensive cardiac rehabilitation programmes are effective, reducing all-cause mortality by 27% following myocardial infarction.2 The National Service Framework for Coronary Heart Disease in England and Wales seeks to expand the uptake and coverage of cardiac rehabilitation to patients following a heart attack, coronary artery bypass graft or coronary angioplasty, and also patients with heart failure and angina.3 The concept of cardiac rehabilitation and secondary prevention has been defined as the effort toward cardiovascular risk factor reduction designed to lessen the chance of a subsequent cardiac event and to slow and perhaps stop the progression of the cardiovascular disease process.4 Uptake of hospital-based cardiac rehabilitation programmes is poor, particularly among women, the elderly and people from minority ethnic groups. Home-based cardiac rehabilitation programmes were first reported in the early 1980s and might be more acceptable and convenient for some patients, thus increasing uptake. This review explores whether there is any evidence that homebased cardiac rehabilitation programmes are superior to usual care in improving cardiac risk factors and mortality and whether benefits occur to patients’ post-myocardial infarction (MI) and after vascularisation procedure. In addition they have explored whether the outcomes from home-based cardiac rehabilitation are similar to centre (or hospital) based programmes.5 Phase II cardiac rehabilitation programs are associated with significantly improving exercise tolerance and functional capacity, increasing psychosocial well being, alleviating activity related symptoms, reducing disability, and decreasing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.6 Exercise based cardiac rehabilitation is associated with significant improvements in autonomic markers of neural regulation of sinoartrial node such as increase in R-R interval of electrocardiogram (ECG), in its variance, and in overall spontaneous baroreflex.7 Relatively few studies have evaluated the effectiveness of cardiac rehabilitation following revascularisation and there is still insufficient evidence about the effects of cardiac rehabilitation on survival. Cardiac rehabilitation programmes have reported some benefits in aerobic capacity a reduction of smoking and lower blood pressure8-9 ; lower anxiety scores 10and improvement in lipoprotein patterns.11 Cardiac rehabilitation has been hypothesized to favourably impact acute hemodynamics by modulating autonomic function. Nishime11 et al. Showed that cardiac rehabilitation only had the tendency toward improved heart rate recovery, where as Tiukinhoy12 et al. Reported a significant enhancement for the rehabilitation group with a similar heart rate recovery in their control group. Although Kligfield13 and associates investigated the effect of age and gender on acute hemodynamics in cardiac patients, the measurement of heart rate recovery was evaluated after submaximal effort rather than after peak exercise. Moreover despite the documented benefits of formal cardiac rehabilitation exercise programs, the cost, lack of time, and accessibility contribute to relatively low participation rates.14 Some studies have demonstrated positive effects for cardiac patients enrolled in home based exercise programs such as in quality of life, modulation of risk factors and peak oxygen consumption.15 The purpose of this study was to investigate whether the cardiac rehabilitation and home based exercise programme had a positive effect on acute hemodynamics and to compare the difference between cardiac rehabilitation and home based exercise programme.
METHODS
Thirty consecutive eligible patients undergone Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) referred by cardiovascular surgeons had participated in this study. All of them had undergone phase I cardiac rehabilitation programme such as early mobilization and walking under supervision after surgery. Patients with previous Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, neurological impairments, severe musculoskeletal diseases, complication during hospitalization, uncontrolled dysrhythmias and who cannot complete stress test at discharge were excluded from the study. After completion of baseline exercise stress test at discharge or within first week after discharge were randomly assigned to one of the following groups for 6 weeks. Group A – Cardiac rehabilitation exercise programme.
Patients in this group had received a 30 – 40 min. of aerobic exercise training session (riding a stationary bicycle or jogging on a treadmill) with the intensity corresponding to 60 – 85 % of the peak heart rate achieved by perceived exertion scale 11 to 13. There was at least 10 min. of stretching exercises for warm up and 10 min of cool down. Heart rate (HR), Blood Pressure (BP), Respiratory Rate (RR) and exercise intensity was monitored by senior cardiopulmonary physical therapist during the exercise session and a total of 18 exercise sessions will be given to the patients. Group B – Home based exercise Patients in this group had received a home based exercise programme with an intensity corresponding to 60 – 85 % of the Peak Heart Rate (PHR) obtained by the rating of perceived exertion scale from 11 to 13. Patient was advised to exercise 3 times per week and exercise session will include a 10 min. warm up, 30 – 40 min. of aerobic training (brisk walking or jogging) and 10 min. cool down. Subjects were asked to document exercise record book
Statistical Analysis
The statistical tests used for the analysis of the result:
1) Paired t-test
2) Unpaired t-test Level of significance was decided to 95%CI.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
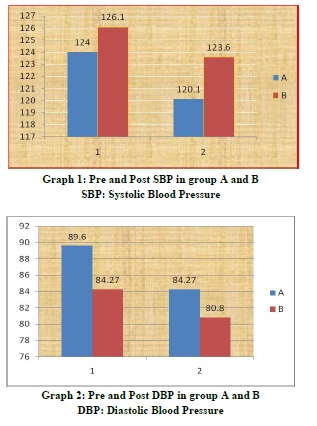
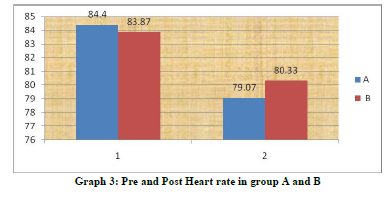
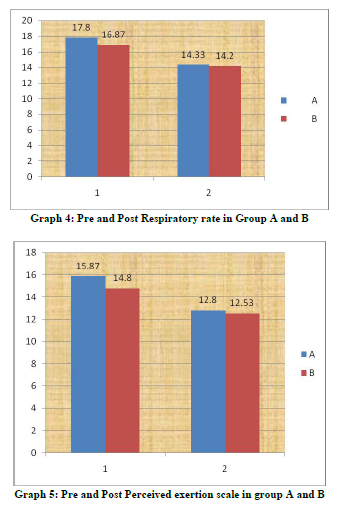
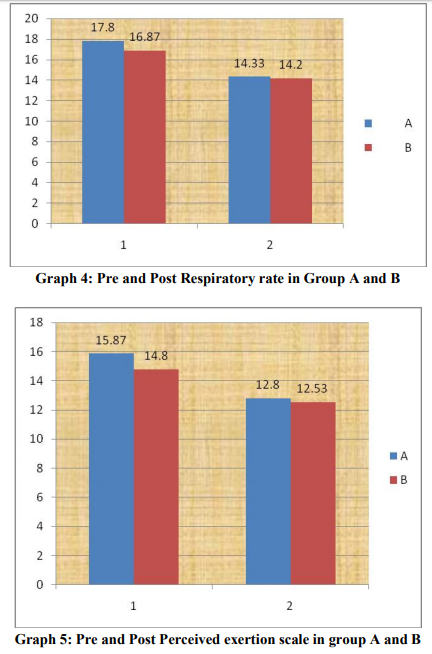
The results of this study showed significant changes in acute hemodynamics (p=0.00) with cardiac rehabilitation at hospital set up and home based exercises. Mean differences were Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP)(3.86±2.2), Diastolic Blood Pressure(DBP) (5.33±3.45), Heart Rate (HR) (5.33±3.45), Respiratory Rate (RR) (3.46±1.55), Rate of Perceived Exertion(RPE) (3.06±0.88) in group who had received hospital based rehabilitation and group who had received home based exercises were Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) (3.46±1.59), Diastolic Blood Pressure(DBP) (3.46±1.59), Heart Rate(HR) (3.53±1.35), Respiratory Rate (RR) (2.53±0.91), Rate of Perceived Exertion( RPE )(2.26±0.96). Intergroup comparison did not show significant changes but clinically hospital based cardiac rehabilitation found to be more effective. The improvements in acute hemodynamics at follow up were consistent with previously published studies. The parasympathetic tone predominates at rest and acute hemodynamics increases during exercises in response to the combination of sympathetic activation and parasympathetic withdrawal and the inverse occurring during recovery after the exercise. The autonomic dysfunction is known to have adverse effects on subsequent clinical outcome in patients with coronary artery disease. One possible explanation for the discrepancies may be that the patients with coronary artery disease are subject to the activation from sympathetic activity after cardiac event.16 Weber17 et al also reported a higher heart rate after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) surgery and a high incidence of supraventricular arrhythmias during the hospital stay. Moreover the subjects in Kavanagh’s 18study were tested 14 week after the cardiac event or surgical procedure and Tiukinhoy’s 13subjects were evaluated after 6 and 9 months for the cardiac rehabilitation and control groups, respectively. This improvement in hemodynamics in both the groups may reflect that long term endurance training increases the parasympathetic activity and decreases the sympathetic activity directed to the human heart. Pardo19 et al indicated that exercise conditioning over a12-week period improved heart rate variability, reduced the resting heart rate in cardiac patients, lowered the risk of sudden cardiac death through increased vagal tone. Studies had also found that sympathetic system increases activity during the first 3 weeks after the onset of a cardiac event, where as the parasympathetic nervous system has been considered to improve gradually during the 3 months period.6,9 The reduction in acute hemodynamics in this study may imply that the balanced sympathetic and parasympathetic tone occurred gradually after CABG. For the comparison between groups at the follow up tests, there were no significant results. The improvements in both the groups were supported by the finding that endurance training has positive effect on the activation of parasympathetic tone.16 Although there was no statistical significance that existed between hospital based cardiac rehabilitation and home based rehabilitation. Home based rehabilitation had similar magnitudes in all test parameters after the intervention when compared with hospital based rehabilitation. Several studies have indicated a tendency toward improvement in peak aerobic capacity, quality of life, and risk factor reduction in home based rehabilitation programmes 14,15 . Smith20 et al. recently reported that the low risk patients whose cardiac rehabilitation was initiated in the home environment may be more likely to sustain positive physical and psychosocial changes over time because of the higher physical habitual activity of home subjects. Autonomic dysfunction is known to adversely affect clinical outcome in patients with cardiovascular disease. However improvement in autonomic regulation on heart rate recovery after cardiac rehabilitation may be an additional benefit of an exercise training program. Exercise is one of the main components of lifestyle change and it may an effect on modifying autonomic imbalance. Therefore, a more structured nature of exercise counselling and a more frequent interaction between staff and patients may be needed to encourage home based exercise subjects to engage in regular physical activity to achieve greater improvement 16 .
CONCLUSION
This study had concluded that both hospital based rehabilitation and home based exercises are effective in improving acute hemodynamics.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Author would like to thank Dr. D. Y. Patil Vidyapeeth, Pune, for funding this research. Authors also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript.
References:
1. Thompson D, Bowman G, Kitson A, de Bono D, Hopkins A: Cardiac rehabilitation services in England and Wales: a national survey. Int J Cardiol 1997, 59:299-304.
2. Campbell N, Grimshaw J, Rawles J and Ritchie L: Cardiac rehabilitation in Scotland: is current provision satisfactory? J Public Health Med 1996, 18:478-480.
3. Taylor RS, Brown A, Ebrahim S, et al. Exercise-based rehabilitation for patients with coronary heart disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Med 2004;116(10):682– 692.
4. Benzer W. Oldridge NB: Current concepts in cardiac rehabilitation medical considerations and outcomes evaluations. J Clin Basic Cardiol 2001;4:211-19
5. Katte Jolly, Rod S. et al: Home based cardiac rehabilitation compared with centre based rehabilitation and usual care: A systematic review and metanalysis. International Journal of Cardiology111(2006);343-351
6. Lucini D, Richard VM, Costantino G, Lavie C, Porta A, Pagani M: Effects of cardiac rehabilitation and exercise training on autonomic regulation in patients with coronary artery disease. Am Heart J 2002;143:977-83
7. Thornton EW, Fabri BM, Fox MA, Jackson M: Predicting blood pressure reactivity and heart rate variability from mood state following coronary artery bypass surgery. Int J Psychophysiol 2003; 47:43-55
8. Hedback B, Perk J, Engvall J, Areskog N: Cardiac rehabilitation after coronary artery bypass grafting: effects on exercise performance and risk factors. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1990,71:1069-1073.
9. Ben-Ari E, Kellerman J, Fisman E, Pines A, Peled B and Drory Y: Benefits of long-term physical training in patients after coronary artery bypass grafting – a 58 month follow-up and comparison with a maintained group. J Cardiopulm Rehabil 1986,6:165-170.
10. Engblom E, Korpilahti K, Hamalainen H, Ronnemaa T and Puukka P: Quality of Life and Return to Work 5 Years After Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery long term results of cardiac rehabilitation. J Cardiopulm Rehabil 1997, 17:29-36.
11. Nishime EO, Cole CR, Wallace GS,et al: Heart rate recovery improved in a cohort of adults after cardiac rehabilitation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;39:164
12. Tiukinhoy S, Beohar N, Hsie M: Improvement in heart rate recovery after cardiac rehabilitation. J Cardiopulm Rehabil 2003;23:84-87
13. Kligfield P, McCormick A, Chai A,Jacobson A,Feuerstadt P, Hao SC: Effect of age and gender on heart rate recovery after submaximal exercise during cardiac rehabilitation in patients with angina pectoris, recent acute myocardial infarction or coronary bypass surgery. Am J Cardiol 2003;92:600- 603
14. Lind L,Andren B: Heart rate recovery after exercise is related to the insulin resistance syndrome and heart rate variability in elder men. Am Heart J 2002;144:666-72
15. Gordon NF, English CD, Contractor AS, et al: Effectiveness of three models for comprehensive cardiovascular disease risk reduction. Am J Cardiol 2002;89:1263-68
16. Wu S-K, Lin Y-W, Chen C-L, Tsai SW:Cardiac Rehabilitation vs Home Exercise after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: A comparison of heart rate recovery. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2006;85:711-717.
17. Weber UK, Pfisterer M et al: Low dose sotalol to prevent supraventricular arrhythimas after CABG surgery and its effect on hospital stay. J Am Coll cardiol 1996;27:309-10.
18. Kavanagh T , Mertens DJ et al : Peak oxygen intake and cardiac mortality in women reffered for cardiac rehabilitation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;42:2139-43.
19. Pardo Y, Merz CN et al: Exercise conditioning and heart rate variability: evidence of a threshold effect. Clin Cardiol 2000; 23: 615- 20.
20. Smith KM, Arthur HM et al: Differences in sustainability of exercise and health related quality of life outcomes following home or hospital based cardiac rehabilitation. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2004:11:313-19.

|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License