IJCRR - 9(5), March, 2017
Pages: 01-08
Date of Publication: 20-Mar-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Application of Road Traffic Accident Modelling for Future Prediction: A Case Study of Kolkata
Author: Tuhin Kanti Ray1, Sukla Bhaduri2
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:At present most of the metropolitan cities of India are going through the burden of increasing road traffic accidents. Road accident modelling is the most efficient way to estimate the future growth of traffic accidents. Present paper does not engage in any kind of model formulation but it gives emphasis on the application of the already formulated models on Road Traffic Accidents (RTA) for the prediction of traffic accidents in India in general and Kolkata in particular. Smeed's model, Andreassen's equation and Regression Based Model are primarily applied for the fulfilment of the objective of the present research paper. Results derived indicate that occurrences of traffic accidents in India are still very high, while in the metropolitan city of Kolkata their numbers has been checked significantly. Assessment of the condition in Kolkata shows that though fatalities due to road accidents are reducing in numbers, the rate of injuries are still quite high, indicating the need to further enhance road safety parameters. But overall estimate of RTA determines that traffic accidents taking place in Kolkata are way below their predicted values indicating increasingly better management of traffic situation in the city.
Keywords: Accident model, Future prediction, Fatalities, Injuries, Traffic management
Full Text:
Introduction:
Success of any kind of hazard management depends on its future prediction. Road traffic accident (RTA) is not an exception. A sustainable management of RTA is very much associated with its future prediction. Around 85 percent of all global road deaths, 90 percent of the disability-adjusted life years lost due to crashes, and 96 percent of all children killed worldwide as a result of road traffic injuries occur in low-income and middle-income countries (WHO, 2004). Therefore gradually it had been realised that modelling of road traffic accidents is an urgent requirement for the developing countries as most of the low and middle income countries belong to the developing world.
Many researchers have devoted their research work to the area of road accident including its prediction and estimation. Initially this kind of modelling was started in the developed country with the increasing burden of vehicular population and road crashes while it started at a much later stage in developing countries.
Application of Prediction techniques to Road Safety:
R.J. Smeed in 1949 first proposed the relationship among traffic fatalities, traffic congestion and country population. In his law traffic congestion was measured by the proxy of motor vehicle registration. Smeed’s analysis was very much criticised by Andreassen for model accuracy. According to his argument it was not applicable universally to all countries. Andreassen produced a generalized relationship incorporating the attributes responsible for fatalities as stated by Smeed but with his modification in 1985. Adams (1987) researched on Smeed’s law and gave some insights in the analysis. Various other researchers like Livneh and Hakkert, Partyka, Jacobs and Cutting have developed models for prediction of road traffic accidents for the developing countries.
The Indian Scenario of Road Traffic Accident Prediction Modelling:
Several notable studies have been conducted by a group of researcher for metropolitan cities in India. Mohan (1985) attempted a study to understand total crash pattern in Delhi. One of the pioneering works has been attempted by Valli and Sarkar in 1993 and it was based on the different states and union territories. Another research in this regard has been done by them (1997) where they developed a model for India based on Smeed’s approach. Valli (2005) developed another road accident model by using Smeed’s and Andreassen’s equation for the large metropolitan cities of India.
In 2004 Valli had done a research work to develop road accident models for large metropolitan cities of India. This work incorporated the scenario of Kolkata with other metro cities of India and calculated rate of change in road accident indices for Kolkata. Here based on Smeed’s model, an attempt has been made to develop relationship among the parameters, namely, road accidents, the number of registered motor vehicles and population (Valli, 2004). Just after this one in 2005 Chakraborti and Roy made another attempt to develop model for Kolkata and it had been taken to predict future accidents following Smeed’s approach (Chakraborty and Roy, 2005).
Objective of the Study:
The prime objective of the study is to predict the future trend of road traffic accident in Kolkata that can be considered as an indicator for the assessment of the efficiency of present management system of traffic accident in this city.
Methodology:
Generally, prediction of accidents is performed by analyzing the various factors responsible for accidents and quantifying their effect on the accidents using statistical techniques (Vhat et all, 2013). Smeed’s formula established the relationship among road traffic accident, traffic congestion and country population whereby an increasing traffic volume causes to an increase in fatalities per capita. But the same is also responsible for the decrease in fatalities per vehicle. Smeed’s formula is expressed as:
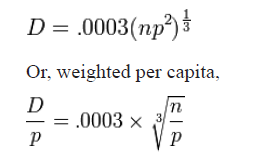
Where
D = annual road deaths,
n = registered number of motor vehicles
p = population
Smeed examined the relationship on a number of road fatalities with those of motor vehicles and the population of twenty countries in 1938. It was observed that ten of the values of death calculated by his formula were within fifteen percent of their actual values, nine were within forty percent and one was in error by sixty seven percent. Smeed and Jaffocate further made an attempt to predict the accident figures of seventy countries for the time period of 1960 to 1967 (Smeed and Jaffocate, 1970). It was found that except five out of seventy countries, Smeed’s model was able to predict the number of fatalities successfully. India was one of them.
However Andreassen had criticised Smeed’s formula for its accuracy and opined that it cannot be applied universally. In 1985 Andreassen formulated a generalised relationship in the form of:
D= const* (N) M1 * (P) M2
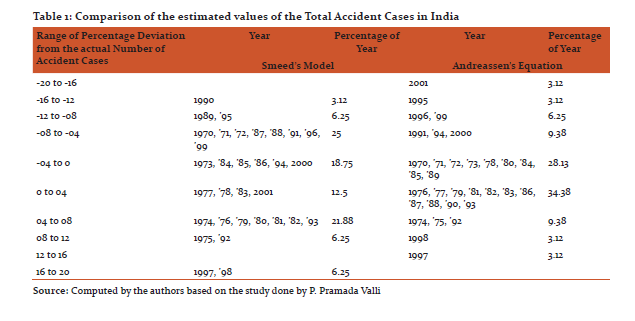
In this present study therefore Smeed’s model has been incorporated to analyse the fatality pattern caused due to road accidents. Nevertheless following Valli (2005) who in his model attempted to make a comparative study based on Smeed’s and Andreassen’s equation values of accident for India from 1970 to 2001, Andreassen’s equation has also been incorporated in this present research work. The comparative analysis according to Valli reveals that the estimated values getting from Andreassen’s equation was less deviated from the actual values than the values obtained from Smeed’s equation. Hence an endeavour has been done to assess the efficiency of the stated equations based on range of percentage deviation from the actual number of accident cases for India in the said time period.
Furthermore for understanding the situation in Kolkata three types of attributes namely number of accident cases, mid-year population and annual growth of motor vehicles for the time period of 1998 to 2014 has been considered. The population of the intermediate years i.e. years between two successive census years has been calculated by the population projection method. Predicted values thereby derived from different models have been used for a comparative study to get the final findings. However to assess the situation in Kolkata along with Smeed’s model Regression analysis has also been applied. Regression Based Model is given by the formula:
The models for total accident, fatality and injury are:
- Model for total accident: C/N = 0.003764(N/P)-0.73 (r = 0.9875) ......... (i)
- Model for fatality: F/N = 0.0001025(N/P)-0.998 (r = 0.9898) ........ (ii)
- Model for injury: I/N = 0.001255(N/P)-0.64 (r = 0.989) ......... (iii)
where:
C/N = Number of total accidents per vehicular population
F/N = Number of fatalities per vehicular population
I/N = Number of injuries per vehicular population and
N/P = Number of registered motor vehicles per population
Discussion and Findings
This paper highlights predicted situation of accidents in India in general and Kolkata in particular.
Case of India
In spite of the fact that India is a low motorised country, urbanization and industrialization is accentuating the need to develop roadways in the country leading to increase in vehicular population as well. As a result, one of the negative influences of such development has emerged very significant i.e. urban areas along roadways and highways are facing the burgeoning problem of road traffic accident. In this situation the estimation of future trend of road traffic accident would help to deal with the negative impacts of development. Keeping this in mind, in this study, the case of India has been taken up and inspiration has been taken from the previous work done by Valli (2005). A comparison was made by him of the estimated values of the total accident cases by the Smeed’s model as well as Andreassen’s equation. Following the same, in this present paper the comparison made of the given years in table 1 has revealed significant difference in their level of accuracy. In case of Andreassen’s equation range of percentage deviation from the actual number of accident cases was lesser than the Smeed’s model. In Andreassen’s equation near about sixty three percent of the years were lying in between -4 to +4 range of percentage deviation where as in
the same range of percentage deviation, the value was near about thirty percent under Smeed’s model. A representation of the same is shown in figure 1 and 2.
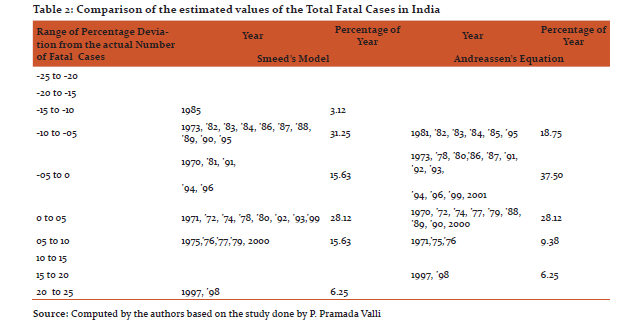
Comparison of the estimated values of the total fatal cases as shown in Table 2 has revealed a higher level of accuracy than the estimation of total number of accident cases. It was observed from the range of percentage deviation of the actual number of fatal cases, that almost sixty six percent of the studied year were lying in between the range of -5 to +5 in Andreassen’s equation and in case of Smeed’s Model the same was near about forty four percent. Though a significant variation can be observed between both the equation, the fact that a relationship exists between fatal cases and increase in population and motor vehicles cannot be overlooked. However, this relation is not as strong as for injury cases as one would observe in the following paragraph.
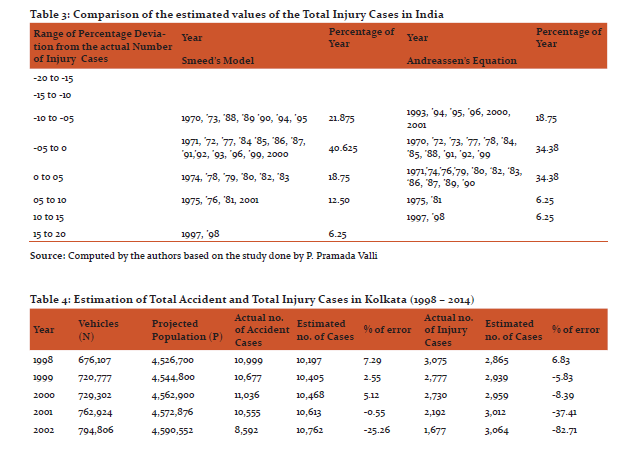
In injury cases (Table 3) near about sixty to seventy percentage of the years during this studied time period were lying in between the percentage deviation range of -5 to +5. This indicates a positive co-relation between number of injury cases with that of population and number of motor vehicles, which have been established by both the models.
The above assessment has revealed that level of accuracy was high for the estimation of total injury cases but for fatal cases and overall accident case estimates the accuracy is low. An alarming fact is that near about forty to fifty percent years, for all cases, were lying in the positively deviated range i.e. in those years the actual values were higher than the estimated values. This may be considered as a resultant effect of the poor management in those respective years. Nevertheless inference drawn therefore implies a chance of further improvement of the existing traffic management system in urban as well as suburban and rural parts of the India, so that the rate of accidents may be checked.
Case of Kolkata
Having assessed the situation of India, the latter half of the paper focuses on the condition in Kolkata. The city of Kolkata is characterised by an unprecedented growth in population numbers accounting to 4.5 million in the core and in its suburbs to 14.1 million (Census, 2011), making it the third most populous metropolitan area in the country. Only in the last decade has there been a decline in population growth rate to -1.9% whereas the population of the suburbs has increased by 11.5%. Not only has this huge population of the city increased the usage of transportation facilities, but also a large section of working population who commutes to the city daily, contributes to the ever increasing travel demand. It has been estimated that about 20 million passengers and 11.04 million vehicles move in and around the city on almost all working days. Furthermore the vehicular population of the city has also been on a rise from 2.61 lakh in 1985 to 11 lakh in 2011. It has been projected that in 2025 vehicle population will increase by 3 million and transit trips to 32 million (Comprehensive Mobility Plan, 2008). This ever increasing number of vehicles and road users enhances the chances of road accidents. Moreover the fact that Kolkata has a very less road space of only 8% of the total area of the city, haphazard road development and mixed vehicular traffic within the same road space augments to the enormity of the problem.
With this background a study has been attempted to understand the present traffic situation and the atrocities of road traffic accidents in the city. For this purpose the regression method has been used to estimate the situation of total number of accident cases as well as the number of injury cases in Kolkata.
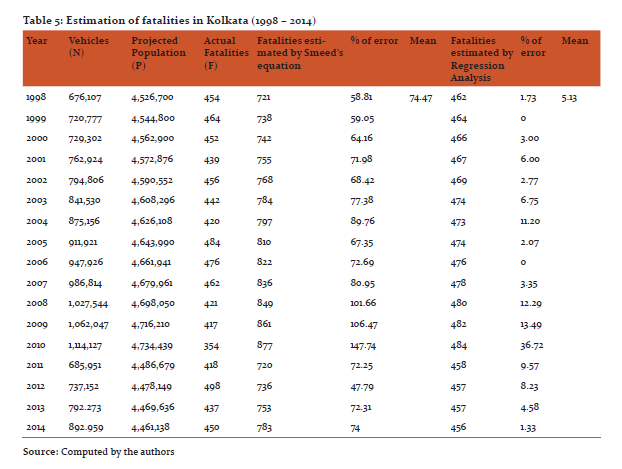
Estimation of the total number of cases reveals that the predicted values were higher than the actual values. However, in the initial phase (1998-2000) of the studied time period, the actual values were slightly higher than the predicted values (Fig 3). This can be attributed to the fact that within these years in comparison to its vehicular and population growth, the rise in the total number of accidents was insignificant. Since then the gap between estimated and actual values have increased and by the year 2004 the gap was more than hundred percent which in between 2005 and 2010 rose more than three hundred percent. Drastic fall in the total number of accident cases during this time period might be cited as responsible for such a huge negative difference between actual and predicted values. Nevertheless after this time period the gap has once again started to decrease due to further enhanced road accident cases.
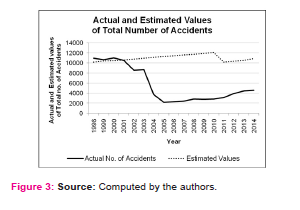
Accidents not only involve fatalities but also injuries. Infact the number of injury cases, be it severe or minor are quite significant along roads both in India as well as Kolkata, particularly due to rash driving and disobey of traffic rules. However, calculations reveal that in almost all the years of the studied time period, the actual values of injury cases were lower than the estimated values of injury cases (Fig 4). This is indicative of the fact that even though Kolkata has been experiencing an overwhelming pressure of vehicles as well as population, Kolkata Traffic Police have been efficient enough to manage the traffic and has been able to enforce the traffic rules and regulations upon the road users, be it drivers or pedestrians. The difference between actual and estimated values in case of injury cases was not as higher as in case of total accident cases and that indicates a further scope of improvement of the injury prevention measures which have been taken by the respective authorities.
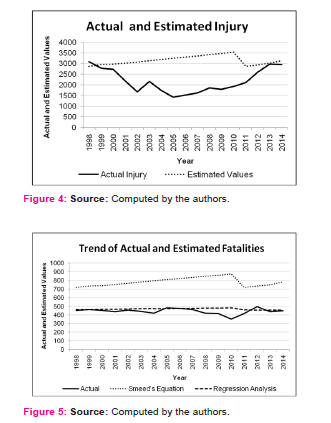
The most atrocious of all accident types are the fatal cases. Though there numbers are much less than that of injuries and further have been curbed due to immense improvements in medical facilities in the country as well as in the metropolis, there occurrences are always of great significance since it questions the management of not only the traffic departments but also the health departments as well. Hence being the most serious of all accident types, to calculate estimated fatalities, both Smeed’s and Regression method has been used. Table 5 calculates the percentage of error and their mean values. A comparison of observed and actual fatalities based on above two approaches as presented in the table depicts that observed values compare quite favourably with regression based model than that of the Smeed’s model of estimation.
In the Smeed’s equation the average gap between the actual fatalities and estimated fatalities was around 74 percent, indicating a better management of traffic accidents on the part of Kolkata Police, as the predicted values are much higher than the actual values.
Regression based model formulated on same parameters, on the other hand, is more useful because in this model it is also possible to estimate total number of accident, fatalities and injuries. In the case of Kolkata it has been observed that the gap between actual and estimated values is negligible. Nevertheless this model also highlights the efficient management of traffic accidents in Kolkata practically because the percentage of error as compared to the mean values in regression model like Smeed’s equation is less diverse.
Conclusion:
This quantitative approach to the study of accident cases unfolds a fact that traffic management though within municipal areas in the country are efficiently carried out (as observed in case of Kolkata), outside its jurisdiction areas a lack in the efficiencies of police personnel is observed. Since the drive towards urbanization is of great significance many a times the rural and suburban roads lack proper driving standards. Inadequate traffic signs, police personnel and inefficient imposition of regulations, beyond municipal boundaries increase accident cases, thus in case of India actual values of occurrences of accidents lie far above the predicted values. Moreover, in other metropolitan areas of the country, where vehicular population in much higher than that of Kolkata, the traffic management system need to be even greater equipped. Contrarily in Kolkata Police Jurisdictional Area total number of accidents, the actual growth of fatalities and injury cases was revealed to be lesser than their model based predicted values. It could be stated here that often accident cases are not recorded by the concerned authorities and to add to the woes though accident cases are recorded their impact on the victims are overlooked. This might create some discrepancies in the final tabulation of fatal and injury cases. But quantification is an important way of supporting field realities. The decreasing number of accidents in general and improved road condition makes the efforts of Kolkata police essentially visible. It is an admirable fact that in spite of its increasing vehicular and passenger pressure, Kolkata police have given their best endeavour to manage its traffic and control the severity of the traffic hazards.
Acknowledgement:
The first author would like to express his sincere gratitude to the Kolkata Police for giving the opportunity and permission of collecting several published as well as unpublished data which were required for the preparation of the present paper. He is also thankful to the Public Vehicle Department, Kolkata, for providing the data related to the growth of motor vehicles during the studied time period in the Kolkata Police Jurisdictional Area. Authors also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.


References:
Andreassen, D. (1985): Linking deaths with vehicles and population, Traffic Engineering and Control Vol.26, Issue11, pp.547-549.
Bhat, P., Hebbani, L.,RamaV, A.,Kolhar,P.(2013):Accident Prediction Modelling for an urban road of Bangalore, International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology,IC-RICE Conference Issue,pp.137-141.
Chakraborty S. and S. K. Roy (2005): Traffic Accident Characteristics of Kolkata, Transport and Communication Bulletin for Asia and the Pacific, No. 74, pp.75-86.
Elvik R. (1995): Analysis of official economic valuations of traffic accident fatalities in 20 motorized countries, Accid Anal Prev., Vol. 27, pp.237-47.
Emenalo, M., Pustelli, A., Ciampi and Joshi, H.P. (1987): Analysis of road traffic accidents data in Zambia, Traffic Engineering and Control, Vol. 28, pp.635-640.
Fieldwick, R. and Brown, R.J. (1987): The effect of speed limits on road casualties, Traffic Engineering and Control, Vol.28, pp.635-640.
Jacobs, G.D. and Cutting, C.A. (1986): Further research on accident rates in developing countries, Accident Analysis and Prevention, Vol. 18 No.2, pp.119-127.
Jamal Al-Matawah and Khair Jadaan (2009): Application of Prediction Techniques to Road Safety in Developing Countries, International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol.7,No.2,pp.169-175
Jamal, R.M. Ameen and Jamil A. Naji. (2001): Causal models for road accident Fatalities in Yemen, Accident Analysis and Prevention, Vol. 33, pp.547-561.
John, G.U. Adams (1987): Smeed’s law : Some further thoughts, Traffic Engineering and
Control, Vol. 28,pp.70-73.
Livneh, M. and Hakkert, A.S. (1972): Some factors affecting the increase of road accidents in developing countries, with particular reference to Israel, Accident Analysis and Prevention, Vol.4,pp.117-133.
Mekky Ali. (1985): Effects of rapid increase in motorization levels on road fatality rates in some rich developing countries Accident Analysis and Prevention, Vol.17,No.2, pp.101-109.
Minter, A.L. (1987): Road casualties improvement by learning processes, Traffic Engineering and Control, Vol. 28, pp.74-79.
Mohan Dinesh (1985): An analysis of road traffic fatalities in Delhi, India, Accident Analysis and Prevention, Vol. 17, No.1, pp.33-45.
Sharmin E. S. C., Md. Ashiqur R., Quazi S. H. and Syed A. A.(2015): Road accident models for Khulna metropolitan city, Bangladesh, Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, Vol.1,No.1,pp.1-8
Smeed, R. J. (1949): Some statistical aspects of road safety research, Journal of Royal Statistical Society, Series: A (Statistics in Society), part1, series 4, pp.1-24.
Smeed, R.J. and Jaffocate (1970): Effects of changes in motorization in various countries on the number of road fatalities, Traffic Engineering and Control, Vol. 12(3): pp.150-151.
Susan, C. Partyka. (1984): Simple models of fatality trends using employment and population data, Accident Analysis and Prevention, Vol. 16, No.3, pp.211-222.
World Health Organization (2004): World report on road traffic injury prevention Ed:
Margie Peden et all, World Health Organization, Geneva, p.4.
Valli, Pramada P. and P.K. Sarkar (1993): Variation in the pattern of road accidents in different states and union territories in India, Proceedings of the third National Conference on Transportation systems studies: Analysis and Policy, pp. 1X-5 to 1X-9.
Valli, P. and P.K. Sarkar (1997): Models for road accidents in India, Highway Research Bulletin, vol. 56, New Delhi, Indian Road Congress, pp. 1-11.
Valli PP (2005) : Road Accident Models for Large Metropolitan Cities of India, IATSS Research, Vol.29 No.1,pp. 57-65.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License