IJCRR - 5(16), August, 2013
Pages: 20-26
Date of Publication: 28-Aug-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF ORAL TRIPLE DRUG COMBINATION (VOGLIBOSE, GLIMEPIRIDE AND METFORMIN) IN THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Author: C. Rao, A. A. Faruqui
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:The prevalence of type 2 diabetes across the world has been described as a global pandemic. Despite the introduction of new agents, efforts for better management of diabetes are disappointing and the control of blood glucose level remains unsatisfactory. When antidiabetic therapy is initiated, it is now recommended that the selection of agents should be directed towards both fasting as well as postprandial hyperglycaemia. Material and method: This study was a post marketing surveillance (PMS) non-randomized, open, non-comparative, mono centric study. The drug administered was a fixed dose combination of Voglibose 0.2mg, Glimepiride 1/2mg and Metformin 500mg SR, 20 type 2 diabetic patients were given fixed dose combination twice daily with major meals for 3 months. Observation: Baseline value was recorded for glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting blood glucose and post prandial blood glucose level. There was significant decrease in glycated haemoglobin value (8.86 \? 0.7111 gm/dl vs. 8.0 \? 0.66 gm/dl), fasting (137\?17.64 mg/dl vs. 116.8 \? 6.129 mg/dl, P < 0.0001) and post prandial blood glucose level ((237.8 \? 59.22 mg/dl vs.173.4 \? 27.6 P < 0.0004) after 3 months of treatment. The combination was found to be effective in controlling both fasting and post prandial glucose level and was well tolerated. Investigator commented that the use of triple drug combination is a good option in the management of type 2 diabetes which controls both fasting as well as post prandial blood glucose. Conclusion: The triple drug fixed dose combination of Voglibose, Glimepiride and Metformin significantly decreased the HbA1c value, fasting plasma glucose level and post prandial glucose level at the end of the treatment.
Keywords: HbA1c, Fasting Plasma Glucose, Post Prandial Blood Glucose, PMS
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes across the world has been described as a global pandemic despite the introduction of new agents to the armamentarium of hypoglycaemic agents; efforts for better management of diabetes are disappointing and the control of blood glucose levels remains unsatisfactory1 . Optimal management of type 2 diabetes requires a consideration on the relationship between glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting plasma glucose and postprandial glucose (the glucose triad). Early and sustained control of glycaemia remains important in the management of type 2 diabetes. The contribution of postprandial glucose levels to overall glycaemic control and the role of postprandial glucose targets in disease management are currently debated2 . However, many patients do not reach HbA1C targets set according to published guidelines.
Guidelines for good glycaemic control have been agreed upon and a patient is generally considered to have achieved successful disease control when their HbA1C is < 7% 3, 4, 5 . It is now more and more clear that physicians are likely to have to consider plasma glucose levels both after the overnight fast and after meals as well as the variability of glucose levels, in order to achieve optimal glycaemic control for each patient. When antidiabetic therapy is initiated, physicians may need to consider selection of agents that target both fasting and postprandial hyperglycaemia. Controlling the Glucose triad (HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose and postprandial glucose): Regardless of the HbA1C goal that is agreed upon, it is doubtful to be reached unless both fasting and postprandial glucose levels are adequately controlled, ideally through a combination of lifestyle modification and appropriate drug therapy2 . Routine measurement of postprandial glucose levels is not currently recommended or even practical for all patients with type II diabetes. However, improved understanding of the relative influence of fasting and postprandial glucose levels throughout the course of the disease might influence the class of drug that is prescribed. Recent research has suggested that intensification of glucose control with insulin therapy may not be advisable for all patients with type 2 diabetes and oral antidiabetic drugs should be used for as long as possible6 . International Diabetes Federation (IDF) guidelines for the management of post meal (postprandial) glucose state that the goal of diabetes therapy should be to achieve glycaemic status as near to normal as safely possible in all three measures of glycaemic control, namely HbA1C, fasting premeal glucose and post meal glucose7 . Treatment of both fasting and postprandial hyperglycaemia should be initiated simultaneously at all levels of HbA1C above agreed levels. Traditional treatments such as metformin and thiazolidinediones primarily lower fasting plasma glucose. As sulphonylureas are generally taken in the morning, they do lower postprandial glucose levels during the day and subsequently have an effect on overnight fasting levels. Therapeutic agents are available that preferentially lower postprandial glucose, including alphaglucosidase inhibitors, glinides, incretin mimetics, dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and rapid acting insulin. Current recommendations of the American Diabetes Association include a trial of diet and exercise as first line therapy for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes8 . If glycemic control is not achieved with diet and exercise within a three-month period, pharmacologic intervention is required. Moreover if adequate control is not obtained with the use of a single agent, combination therapy is an option. Several of the available oral agents have been studied in combination and have been shown to further improve glycemic control when compared to monotherapy.9 Some physicians now advocating the therapy combining three oral agents (sulfonylurea, metformin, alpha-glucosidase inhibitor or sulfonylurea, metformin, thiazolidinedione) in the management of type 2 diabetes 10 . This study was conducted to evaluate the safety of triple drug combination (i.e. Voglibose, Metformin and Glimepiride) and its impact on Glucose Triad.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
A total of 20 type 2 diabetic patients were enrolled and completed the treatment. At the time of entry into the study, base-line data were recorded. Patients were observed on 1st month of treatment, than subsequent 2nd and 3rd month of the treatment. The patients were asked for the determination of FPG and PPG regularly at the interval of each month. The HbA1C level was examined only before the treatment and after 3 months of treatment. The glycosylated haemoglobin determination was carried out by using BIORAD Micromat II HbA1C instrument, while FPG and PPG were determined in the laboratory.
INCLUSION CRITERIA
Known cases of type 2 diabetes patients with age more than 35 yrs, of either sex & glycosylated haemoglobin > 7% were included in the study. Clinical criteria for the evaluation included fasting blood glucose level, post prandial blood glucose level and glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) value. Patients were prescribed to receive fixed dose combination of Voglibose 0.2mg, Glimepiride 1/2mg and Metformin 500mg SR, one tablet twice daily with major meals for three months.
EXCLUSION CRITERIA
Patients with current insulin therapy or received insulin for more than six weeks in last 3 months, who had known hypersensitivity to Biguanides and sulphonylurea, who are on chronic medication known to affect glucose metabolism were excluded from the study. Also the patients with renal disease or renal dysfunction, with congestive heart failure, hepatic insufficiency, alcoholic person and pregnant and lactating women were excluded from the study.
EFFICACY AND SAFETY EVALUATIONS
The primary efficacy variable was the change in HbA1C, FPG & PPG from baseline to 3 month. Safety outcomes included adverse events, particularly hypoglycaemic symptoms. The patients were interviewed and asked for any type of adverse events throughout the study. The patients were specially asked for the hypoglycaemic symptoms. The daytime hypoglycaemic episodes are usually recognized by sweating, nervousness, tremor, and hunger while night time hypoglycemia may be without symptoms or manifest as night sweats, unpleasant dreams, or early morning headache.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The analysis of Glycosylated haemoglobin and fasting and post prandial glucose was carried out by using graph pad prism 6. Comparison between the baseline values with the value on the 1st, 2nd and 3rd month of treatment were made, as well as comparison in between these months was done by applying one way analysis of variance & the Turkeys multiple comparison test. Value of P<0.001 were considered significant.
RESULTS
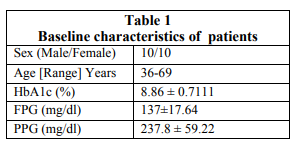
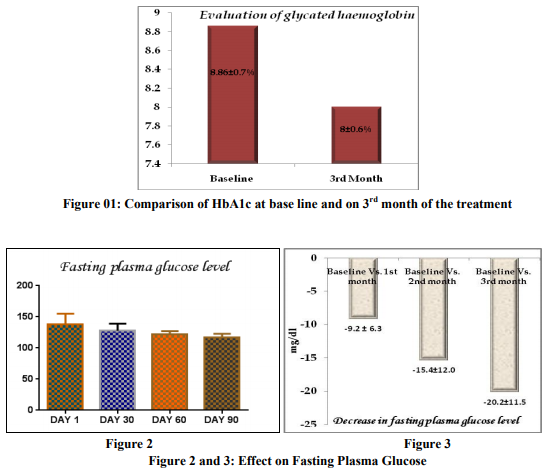
A total of 20 patients were screened and randomized into the treatment groups and they completed the study. The baseline characteristics of all patients at randomization are summarized in the table 1. Evaluation of Glycaemic Control Glycosylated Haemoglobin Glycated haemoglobin value was significantly reduced from the baseline after using the triple combination of voglibose, glimepiride and metformin. During the study there was significant difference found in the value of HbA1c at the baseline to the value observed after the completion of the treatment (8.86 ± 0.7111 to 8.0 ± 0.66, 95% CI of diff. 0.2858 to 1.424) as shown in the figure 1. Evaluation of Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) level The FPG level was reduced throughout the study period of 3 month. The fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level was measured at base line and then subsequently at 1st, 2 nd and 3rd month of the treatment. The FPG level was 137±17.64 mg/dl at baseline. The Fasting plasma glucose level was significantly reduced just after 1month of the treatment from the baseline value (137 ± 17.64 mg/dl vs. 127.8 ± 11.29 mg/dl). But the level of significance was highest between the FPG at baseline and on 3rd months of the treatment (137±17.64 mg/dl vs. 116.8 ± 6.129 mg/dl, P < 0.0001).There was insignificant change between the 1st month and 2nd month of the treatment (127.8 ± 11.29mg/dl vs. 121.6 ± 5.549 mg/dl) and between 2 nd and 3rd month of the treatment (121.6 ± 5.549 vs. 116.8 ± 6.129). Overall the fasting plasma glucose level was significantly (p<0.0001) decreased by 20.2 ± 11.52 mg/dl from the baseline after the completion of the study of 90 days (Fig. 2). The comparative decrease in fasting plasma glucose level from the baseline to the subsequent month of treatment has been depicted in the figure no. 3.
Evaluation of Post Prandial Blood Glucose (PPHG) level
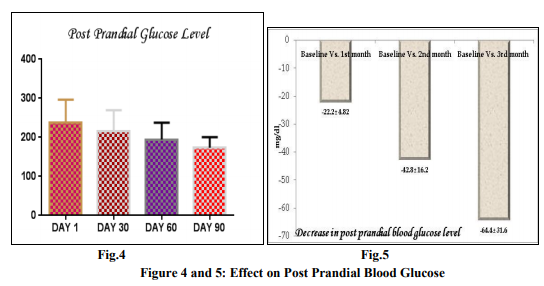
The post prandial blood glucose (PPBG) level was reduced throughout the study period of 3 month. The post prandial blood glucose level was measured at base line and then subsequently at 1st , 2 nd and 3rd month of the treatment. The PPBG level was 237.8 ± 59.22 mg/dl at baseline. The PPBG level was significantly reduced on 2nd month of the treatment vs. baseline (237.8 ± 59.22 mg/dl vs. 195 ± 43 mg/dl). But the level of significance was highest between the PPBG at baseline and to that on the 3rd months of the treatment (237.8 ± 59.22 mg/dl vs.173.4 ± 27.6 P < 0.0004). By applying the turkey’s multiple comparison it was observed that there was insignificant changes in post prandial blood glucose level between the 1st month of treatment to the 2nd month of treatment (215.6± 54.44 mg/dl vs. 195 ± 43mg/dl) and also in between 2nd and 3rd month of the treatment (215.6± 54.44 mg/dl vs. 173.4 ± 27.6 mg/dl ). Overall the post prandial blood glucose level was significantly decreased by 64.4 ± 31.62 mg/dl from the baseline after the completion of the study period of 90 days (Fig. No.5). The comparative post prandial blood glucose level at baseline and the subsequent month of treatment is shown in the figure no.4./figure no.5
Evaluation of Hypoglycaemic and other adverse effect
The patients were interviewed at the end of the study for the detection of any hypoglycaemic episode and about other side effects like nausea, vomiting, headache or flatulence. No patient complaint about any side effect including nausea, vomiting, headache or flatulence at the given doses of medication.
Evaluation of Global efficacy and tolerability
As per investigators assessment about efficacy and tolerability of fixed dose combination of Voglibose + Metformin + Glimepiride, 100% of patient tolerated the treatment very well.
DISCUSSION
Higher levels of post-prandial glucose and the disparity between fasting and post-prandial glucose are significantly associated with increased risk of cardiovascular and all-cause death, even after adjustment for established cardiovascular risk factors. However, higher fasting hyperglycaemia was not significantly associated with CVD risk. Post-prandial glucose, similar to post-challenge glucose, was related to CVD than fasting glucose 11-13. Previous analyses suggested that fasting hyperglycaemia tended to be associated with beta cell dysfunction, whereas post-challenge hyperglycaemia tended to be more strongly related to insulin resistance, higher blood pressure, obesity, and dyslipidemia 14. In clinical practice and in lifestyle and pharmacologic interventions, post-prandial glucose, should still be emphasized as a target to reduce diabetes incidence and CVD risk15 . But recently it is now recommended that for the optimal management of type 2 diabetes there is the requirement to understand the relationships between glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting plasma glucose and postprandial glucose (the glucose triad), and how these change takes place during development and progression of the disease. Early and sustained control of glycaemia remains important in the management of type 2 diabetes. The contribution of postprandial glucose levels to overall glycaemic control and the role of postprandial glucose targets in disease management are currently debated as previously understood. When antidiabetic therapy is initiated, physicians may need to consider selection of agents that target both fasting and postprandial hyperglycaemia. During the study there was significant differences found in the value of HbA1c at the baseline to the value observed after the completion of the treatment (8.86 ± 0.7111 to 8.0 ± 0.66, 95% CI of diff. 0.2858 to 1.424). Similarly fasting plasma glucose level was significantly (p<0.0001) decreased by 20.2 ± 11.52 mg/dl from the baseline after the completion of the study. The post prandial blood glucose level was decreased significantly by 64.4 ± 31.62 mg/dl from the baseline after 3 months of treatment.
CONCLUSION
The triple drug fixed dose combination of Voglibose, Glimepiride & Metformin significantly decreased the glycated HbA1c value, fasting plasma glucose level and post prandial glucose level after 3 months of treatment. Investigator observed that it is safe and well tolerated and an excellent option for the optimal management of Type II diabetes. Conflict of interest-Nil Abbreviations: HbA1c -Glycated haemoglobin IDF -International Diabetes Federation PPG-Post Prandial Glucose FPG-Fasting Plasma Glucose CVD-Cardiovascular Disease PMS -Post marketing surveillance
References:
1. Nathan DM, Kitrick C, Larkin M, Schaffran R, Singer DE. Glycemic control in diabetes mellitus: have changes in therapy made a difference? Am J Med 1996;100:157-63.
2. A. Ceriello. The glucose triad and its role in comprehensive glycaemic control: current status, future management: Int J Clin Pract, November 2010; 64(12): 1705–1711.
3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008; 31(Suppl. 1): S12–54.
4. Canadian Diabetes Association. Canadian Diabetes Association 2008 clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes in Canada. Can J Diabetes 2008; 32(Suppl. 1): S1–201.
5. Ryden L, Standl E, Bartnik M et al. Guidelines on diabetes, prediabetes, and cardiovascular diseases: executive summary. The Task Force on Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J 2007; 28: 88–136
6. Currie CJ, Peters JR, Tynan A et al. Survival as a function of HbA1c in people with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2010; 375: 481–9
7. Ceriello A, Colagiuri S, Gerich J, Tuomilehto J. Guideline for Management of Postmeal Glucose. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation, 2007.
8. American Diabetes Association. The pharmacological treatment of hyperglycemia in NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1995;18:1510-8.
9. Riddle M. Combining sulfonylureas and other oral agents. Am J Med 2000;108 (suppl 6a):15S-22S.
10. Ovalle F, Bell DSH. Triple oral antidiabetic therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract 1998;4:146-7
11. Glucose tolerance and mortality: comparison of WHO and American Diabetes Association diagnostic criteria. The DECODE study group. European Diabetes Epidemiology Group. Diabetes Epidemiology: Collaborative analysis Of Diagnostic criteria in EuropeLancet 1999; 354: 617–621.
12. Glucose tolerance and cardiovascular mortality: comparison of fasting and 2-hour diagnostic criteria, Arch. Intern. Med. 2001; 161 397–405.
13. F. Cavalot, A. Petrelli, M. Traversa, K. Bonomo, E. Fiora, M. Conti, et al., Postprandial blood glucose is a stronger predictor of cardiovascular events than fasting blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus, particularly in women: lessons from the San Luigi Gonzaga Diabetes Study, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91 (2006) 813–819.
14. Kuo-Liong Chien a,b, Bai-Chin Lee b, HungJu Lin b, Hsiu-Ching Hsu b, Ming-Fong Chen; Association of fasting and post-prandial hyperglycemia on the risk of cardiovascular and all-cause death among non-diabetic Chinese: Diabetes research and clinical practice 2009; 83:e4 7– e50
15. S. Yamagishi, K. Nakamura, M. Takeuchi, Inhibition of postprandial hyperglycaemia by acarbose is a promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of patients with the metabolic syndrome, Med. Hypotheses 65 (2005) 152– 154.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License