IJCRR - 5(16), August, 2013
Pages: 08-14
Date of Publication: 28-Aug-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY TO FIND THE EFFECT OF MYOFASCIAL RELEASE ON CHEST EXPANSION IN CEREBRAL PALSY CHILDREN
Author: Albin Jerome, Nishta Passi, Snehal Koli
Category: Healthcare
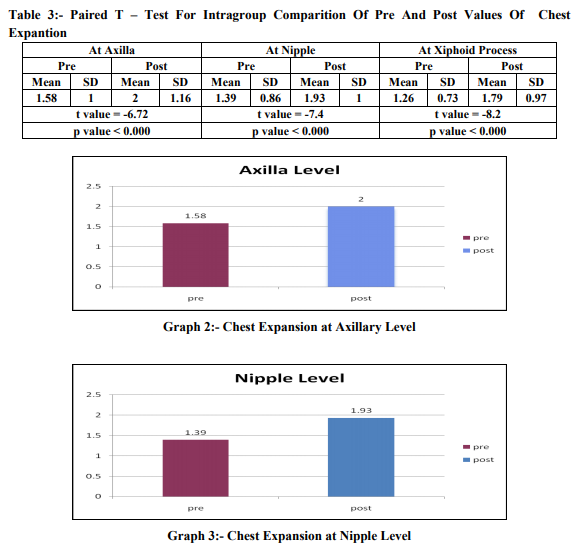
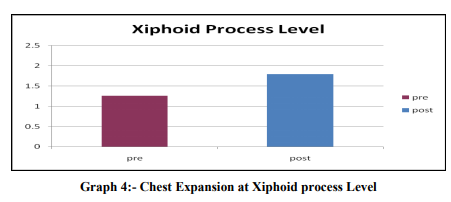
Abstract:Background: Cerebral palsy is defined as a non-progressive insult to a developing or immature central nervous system (CNS), particularly to those areas that affect motor function. People with spastic cerebral palsy, the stabilization of the rib cage is not proper so with each respiration there occurs flaring of the lower ribs, which should otherwise be fixated by abdominals so as to provide diaphragm with a stable base to contract upon. A disturbance in this synergy causes the whole process to become inefficient. Purpose of the study: The aim of this study is to find out an effective method to improve chest expansion in spastic Cerebral palsy children. Method: 50 Spastic cerebral palsy children of both genders with age 5-12 years satisfying inclusion criteria were included for the study. The children were taken in supine position on the mat/plinth and were made to relax. Then command was given to exhale as much as possible and hold the position to take the chest circumference at the maximal voluntary expiration (Cexp).This was followed by deep breath as much as possible and was held for chest circumference at the maximal voluntary inspiration (Cinsp). The children were made to practice this process and then the mean of the highest value of Cinsp and the lowest value of Cexp difference in best three attempts were recorded for all the children. The chest measurements were taken at three levels at axilla, nipple level and tip of xyphoid process. These readings were documented as Pre Test Score. Myofascial release was given to the Pectorals (major and minor) bilaterally, Rib cage (Intercostals), anterior chest wall and the Diaphragm, with the subject in supine position.Post treatment data was taken and statistical analysis was performed. Results: The difference of the pre and post readings of the expansion at the axilla level shows a mean difference of 0.42 which is significant statistically, p value being < 0.000, at the nipple level shows a significant difference, the difference being 0.54 and the p value < 0.000. Similarly the difference of the readings at the xiphoid process level 0.53 is significant, p value being < 0.000. Conclusion: The result shows that the chest expansion increased significantly at all the three levels.The expansion improved maximally at the nipple level.
Keywords: Cereberal Palsy, Chest Expansion, Myofascial release.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a non-progressive disorder of movements and posture resulting from an insult to the growing brain usually in first 2 years of life. It is a group of disorders affecting the development of movement and posture, causing activity limitation; those are attributed to nonprogressive disturbances that occurred in the developing fetal or infant brain.1 It is defined as an “umbrella, term covering a group of non progressive, but often changing, motor impairments syndromes secondary to lesions or anomalies of the brain arising in the early stages of its development.” 2 Research has shown that the lesion that causes cerebral palsy most often causes damage to more then one system, resulting in impairment that influence movement control. The impairment could be: - Primary impairments - Secondary impairments Primary impairments are those that are immediate and the direct result of the lesion, while secondary impairments develop in system or organs over time because of the effects of one or more primary impairment.3 Thus understanding the development of these impairments is extremely important. The physiotherapist may have a strong influence on the course of development of these secondary impairments than primary impairments.3 Therefore an understanding of how secondary impairments develop offers the opportunity to intervene as much as possible before they begin.3 Respiratory system muscles which support the posture and movements are usually compromised in a child with Spastic cerebral palsy and they suffer from a high incidence of respiratory dysfunction such as recurrent pneumonia, atelectasis, bronchiectasis, sleep apnea, chronic obstructive lung disease, and restrictive lung disease. A number of these conditions are secondary and develop over time or due to failure of development of more mature respiratory pattern from the infant belly breathers. Respiratory dysfunction is known to be a leading cause of death among individuals with CP.4 As CP does not have articular involvement, the limited chest mobility may be attributed to impaired neuromotor control and incoordination, weakness, spasticity and secondary changes in the respiratory muscles. The inability of the respiratory muscles to adequately increase and decrease the volume of the thoracic cavity may result in stiffening of the costovertebral joints, which may also decrease chest expansion. While Cerebral palsy itself does not directly cause airway or parenchymal lung dysfunction, consequences of neuromuscular impairment may lead to lung damage and reduced lung function. Poor nutritional status, drooling, aspiration, gastroesophageal reflux, impairment of airway clearance by muscular weakness or incoordination and poor pulmonary reserve (due to chest wall or spine deformity and spasticity) increases the risk of significant morbidity and mortality from respiratory infections.5 However, respiratory dysfunction in children with severe CP has not been well studied, possibly due to the difficulty of testing these uncooperative young children. Chest expansion reduces in these children because of many reasons, as the secondary complications develop. The rib cage is either barrel shaped with excessive sustained superficial muscle activity or is flattened with distal rib flaring. The shape of rib cage changes due to over activity of the trunk muscles, including intercoastals, diaphragm and rectus abdominis. This results in shallow respiration with an immobile rib cage during inhalation and exhalation.3 As in the patients of Spastic cerebral palsy, the stabilization of the rib cage is not proper so with each respiration there occurs flaring of the lower ribs, which should otherwise be fixated by abdominals so as to provide diaphragm with a stable base to contract upon. A disturbance in this synergy causes the whole process to become inefficient. Along with this there occurs adaptive soft tissue tightness or shortening at the chest wall in response to the altered position of the chest (e.g. barrel shaped chest). Added to the inefficient expansion mechanism of the chest, this tightness of the muscles, fascia and the skin overlying the chest reduces the overall excursion of the chest thus all the more reduced expansion of the chest.
It has been documented that reduced chest expansion will lead to compromised cardiopulmonary functions. The physiotherapist working with Cerebral palsy children should identify these secondary problems and treat it in order to help the children achieve functions that are not likely to develop if left untreated. The fascia which surrounds every muscle, bone, nerve, blood vessel and organs of the body, all the way down to the cellular level is a tough connective tissue which spreads throughout the body in a three dimensional web without interruption. Because the fibres in fascia run in all directions, fascia is distensible in all directions to accommodate changes in muscle bulk and to permit stretching. Fascia (also called connective tissue) is a tissue system of the body to which relatively little attention has been given in the past. Fascia is composed of two types of fibers: ? Collagenous fibers which are very tough and have little stretch ability. ? Elastic fibers which are stretchable. From the functional point of view, the body fascia may be regarded as a continuous laminated sheet of connective tissue that extends without interruption from the top of the head to the tip of the toes. It surrounds and invades every other tissue and organ of the body, including nerves, vessels, muscle and bone. Fascia is denser in some areas than others. Myofascial system is made up of muscles and fascia. Each time when there is a trauma, or an inflammatory process or poor postures over time, the fascial system becomes restricted. These restrictions act like the concentric layers of an onion. These adaptive layers slowly tighten and lead to lose of physiologic adaptive capacity and begin to pull out of three-dimensional orientation with gravity. 6 This is fascial sweater concept which states that fascial restriction in one area will strain areas away from the restriction and cause abnormal movement patterns. 7 Thus the tight myofascia should be stretched to its normal length. Myofascial release is a system of manual therapy involving massage and stretching techniques that are advocated to cause changes or "releases" in restricted or pathological fascial structures. A "release" is defined by Upledger and Vredevoogd and Manheim and Lavett as a "softening" or "letting go" when resistance melts and the tissue is felt to relax and elongate. According to Manheim and Lavett the elongation helps alleviate impediments to normal movement. Myofascial release techniques can involve direct superficial or deep pressure at the point of restriction or lowload prolonged gentle distraction of restricted tissues.8 The goal of Myofascial Release is to help return the individual's physiological adaptive capacity by increasing space and mobility and restoring threedimensional balance and returning the structure to as close as potentially possible to its vertical orientation with gravity. This equilibrium allows the individual's self-correcting mechanisms to come into play and alleviate symptoms and restore proper function.
METHODOLOGY
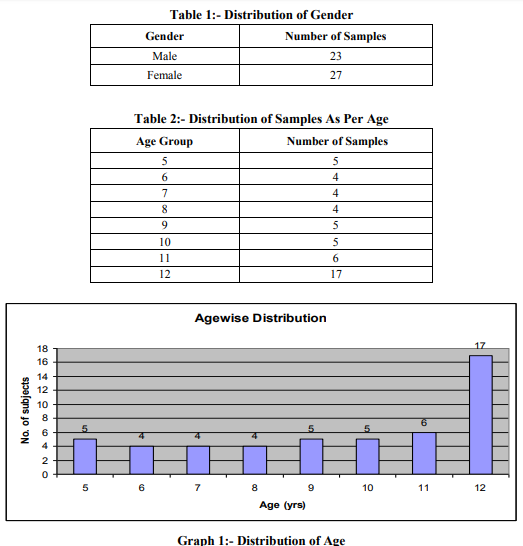
50 Spastic cerebral palsy children of both genders with age 5-12 years satisfying inclusion criteria were included for the study. The children were taken in supine position on the mat/plinth and were made to relax. Then command was given to exhale as much as possible and hold the position to take the chest circumference at the maximal voluntary expiration (Cexp).This was followed by deep breath as much as possible and was held for chest circumference at the maximal voluntary inspiration (Cinsp). The children were made to practice this process and then the mean of the highest value of Cinsp and the lowest value of Cexp difference in best three attempts were recorded for all the children. The chest measurements were taken at three levels at axilla, nipple level and tip of xyphoid process. These readings were documented as Pre Test Score. Myofascial release was given to the Pectorals (major and minor) bilaterally, Rib cage (Intercostals), anterior chest wall and the Diaphragm, with the subject in supine position .Post treatment data was taken and statistical analysis was performed.
DATA ANALYSIS AND RESULTS
The difference of the pre and post readings of the expansion at the axilla level shows a mean difference of 0.42 which is significant, p value being <0.000.The difference of the pre and post readings of the chest expansion at the nipple level shows a significant difference, the difference being 0.54 and the p value<0.000.Similarly the difference of the readings at the xiphoid level (0.53) is significant, p value being <0.000.Thus the result shows that the chest expansion shows significant difference at all the three levels. The expansion improved maximally at the nipple level.
DISCUSSION
Cerebral Palsy is a dynamic disorder of posture and mobility being the motor manifestation of non progressive brain damage sustained during the period of brain growth in fetal life, infancy or childhood. It is the most common cause of severe physical disability in childhood and is characterized by spasticity, movement disorders, muscle weakness, ataxia, and rigidity.9 In their study Ersoz et. al., investigated that there was marked decrease in chest mobility and vital capacity in children with spastic Cerebral Palsy. In these studies, mean vital capacities were 23-67% of the predicted normal values. It can be speculated that the limited chest expansion observed in this study may have a major role in decreased vital capacity seen in Cerebral Palsy patients.5 In another study done by Eun Sook Park et. al., revealed a deviation from optimal chest wall structure in children with Spastic Quadriplegic Cerebral Palsy. They found that the ratio of the upper to lower chest wall of the Cerbral Palsy group was significantly lower than that of the control group and this difference in the chest expansion ratio increased significantly with age.4 As Cerebral Palsy does not have articular involvement, the limited chest mobility is attributed to impaired neuromotor control and incoordination, weakness, spasticity and secondary changes in the respiratory muscles. The inability of the respiratory muscles to adequately increase and decrease the volume of the thoracic cavity may result in stiffening of the costovertebral joints, which may also decrease chest expansion. The results of the present experimental study provide evidence that the mean chest expansion is increased with Myofascial Release at all the three levels i.e. at the apical, mid thoracic and the lower thoracic segment of thorax. Thus, proving that the technique is effective for increasing chest expansion in Spastic Cerebral Palsy children. Myofascial Release therapy uses hands on manipulation of the whole body to promote healing and relieving pain. Injuries, stress, trauma and poor postures cause restriction to fascia. The goal of Myofascial Release is to release fascial restriction and restore its tissue so as to aid normal mechanics and functions. This technique is used to ease pressure in the fibrous bands of the connective tissue, or fascia by application of sustained pressure and gliding techniques.10 Significant loss of ground substance is reported to occur due to immobilization. One of the primary functions of ground substance is to lubricate the area between adjacent collagen fibers. Collagen fiber lubrication is associated with the maintenance of the critical interfiber distance. This is the distance that must be maintained between collagen fibers to allow them to glide smoothly and to prevent micro adhesions between fibers. When the critical interfiber distance is not maintained, due to decreased or no mobility, then the collagen fibers approximate and eventually become cross linked by newly synthesized collagen. The newly synthesized collagen then binds to the adjacent collagen fibers, decreasing the extensibility of the tissue.7 Researchers have identified the involvement of interstitial muscle receptors in fine tuning of the blood flow. When Myofascil Release is given, the interstitial fiber signals the blood vessels which increases the renewal speed of the ground substance i.e. extrusion of the plasma from the blood vessels into the interstitial fluid matrix. This in turn causes hydration of the ground substance thus lubricating the space between the fibers and maintaining the inter-fiber distance.11 Gentle and sustained stretching of Myofascial Release frees the adhesions and softens and lengthens the fascia. The effects are because of the force applied in a particular direction which is against the lines of fascial restriction. As the neuromotor system is released from dysfunction via Myofascial Release, the fascia is stressed by appropriate and orderly movement causing the collagen to lay down in the direction of the stress. A combination of increased level of ground substance with more orderly arrangement of the fibers therefore causes break down of the cross linkage and increases the extensibility of the muscle thus improving the chest expansion.7 Therefore the effect of the myofascial release technique was proved to be effective in the present study. As the fascial and muscular restrictions were released the thoracic cage had better expansion scope in turn improving the respiration. But further studies are needed to investigate the improvement in respiration and gaseous exchange with improved thoracic expansion.
CONCLUSION
The results indicated substantial functional improvement in children with modest to severe spastic cerebral palsy who received myofascial release. There was an effective increase in chest expansion at all the three levels in spastic cerebral palsy children after the myofascial release.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The great help received from the scholars whose articles cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. Authors are grateful to IJCRR editorial board members and IJCRR team of reviewers who have helped to bring quality to this manuscript.
References:
1. Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, et al; “Proposed definition and classification of Cerebral palsy [review]”; Dev Med Child Neurol 2005; vol: 47:571–6.
2. Sankar Chitra, Mundkur Nandani ; “Cerebral Palsy – Definition, Classification, Etiology and Early Diagnosis” ; Indian Journal of Pediatrics ; Oct 2005 ; vol 72
3. Stamer M. Posture and movement of the child with cerebral palsy. Congenital hemiplegia, 1st Edition, Therapy Skill Builder, 2000; 9-16
4. Eun Sook Park, Jung Hyun Park, Dong-Wook Rha, Chang Il Park, and Chan Woo Park; Comparison of the Ratio of Upper to Lower Chest Wall in Children with Spastic Quadriplegic Cerebral Palsy and Normally Developed Children; Yonsei Med J Vol. 47, No. 2, 2006, pp 237 – 242.
5. Ersoz M, Selçuk B, Gündüz R, Kurtaran A, Akyüz M; Decreased chest mobility in children with spastic cerebral palsy; Turk J Pediatr 2006; 48; No 4; 344-350.
6. Manhein CJ; The myofascial release Manual; 3rd Ed; Slack Publications; 2001; 1-36, 123- 131, 180-185.
7. Cantu RI, Grodin AJ; Myofascial manipulation: theory and clinical application; 2nd Ed; Aspen publication, Maryland; 2001; 15-90.
8. William P. Hanten, Sandra D. Chandler; Effects of Myofascial Release Leg Pull and Sagittal Plane Isometric Contract-Relax Techniques on Passive Straight-Leg Raise Angle; JOSPT, 20, No. 3 Sep 1994; 138-144.
9. Karen J D, Nichols F T, Kerr Graham. A randomized controlled trial of strtength training in young people with cerebral palsy. Developmental medicine and child neurology, 2003; 45: 652-657.
10. Suman Kuhar, Khatri Subhash, Jeba Chitra; Effectiveness of myofascial release in treatment of plantar fasciitis: a rct; Indian Journal of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy. July-Sept., 2007, Vol. 1, No. 3.
11. Michael Stanborough; Direct Release Myofascial Technique; 3rd Ed, Elsevier Publishers, 2001, 3-23.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License