IJCRR - 5(17), September, 2013
Pages: 28-35
Date of Publication: 12-Sep-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
PHENOTYPIC ASSAYS FOR DETECTION OF ESBL AND MBL PRODUCERS AMONG THE CLINICAL ISOLATES OF MULTIDRUG RESISTANT PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA FROM A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
Author: Kalaivani R., Shashikala P., Sheela Devi C., Prashanth K., Saranathan R.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Pseudomonas aeruginosa has been a major nosocomial pathogen associated with nosocomial pneumonia, surgical site infections and UTI in patients admitted to intensive care units in the recent past(1). Major risk factors includes prolonged hospitalization, ventilation, underlying immunocompromised state and inadequate or irrational antimicrobial therapy(2). Despite improvements in therapy due to introduction of newer antimicrobials, P. aeruginosa is intrinsically resistant to number of antimicrobials, they aroused a major challenge to overcome the morbidity and mortality caused by multidrug and pan drug resistant P. aeruginosa(3). Drug resistance in turn leads to prolonged hospital stay and increased expenditure, which causes increased cross infections and poorer clinical outcomes. The present study investigated the prevalence of resistance mechanisms among Multi Drug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRPA) clinical isolates from a tertiary care hospital. Methods: Seventy-five MDRP. aeruginosa isolates were obtained from 226 patients admitted in various wards. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed by disk diffusion method and all these isolates were found to be MDR. All the isolates were subjected to different phenotypic assays to detect the production of enzymes such as ESBL, AmpC and MBL,. MIC determination was done by agar dilution method for Meropenem and Polymyxin B. Further, quantitative evaluation of biofilm production by was carried out by microtitre plate assay, since many studies have shown positive correlation between MDR and biofilm formation. Results: Of the 75 MDR P. aeruginosa, 36% were resistant to imipenem and 80% to meropenem. All the isolates were sensitive to polymyxin B. MBL production (38.67%) was found to be the predominant resistance mechanism followed by ESBL production (26.67%). None of them showed AmpC production. Ninety three percent (93%) of the strains produced abundant biofilms. Conclusion: P. aeruginosa was shown to be predominant nosocomial pathogen showing resistance to most of the available antibiotics including carbapenems. MBL is shown to be predominant mechanism for development of resistance in the present study.
Keywords: MDR, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, ESBL, MBL.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the significant Gram-negative bacteria causing hospital-associated infections(4). Among the common multidrug resistant (MDR) nosocomial pathogens emerged in medical centers, P. aeruginosa is the most frequent pathogen causing life threatening infections markedly, respiratory tract infections, surgical site and urinary tract infections in patients from intensive care units (ICUs)(5). It has significant role in causing chronic debilitating respiratory infections in cystic fibrosis patients due to mucoid strains, which leads to increased mortality. Prolonged endotracheal intubation, associated with exposure to inappropriate antimicrobial therapies leads to colonization of the upper respiratory tract thereby complicates the eradication (6).
A major challenge has aroused regarding the treatment of infections caused by opportunistic pathogens, predominantly those with pan drug resistant P. aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii strains, which has extreme ability to acquire resistance (7, 8). P. aeruginosa possesses the ability to acquire resistance genes from the environment as well as from other bacteria (4). High mortality may be attributable to the inherent virulence of the organism as well as the fact that it often occurs with immunosuppression and co morbidity conditions (9, 10). In addition, P aeruginosa is susceptible to a limited number of antimicrobial agents, which increases the likelihood of inappropriate empirical antimicrobial therapy. Reported rates of Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRPA) varied from 0.6% - 32% according to various surveillance studies held in different geographic locations (11, 12). The prevalence of MDRPA has increased over the past decade and has become a major concern among hospitalized patients. Several mechanisms can contribute to resistance in P. aeruginosa, including β-lactamase production, up regulation of efflux systems, biofilm formation and decreased outer membrane permeability.
However, production of β- lactamases such as Metallo- β- lactamases (MBL) and Extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL) are the most common resistant mechanisms documented in P. aeruginosa. As carbapenems are the most potent β-lactams against P. aeruginosa, intensive use of carbapenems facilitated the emergence of carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa(14). Resistance to all antibiotics except polymyxins is now a reality in many medical centers. Despite of abundant literature, little is known about the prevalence of these mechanisms among the clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa from India. Hence, this study was carried out to understand the prevailing mechanisms of resistance among the clinical isolates of MDRPA from in-patients of a tertiary care hospital. This possibly will help to prevent the associated morbidity and mortality caused by this organism by implementing proper infection control measures, which can reduce the duration of hospital stay and expenditure.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
A descriptive study was conducted during the period of November 2009 to October 2010. Seventy-five MDR P. aeruginosa isolates were obtained from 226 patients admitted in various wards of the hospital. All the clinically significant MDRPA isolates collected in the Department of Clinical Microbiology laboratory from wound swabs, endotracheal aspirates, urine, blood, broncheoalveolar lavage, drain tip and tissue samples were investigated. Repeat isolates were excluded from the study. All the isolates were identified by standard microbiological techniques. ATCC P. aeruginosa 27853 strain was used as quality control reference strain for all experiments with satisfactory results.
Antibiotic susceptibility testing was performed by Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method. All these isolates were found to be MDR and were responsible for clinically significant infections. Isolates were also tested for carbapenemase production, if they were found to be intermediate or resistant to either Imipenem or meropenem in disc diffusion method. MIC values were determined by agar dilution method for clinically relevant antibiotics such as meropenem (Astra Zeneca, Bangalore) and polymyxin B (Hi-Media, Mumbai) as per CLSI guidelines.
All the MDR P. aeruginosa were subjected to different phenotypic assays to detect the production of enzymes such as ESBL, AmpC and MBL, which are implicated for causing multiple drug resistance. Phenotypic confirmatory test for ESBL production was performed by placing ceftazidime (30 μg) and ceftazidime + clavulanic acid disc. Detection of Metallo-ß-lactamases was carried out by combined disc diffusion test. AmpC detection was done using AmpC discs method.
Microtitre plate assay for Biofilm production
Since many studies have shown positive correlation between biofilm and multiple drug resistance, quantitative evaluation of biofilm production by P. aeruginosa isolates was carried out by microtitre plate assay (16), (17). Biofilm negative E. coli isolate from our collection and ATCC P. aeruginosa 27853 were used as negative and positive controls respectively. Based on the OD values, the extent of biofilm formed by the clinical isolates were classified as follows,
- OD ≤ ODc - Non adherent
- ODc < OD ≤ 2 × ODc- Weakly adherent
- 2 × ODc < OD4 × ODc- Moderately adherent
- 4 × ODc < OD - Strongly adherent (20).
RESULTS
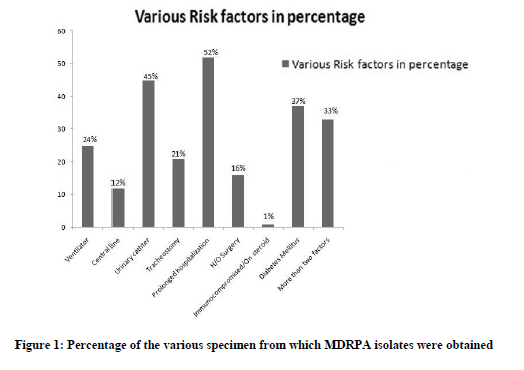
Among the seventy-five patients with MDRPA infection, males were found to be more predominant (66.7%) than females (33.3%). MDR P. aeruginosa infections were found to be 34.7% between 21 to 40 years of age group. MDR P. aeruginosa were mainly isolated from wound infections (43%), followed by endotracheal aspirates (19%), urine (16%), and blood (11%), bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)( 7%,) drain tip (3%) and tissue (1%) respectively(Fig.1). Various risk factors for MDRPA infection were patients with prolonged hospitalization (52%), patients who are on Foley’s catheter (45%), patients with diabetes mellitus (37%), on ventilator (25%), on tracheostomy (21%), post operative patients (16%), on central line catheter (12%) and on steroids (1%). Thirty-three percentage of patients (n=25) were found to have more than two risk factors.
MDRPA isolates showed markedly high-level resistance towards ciprofloxacin (95%), tobramycin (92%), ceftriaxone and gentamicin, (83%). Forty-four isolates (59%) showed resistance to amikacin and 51% resistance was noticed for piperacillin + tazobactum. Among carbapenems, imipenem showed 36% resistance and meropenem 53% resistance. None of the isolates was resistant to polymyxin B. Among the 75 MDRPA isolates, 13 isolates, which were isolated from urine samples, showed 77% of resistance to norfloxacin and carbenicillin.
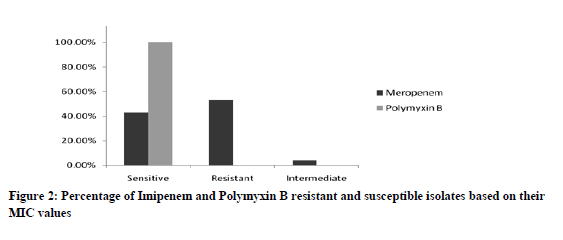
MIC for meropenem ranged from 0.5µg/ml to >64µg/ml. Forty out of seventy five (53.33%) isolates of MDRPA were found to be resistant to meropenem. The isolates were categorized resistant if the MIC value was more than 8µg/ml. Thirty two (42.67%) isolates showed sensitive MIC value (≤4µg/ml) and 4% (3) isolates showed intermediate MIC value (8µg/ml). All the isolates showed lower MIC of 0.5µg/ml to 1µg/ml for polymyxin B (Break point MIC for Pseudomonas aeruginosa ≤2µg/ml to ≥8µg/ml) and none of these isolates showed resistant or intermediate MIC values (Fig.2).
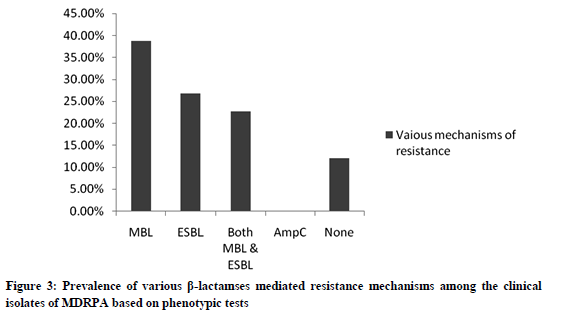
Thirty-nine percent of isolates were found to produce MBL and only, 27% isolates showed ESBL production, none of the isolates showed AmpC production. Twelve percent (9) of isolates were found to be negative for phenotypic production of all β-lactamases (fig.3). Almost all isolates (93%) from our collection were biofilm producers, wherein 75% of the isolates were strongly adherent, 8% moderately adherent and 11% weakly adherent. The percentage of non-adherent cells or biofilm negative isolates was found to be a meager of 7%.
DISCUSSION
P. aeruginosa is a leading cause of nosocomial infections, and it exhibits intrinsic resistance to almost all commercially available antimicrobial agents. However, acquired resistance to anti-pseudomonal β-lactam antibiotics such as ticarcillin, piperacillin, ceftazidime, cefepime, aztreonam and especially carbapenems can be a major challenge in managing MDRPA infections, mostly when it is associated with co-resistance with other classes of drugs namely aminoglycosides and quinolones. Acquired ESBL and metallo-β-lactamases are the major β-lactamases produced by P. aeruginosa.
The prevalence of MDR P. aeruginosa was found to be 33.2% in our investigation, which is in accordance with a similar recent study from India that showed the predominance rate of 44% (18). However, comparatively lesser prevalence of MDRPA (26.7%) responsible for burn wound infections in Iran (19). Likewise, one more investigation from India reported 22% MDRPA and 4% Pandrug resistant P aeruginosa (20), wherein, we recorded a higher level of MDRPA incidence. Factors such as age and sex among MDRPA infection were found to have significant association with MDRPA, wherein the incidence was more among the age groups between 21 and 40 (34.7%) and males being predominant (67%) which is the likely case in earlier reports (21). Possibly, it may be due to high incidence of road traffic accidents among males, leading to hospitalization thereby high incidence of P. aeruginosa infection through catheterization.
Earlier investigations have reported the major source of MDRPA to be sputum, tracheostomy specimen, pus, respiratory tract, surgical sites and endotracheal aspirate (22, 23 24, 25). In the present study, the major source of MDRPA was found to be wound swabs (43%), followed by endotracheal aspirate (19%) implying that wound infections and respiratory tract infections are most significant infections caused by MDRPA in most of the hospitals including our setup. The major risk factors were prolonged hospitalization followed by patients on Foleys catheter. Foot infections and surgical site infections were found to be common source of MDRPA among the diabetic patients.
MDRPA isolates showed markedly high-level resistance towards ciprofloxacin (95%), tobramycin (92%), ceftriaxone and gentamicin, (83%). Forty-four isolates (59%) showed resistance to amikacin and 51% resistance was noticed for piperacillin/ tazobactum combination. Among carbapenems, imipenem and meropenem resistance was observed to be 36% and 53% respectively. None of the isolates were resistant to polymyxin B. Among the 75 MDRPA isolates, 13 isolates, which were isolated from urine samples, showed 77% of resistance to norfloxacin and carbenicillin.
MIC for meropenem ranged from 0.5µg/ml to >64µg/ml. Forty out of seventy five (53.33%) isolates of MDRPA were found to be resistant to meropenem. The isolates were categorized resistant if the MIC value was more than 8µg/ml. Thirty two (42.67%) isolates showed sensitive MIC value (≤4µg/ml) and 4% (3) isolates showed intermediate MIC value (8µg/ml). All the isolates showed lower MIC of 0.5µg/ml to 1µg/ml for polymyxin B (Break point MIC for Pseudomonas aeruginosa ≤2µg/ml to ≥8µg/ml) and none of these isolates showed resistant or intermediate MIC values.
Among various mechanisms of resistance, MBL and ESBL enzymes were found to be more effective and the incidence of MBL production in P.aeruginosa has been reported to be 10-30% from different clinical setups in India (26). Recent studies have shown a very high incidence of MBL (47%), AmpC (50%) and ESBL (13.3%) among the MDRPA isolates tested (29). In our study, also we have observed a high prevalence of MBL (39%), ESBL (27%) producers and 22% of MDRPA isolates were found to produce both MBL and ESBL, which appears to be significant. Around 12 % of isolates did not show any of the mechanisms studied which might follow altogether different resistance mechanisms like formation of biofilms and/or cell wall permeability defects and efflux pump mechanisms (27)
High percentage of biofilm producers were observed in our study, which may be due to the increase number of MDRPA isolates encountered. Morten Hentzer et al. earlier reported the strong correlation between biofilm formation and multiple drug resistance in Gram-negative pathogens (29). Thus, biofilm formation appears to be one of the mechanisms among these strains to develop multi drug resistance, which is evident from the earlier reports from India (28).
CONCLUSION
In summary, MDR P. aeruginosa is a notable cause of hospital acquired infections and known to cause a wide spectrum of life threatening diseases. These organisms are resistant to almost all commonly available antibiotics with limited treatment options. Thirty-six percent of isolates showed resistance to imipenem and 53% to meropenem, which is an “alarming sign”, since carbepenems were the present drug of choice. Furthermore, 93% of isolates had the ability to form biofilm that might aid in the persistence of MDRPA thereby imparts resistance.
References:
- Elkhatib WF, Haynes VL, Noreddin AM. Unexpected induction of resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm to fluoroquinolons by diltiazem: a new perspective of microbiological drug-drug interaction.J.Infect. Public health.2008; 1(2):105-12.
- Levine, S. A., and M.S.Niederman The impact of tracheal intubation on host defenses and risks for nosocomial pneumonia. Clin. Chest Med. 1991; 12:523-543.
- Galdstone P, Rajendran P, Brahmadathan KN. Incidence of carbapenem resistant nonfermenting gram-negative bacilli from patients with respiratory infection in the intensive care unit. IJMM. 2005;23:189-91.
- Ana Lucia Peixoto de Freitas and Afonso Luis Barth. Antibiotic resistance and molecular typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Focus on Imipenem.The Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases.2002; 6(1):1-7.
- Gaynes R, Edwards JR. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system. Overview of nosocomial Infections caused by Gram-negative bacilli. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 41:848-54.
- Obritsch, M.D., D.N.Fish, R.MacLaren, R.Jung, I.Friedland, G.Gallagher, T.King, G.L.Woods, et al. National surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates obtained from intensive care unit patients from 1993 to 2002. Antimicrob.Agents Chemother.2004; 48:4606-4610.
- Neu HC. The role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in infections. JAntimicrob Chemotherapy. 1983; 11 Suppl B: 1-13.
- Ami Varaiya, Nikhil Kulkarni, Manasi Kulkarni, Pallavi Bhalekar, Jyotsana Dogra. Incidence of metallo beta lactamase producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in ICU patients. Indian J Med Res.April 2008; 127: 398-402.
- MacArthur, R.D., M. Miller, T.Albetson, E.Panacek, D.Johnson, L.Teoh, et al., Adequacy of early empirical antibiotic treatment and survival in severe sepsis: experience from the MONARCS trail. Clin. Infect. Dis.2004; 38:284-288.
- Regina B Osih, Jessina C. McGregor, Shayna E. Rich, Anita C. Moore, Jon P.Furuno, Eli N.Perencevich, et al., Impact of empiric antibiotic therapy on outcomes in patients with Pseudomonas aeruuginosa bacteremia. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 2007; p.839-844.
- Cao B, Wang H, Sun H. Risk factors and clinical outcomes of nosocomial multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. J Hosp Infect. 2004 Jun; 57(2):112-8.
- Lister PD. Chromosomally-encoded resistance mechanisms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Am J Pharmacogenomics. 2002; 2(4):235-43.
- Davies, J.C., Bilton D. Bugs, Biofilms, and resistance in cystic fibrosis. Respir. Care. 2009; 54:628-640.
- Livermore. DM. Of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, porins, pumps and carabapenems. J.Antimicrob.Chemother.2007; 47: 247-250.
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial disk tests; Approved standards, 9th edition. CLSI Document M2-A9, Vol.26 No1. Wayne PA 2006.
- Stepanovic S, Vukovic D, Dakic I, Savic B. A modifiedmicrotiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J.Microbiol. Methods.2000; 40: 175-179.
- Davies J.C, Bilton D. Biofims and reistance in cystic fibrosis. Respir. Care. 2009; 54: 628-640.
- Shankar EM, Mohan V, Premalatha G. Bacterial etiology of diabetic foot infections in South India. Eur J Intern Med. 2005 Dec; 16(8):567-70.
- Antonopoulo A, Raftogiannis M, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ. Early apoptosis of blood monocytes is a determinant of survival in experimental sepsis by multi-drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007 Jul; 149(1):103-8.
- Jayakumar S, Appalaraju B. Prevalence of multi and pan drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with respect to ESBL and MBL in a tertiary care hospital. Indian Journal of pathology and Microbiology .2007; 50(4):922-5.
- Kiran Ruhil, Bharti Arora, Himanshu Adlakha. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolation of Post-operative wound in a referral hospital in Haryana, India. JInfect Dis Antimicrob Agents 2009; 26:43-8.
- Aggarwal R, Chaudhary U, Bala K. Detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2008 Apr-Jun; 51(2):48-51.
- Shanthi M, Sekar U. Multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii infections among hospitalized patients: risk factors and outcomes. J Assoc physicians India. 2009 Sep; 57:636-645.
- Toniolo A, Endimiani A, Luzzaro F. Microbiology of postoperative infections.Surg Infect.2006; 7 suppl 2:S13-16.
- Shashikala, Kanungo R, Srinivasan S, Devi S. Emerging resistance to carbapenem in hospital acquired Pseudomonas infection: Indian J Pharmacol 2006; 38:287-8.
- Navaneeth BV, Sridaran D, Sahav D, Belwadi MR.A preliminary study on MBL producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in hospitalized patient. Indian journal of Medical Research.2002; 116:264-7.
- Poirel L, Naas T, Nicholas D, Collet L, Bellais S, Cavallo JD, et al. Characterization of VIM-2, a Carbapenem-hydrolyzing metallo-beta-lactamase and its plasmid-and integron-born gene from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate in France. Antimicrob Agents Chemotherapy. 2000; 44:891-97.
- Nagaveni S, Rajeshwari H, Ajay Kumar oli, S.A. Patil and R.Kelmani Chandrakanth, Evaluation of Biofilm forming ability of the multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The Bioscan 5(4):563-56, 2010.222-4.
- Morten Hentzer,L Gail M. Teitzel, Grant J. Balzer,Arne Heydorn,L Søren Molin,L Michael Givskov,L , Matthew R. Parsek.Alginate Overproduction Affects Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Biofilm Structure and Function .Journal of Bacteriology. 2001; 5395–5401.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License