IJCRR - 5(19), October, 2013
Pages: 110-120
Date of Publication: 19-Oct-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
INTERACTION OF EMBLICA OFFICINALIS WITH FAMOTIDINE AND PANTOPRAZOLE IN PYLORUS LIGATION INDUCED GASTRIC ULCERS IN RATS
Author: Kanani Neeta J., Bhave Amol L., Bhatt Jagatkumar D.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Emblica officinalis (EO) is widely used in Ayurveda for various ailments on account of it's medicinal properties of which it has stood test of time for its use in peptic ulcer. However currently there is no report in literature about combining it with allopathic anti-ulcer agents used in peptic ulcer. Objective: To study interaction of EO with antiulcer agents, famotidine and pantoprazole in pylorus ligation induced gastric ulcers in rats. Materials and Methods: Gastric ulcers in rats were induced by method of pyloric ligation as described by Shay et al. Effects of different doses of famotidine, pantoprazole and EO on volume, pH, acidity, and ulcer index were observed. Also effects of EO in combination with famotidine or pantoprazole were studied for the same. Results: Famotidine (4mg/kg i.p.), pantoprazole (4mg/kg i.p.) and EO (100mg/kg p.o.) produced significant anti-ulcer effects in terms of reduction in acidity and ulcer index. Famotidine (1mg/kg i.p.), pantoprazole (1mg/kg i.p.) and EO (50mg/kg p.o.) did not alter the above parameters significantly.Simultaneous administration of (50mg/kg) and famotidine (1mg/kg) showed significant anti-ulcer effects which were apparent from reduction in acidity and ulcer index without causing any change in pH value. Similarly, pantoprazole (1mg/kg) combined with EO (50mg/kg) showed significant anti-ulcer effects on similar lines but with significant rise in volume of gastric secretion. Conclusion: EO produced pantoprazole with EO may be recommended for management of peptic ulcer with an advantage of minimizing side effects and drug interactions of former drugs while getting benefits from EO like its antioxidant property.
Keywords: Combined Therapy, Emblica officinalis, famotidine, pantoprazole, pyloric ligation
Full Text:
Peptic ulcer has become a major health problem, both in terms of morbidity and mortality and accounts for a vast amount of drug consumption in many developing countries. Though multifactorial etiology has been implicated, an ulcer is thought to be formed when there is an imbalance between aggressive factors i.e. the digestive power of acid and pepsin and defensive factors i.e. the ability of the gastric and duodenal mucosa (intact gastric mucosal barrier) to resist this digestive power.[1] In majority of patients with ulcer, damage to the gastric mucosal barrier is necessary to facilitate the damaging effect of acid and pepsin and this damage is found to be provoked by factors like NSAIDS, H. pylori, alcohol and stress.
It appears that exposure of the involved tissue to acid is essential for the development of clinical symptoms in most instances of the disease.[2] On this basis, control of gastric acidity is a cornerstone of therapy in peptic ulcer disease, even though this approach may not address the fundamental pathophysiological process. Antacids were the only affordable medication for the treatment of peptic ulcer disease in developing countries; but its long term use was associated with pneumonitis, potential drug interactions and a very poor compliance to two hourly administrations.[3] After years of use of antacids, considerable advances in understanding the pathogenesis as well as the treatment of acid peptic disease have culminated in the discovery of H2- blockers, proton pump inhibitors and anti-H. Pylori regime.[2] Though used quite successfully, reports on clinical evaluation of these drugs show that there are incidences of relapses, adverse effects and dangers of drug interactions during therapy. Tolerance to the acid-suppressing effects of H2-receptor antagonists is well described and may account for a diminished therapeutic effect with continued drug administration. Tolerance can develop within 3 days of starting treatment and may be resistant to increased doses of the medications.[4] Increased bacterial counts in the upper gastrointestinal tract have been reported as a consequence of continuous inhibition of acid secretion by proton pump inhibitors.[5] This is associated with increased incidence of Campylobacter jejuni enteritis.[6] Nonetheless cessation of treatment in peptic ulcer disease is associated with relapse rates of 50 – 80% per year.[7]
Recent advances have stressed on prevention of gastroduodenal ulceration by measures directed at strengthening the mucosal defense system rather than attenuating the aggressive factors i.e. using a gastric mucosal protective agent.[8] However the efficacy of these drugs is debatable as far as permanent cure is concerned. Peptic ulcer disease therapy is more or less a success, but the quest still continues for better drug and now the limelight has shifted to alternative medicine. Ample references are available in Ayurveda and Unani medicine about the utility of Musa paradisiaca (Vegetable banana), Azadirachta indica (Neem), Ocimum sanctum Linn (Tulsi), Emblica officinalis (Amla) and the list is endless, in treating patients of peptic ulcer but they lack inadequate scientific data. Of these, few scientific studies have been done to evaluate antiulcer activity of Emblica officinalis (EO). Study with methanolic extract of EO against ulcers have showed significant ulcer protective and healing effects in various gastric ulcer model of rats.[9] This might be due to its effects both on defensive and offensive mucosal factors. Study by Rajeshkumar et al,[10] on antiulcerogenic activity of fresh fruit juice of EO and its methanolic extract evaluated in various experimental models of ulcers in rats have showed a dose dependent protective effect against gastric mucosal damage. This protection afforded by EO was found to be better than that of ranitidine.
However at present there is no report in literature regarding the combination study of EO with conventional antiulcer drugs. Therefore Loading...Please wait while the content of the page loads the present study was undertaken to demonstrate the antiulcer effects of EO as well as its interaction with a H2-blocker famotidine and a proton pump inhibitor pantoprazole in pylorus ligated (PL) gastric ulcer model in rat.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Wistar strain albino rats of either sex weighing 200-250 g were kept in the departmental animal house at room temperature (25oC to 30oC) and were given regular laboratory diet with water ad libitum. Principles of laboratory animal care and use were followed throughout the study. The study was designed with due permission of animal ethics committee.
Rats were divided into various groups viz., Control(saline treated), DMSO (vehicle) treated, famotidine treated (1mg/kg and 4mg/kg), pantoprazole treated (1mg/kg and 4mg/kg), EO powder treated (50mg/kg and 100mg/kg) and finally a combination treatment of EO powder (50mg/kg) with famotidine (1mg/kg) and EO powder (50mg/kg) with pantoprazole (1mg/kg). Drugs were administered intraperitoneally (i.p.), 1 hr prior to pyloric ligation (PL) for all groups except EO which was administered orally twice a day with food for seven days. Control group received normal saline while vehicle treated two groups received DMSO i.p.4 hr and 1 hr prior to PL. The volume of all the above injections was in the range of 0.2 to 0.4 ml.
Pyloric ligation was performed as described by Shay et al.[11] The gastric contents were collected and subjected to centrifugation at the rate of 3000 rpm for 10 minutes for estimation of volume, pH, free acidity and total acidity.
pH was estimated by using Indikrom pH strips [Glaxo India Limited] with pH range of 2.0 – 4.5 and 5.0 – 8.5 with range difference of 0.5. Free acidity and total acidity were estimated by titrating one ml of centrifuged sample with 0.01 N NaOH using Topfer’s indicator and Phenolphthalein indicator respectively. Acidity was expressed in clinical units i.e. the amount of 0.01 N NaOH base required to titrate 100 ml of gastric secretion. For estimation of ulcer index, the stomach was cut open along the greater curvature and the inner surface was examined for ulceration with the help of simple dissecting microscope. Usually, circular lesions were observed but, many times, linear lesions were also seen. Ulcer index was calculated by using the formula;
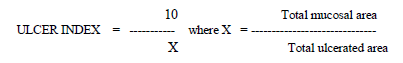
Drugs Used
Fresh solutions of famotidine and pantoprazole [Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Vadodara] were prepared daily in DMSO. Dry powder of EO fruit was obtained from Amlaki Capsule [500 mg; Intel Pharmaceuticals, Calcutta]
Statistical Analysis
All data are expressed as Mean + Standard error of mean (S.E.M.). For comparison amongst different groups, post hoc one way ANOVA was performed. Value of P less than 5% (P<0.05) is considered to be statistically significant.
RESULTS
- Effects of DMSO (Vehicle) on various parameters:
In agreement to previous studies DMSO, whether administered 4h or 1h prior to pylorus ligation did not cause any significant change in the volume of gastric secretion, pH, free acidity, total acidity and ulcer index as compared to the control values. Pylorus ligation in control and DMSO treated rats induced significant ulcers [Figure 1].
- Effects of famotidine and pantoprazole on various parameters:
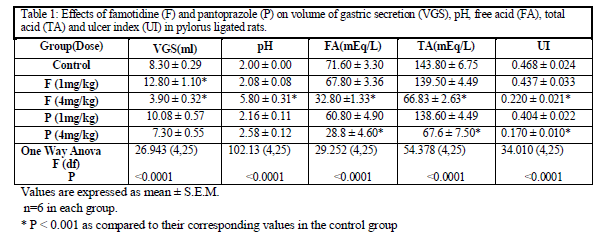
Famotidine in dose of 1mg /kg did not produce any significant change in any parameters as compared to their respective control values except that the volume of gastric secretion increased significantly after the treatment [Table 1]. However 4mg/kg famotidine produced significant decrease in the volume of gastric secretion, free acidity, total acidity and ulcer index alongwith significant increase in the pH as compared to their respective control values [Table 1]. Pantoprazole in dose of 1mg/kg did not produce any significant change in any parameters as compared to their respective control values [Table 1]. While, 4mg/kg pantoprazole did not produce significant change in volume of gastric secretion and pH, but significantly decreased free and total acidity and ulcer index as compared to their respective control values [Table 1]. Both the drugs in dose of 4 mg/kg produced significant protection against pyloric ligation induced gastric ulcers.[Figure 2 and 3]
3. Effects of EO on various parameters:
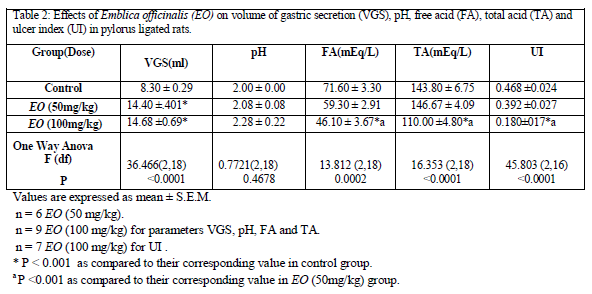
EO in dose of 50mg/kg did not modify pH, free acidity, total acidity and ulcer index, but caused significant increase in volume of gastric secretion as compared to that of control group [Table 2]. However, in dose of 100mg/kg, it produced a significant decrease in free acidity, total acidity and ulcer index [Figure 4] with significant increase in volume of gastric secretion as compared to their respective control values without significantly affecting pH value [Table 2].
4. Effects of combined treatments on various parameters:
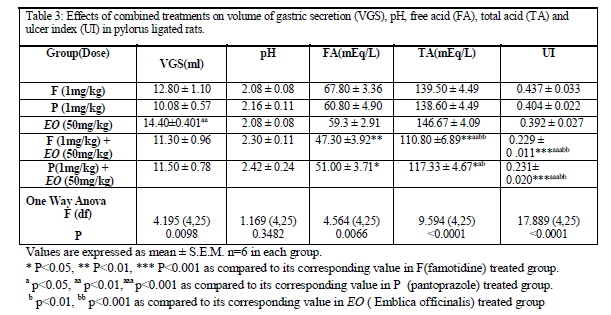
Combined treatment consisting of famotidine (1mg/kg) with EO (50mg/kg) did not significantly modify the volume of gastric secretion and pH values as compared to famotidine treated group; but it significantly decreased free acidity as compared to famotidine group. While total acidity and ulcer index were significantly reduced as compared to the famotidine, pantoprazole and EO treated groups [Table 3].
Similarly combined treatment consisting of pantoprazole (1mg/kg) with EO (50mg/kg) when compared with famotidine, pantoprazole and EO treated groups showed significant decrease in free acidity, total acidity and ulcer index without any modification in the volume of gastric secretion and the pH value [Table 3].
The above combinations produced significant protection against pylorus ligation induced gastric ulcers [Figure 5 and 6].
DISCUSSION
Peptic ulcer is a benign lesion of gastric or duodenal mucosa. It is generally accepted that it results from an imbalance between aggressive factors and maintenance of mucosal integrity through endogenous defense mechanisms. To regain the balance, different therapeutic agents, including plant extracts are used to inhibit gastric acid secretion or to boost the mucosal defense mechanisms by increasing mucus production, stabilizing the surface epithelial cells or interfering with prostaglandin (PG) synthesis.[8]
Famotidine, a competitive antagonist at H2- receptor is capable of reducing over 90% of basal and nocturnal secretion of gastric acid and that stimulated by food, histamine, gastrin, cholinomimetic drugs and vagal stimulation.[12]
Proton pump inhibitor, pantoprazole produces small and inconsistent changes in volume of gastric secretion and in secretion of pepsin but does not affect gastric motility. It irreversibly inhibits the gastric acid (proton) pump which is the final common pathway for acid secretion in response to all varieties of stimuli.[13] In our study, famotidine and pantoprazole in dose of 1mg/kg did not produce any significant change in any of the parameters. While both the drugs in dose of 4mg/kg significantly reduced free and total acidity and ulcer index. These observations are in accordance with those reported in the literature.
In the present study, EO (50 mg/kg) did not produce any significant alterations in any of the parameters except that volume of gastric secretion (VGS) was found to be significantly increased as compared to control group. Therapeutically equivalent dose of EO (100 mg/kg) produced significant decrease in free and total acidity and ulcer index without any alteration in gastric pH along with significant increase in VGS. Significant increase in VGS observed with both the doses of EO is a paradoxical observation as compared to that observed with conventionally used antiulcer drugs. [14]
In the present study, 1mg/kg dose of famotidine and pantoprazole and EO (50 mg/kg) did not produce any antiulcer effects. Therapeutically equivalent dose of EO (100mg/kg) produced significant protective effect against experimental gastric ulceration in rats. However, combination of either famotidine or pantoprazole (1 mg/kg) with EO (50 mg/kg) significantly enhanced their antiulcer effects. The enhancement of the above antiulcer effects by EO may be attributed to its multiple mechanisms involved.
The cause of gastric ulceration after pyloric ligation is believed to be stress induced increase in gastric acid secretion and/or stasis of acid.[11] Neurogenic mechanisms have also been proposed to play role in the formation of gastric ulcers in pylorus ligation model.[15] Kitagawa et al,[16] reported decreased central norepinephrine levels in restraint stress models. Similarly, improvement in gastric function is shown to occur with increase in central norepinephrine levels.[17] A study by Bharaj et al,[18] in guinea pigs confirmed that reduction in levels of ascorbic acid in brain produces a simultaneous significant decline in central norepinephrine levels.
Ascorbic acid is one of the major constituents of EO. Ascorbic acid, dehydroascorbic acid and glutathione have considerable influence in regulating the overall reducing status of the body. Moreover it is well known that vascular histamine content markedly increases in patients of peptic ulcer which is associated with decreased levels of glutathione and poor ascorbic acid content of adrenal glands.[19] Subramanian et al,[20] concluded that one of the functions of ascorbic acid is detoxification of excess of histamine in response to biochemical stress. It has also been reported that depletion of gastric glutathione is associated with a generation of gastric lesions in rats.[21] Also treatment with EO extract was found to cause significant induction in the levels of the glutathione content, and of antioxidant and detoxification enzymes in the liver of mice.[22] Bhattacharya et al,[23] reported that EO exerts its antioxidant action by increasing the concentrations of oxidative free radical scavenging enzymes in brain and thus decreasing lipid peroxidation. Recently anti-ulcer activity of EO has been shown to be attributed to its antioxidant mechanism of action.[24] Thus it is likely that EO may exert its antiulcer activity by central and peripheral antioxidant mechanisms.
Though accumulation of acid secretion is thought to be the major gastric insult, when weakened gastric mucosal defenses are also involved – total acid neutralization in pylorus ligated rats fails to prevent ulceration,[25] while strengthening the gastric mucosal defense has led to prevention of ulcer formation. As apparent in the results of the present study EO was observed to exert antiulcer effect without altering the gastric pH – implying that EO may be exerting this effect through improving gastric mucosal defense suggesting the novel cytoprotective activity of EO on gastric mucosal cells.[10] Role of flavanoids present in the EO fruit has been suggested to produce significant protection against various models of gastric ulcers in rats.[26-28]
As the combination does not alter the gastric pH significantly, it thus provides an optimal milieu for the functioning of gastric digestive enzymes and also mediates the negative feedback loop controlled by gastric pH to inhibit gastric acid secretion. The above advantages are abolished due to an increase in gastric pH with therapeutic doses of famotidine or pantoprazole. Yeomans,[29] has also reported slightly increased risk of some enteric infections (mainly C. Jejuni) due to increased gastric pH. From the observations of our study, it is suggested that the enhancement of antiulcer effects of famotidine and pantoprazole by EO may be mediated through its antioxidant and cytoprotective properties.
CONCLUSION
Thus it is concluded that EO produced significant protective effect against gastric ulceration and also significantly enhanced the antiulcer effects of famotidine and pantoprazole without further significant alteration of pH and volume of gastric secretion. Thus, the above combination therapy offers better option for rationale management of peptic ulcer as compared to monotherapy with conventional agents as this would definitely reduce the incidence of side effects and numerous drug interactions associated with the conventional antiulcer agents while getting benefits from EO like its antioxidant property. Further detailed studies are required to confirm our above observations.


References:
- Friedman LS, Peterson WL. Peptic ulcer and related disorders. In: Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Isselbacher KJ, Wilson JD, Martin JB, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, editors. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine.Vol.2. 14th ed. USA: McGraw Hill. Health Professions Divison; 1998. p. 1596-99.
- Hoogerwerf WA, Pasricha PJ. Agents used for control of gastric acidity and treatment of peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Gilman AG, editors. Goodman and Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed.USA: McGraw Hill. Medical Publishing Divison; 2001.p. 1005-19.
- Ching C, Lam S. Antacids: Indications and Limitations. Drugs 1994; 47(2):305-17.
- Sandvik AK, Brenna E, Waldum HL. Review article: The pharmacological inhibition of gastric acid secretion – tolerance and rebound. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997; 11(6):1013-8.
- Lewis SJ, Franco S, Young G, et al. Altered bowel function and duodenal bacterial overgrowth in patients treated with omeprazole. Aliment Pharm Ther 1996; 10:557-61.
- Neal KR, Scott HM, Slack RCB, et al. Omeprazole as risk factor for Campylobacter gastroenteritis a case control study. BMJ 1996; 312(7028):414-5.
- Festen HPM. Profound gastric acid inhibition, advantages and potential hazards. Scan J Gastroenterol 1989;(171):99-105.
- Dhuley JN. Protective effect of Rhinax, a herbal formation against physical and chemical factors induced gastric and duodenal ulcers in rats. Ind J Pharmacol 1999; 31: 128-32.
- Sairam K, Rao ChV, Babu MD, Kumar KV, Agarwal VK, K Goel RK. Antiulcerogenic effect of methanolic extract of Emblica officinalis: an experimental study. J Ethnopharmacol 2002; 82(1):1-9.
- Rajeshkumar NV, Therese M, Kuttan R. Emblica officinalis fruits afford protection against experimental gastric ulcers in rats. Pharmaceutical Biology 2001;39(5):375-80.
- Shay M, Komarov SA, Fels D, Meranze D, Gruenstein H, Siplet H. A simple method for the uniform production of gastric ulceration in the rat. Gastroenterology 1945; 5: 43-61.
- Parmar NS. Anti-ulcer drugs: Present status and new targets. Indian Drugs 1989; 26 : 381-7
- Richardson P, Hawkey CJ and Stack WA. Proton pump inhibitors. Pharmacology and rationale for use in gastrointestinal disorders. Drugs,1998;56:307-33
- Bhave AL, Bhatt JD, Hemavathi KG. Antiulcer effect of amlodipine and its interaction with H2 blocker and proton pump inhibitor in pylorus ligated rats. Ind J Pharmacol, 2006;38(6):403-407.
- Anichkov SV, Zarodskua IS, Noreva EV, Korkhov VV. Effect of dihydroxyphenyl alanine (DOPA) upon development of experimental neurogenic gastric ulcers. In: Pfeiffer CJ, ed. Peptic Ulcer. Copenhagen: Munks guard 1971; 307-11.
- Kitagawa H, Fujiwara M, Osumi Y. Effect of water immersion stress on gastric secretion and mucosal blood flow in rats. Gastroenterol 1979; 77:298-302.
- Okuma Y, Nagata M, Osumi Y. Effects of acetylcholine and noradrenaline applied into lateral hypothalamic area on gastric function in rats. Jap J Pharmac 1980;30(suppl.),p. 220.
- Bharaj BS, Nduati SN, Telang BV. The effect of Ascorbic acid deficiency on brain catecholamines and monoamine oxidases. Ind J Physiol Pharmac 1980; 24(3):251-253.
- Dubey SS, Sinha KK, Gupta JP, Banu N. Ascorbic acid, dehydroascorbic acid, glutathione and histamine in peptic ulcer patients. Ind J Med Res 1982; 76:859.
- Subramanian N, Nandi BK, Majumdar AK, Chatterjee IB. Role of ascorbic acid on detoxification of histamine. Biochemical Pharmacology 1973; 22:1671.
- Body SC, Sasame HA, Body MR. Gastric glutathione depletion and acute ulcerogenesis by diethyl maleate given subcutaneously to rats. Life Sci 1981; 28:2987-92.
- Sharma N, Trikha P, Athar M, Raisuddin S. Inhibitory effect of Emblica officinalis on the in vivo clastogenicity of benzo {a} pyrene and cyclophosphamide in mice. Human and Experimental Toxicology 2000; 19(6):377-84.
- Bhattacharya A, Chatterjee A, Ghosal S, Bhattacharya SK. Antioxidant activity of active tannoid principle of Emblica officinalis (amla). Indian Journal of Experimental Biology 1999; 37(7):676-80.
- Bafna, PA; Balaraman R. COPYRIGHT 2008 Urban and Fischer Verlag. This material is published under license from the publisher through the Gale Group, Farmington Hills, Michigan. All inquiries regarding rights or concerns about this content should be directed to customer service. (Hide copyright information) Anti-ulcer and antioxidant activity of DHC-1, a herbal formulation. J Ethnopharmacol 2004;90(1):123-127
- Dai S, Ogle CW. Gastric ulcers induced by acid accumulation and by stress in pylorus – occluded rats. Eur J Pharmacol 1974; 26:15.
References and further reading may be available for this article. To view references and further reading you must purchase this article.
- Raj Narayana K, Sripal Reddy M, Chaluvadi MR, Krishna DR. Bioflavonoids classification, pharmacological , biochemical effects and therapeutic potential. Ind J Pharma 2001; 33:2-16.
- Habib–ur-Rehman, Yasin KA, Choudhary MA, Khaliq N, Atta-ur-Rahman, Choudhary MI and Malik S. Studies on the chemical constituents of Phyllanthus Emblica. Nat Prod Res 2007;20;21(9):775-81.
- Al Rehaily AJ, Al Howiriny T.A., Al Sohaibani M.O. and Rafatullah S. Gastroprotective effects of 'Amla' Emblica officinalis on in vivo test models in rats. Phytomedicine. 2002; 9(6): 515-22.
- Yeomans ND. Drugs that inhibit acid secretion. JAMA 2000; 3(12):89-91.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License