IJCRR - 5(19), October, 2013
Pages: 81-87
Date of Publication: 19-Oct-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
PREVALENCE AND ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF EXTENDED SPECTRUM BETA LACTAMASE PRODUCING KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIAE ISOLATED FROM RESPIRATORY SAMPLES IN A SOUTH INDIAN TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
Author: Ranjan Basu , Raghav Rao, Arijit Sarkar, Bidyarani Kongbrailatpam
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: Klebsiella pneumoniae is important in causing a classic form of primary pneumonia and the leading causes of nosocomial infection, being hard to eradicate due to development of multidrug-resistant strains that produce extended\?spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) enzyme. The present study was conducted to find out the prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of respiratory isolates of ESBL producing Klebsiella pneumoniae at our hospital . Methods: Respiratory samples of RTI patients from different IPDs and OPDs sent for culture and sensitivity prior to starting of any antibiotics, during January 2012 to June 2013 were included in the study. Klebsiella pneumoniae was identified by standard laboratory procedure as per CLSI guideline. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was done by Kirby-Bauer's disk diffusion method in Mueller Hinton Agar media. ESBL producing strains were confirmed by Double Disk Synergy test after initial screening with 3rd generation cephalosporins. Results: Out of 400 respiratory samples ,140 Klebsiella pneumoniae were isolated among which 38 ( 27.14 % ) were ESBL producers and 102 ( 72.86 % ) were non ESBL strains . A 131 ( 93.57% ) isolates were obtained from IPDs. and 9 ( 6.43 %) were from OPDs .Male to female ratio for ESBL producing K. pneumonia was 1.7 : 1. TBCD dept. and ICCU were the major contributors of those positive isolates. A 64% multi drug resistance were observed among ESBL isolates. Apart from 3rd generation cephalosporins, they were also highly resistant to common antibiotics like Ampicillin, Aztreonam, Gentamycin, Erythromycin and Co-trimoxazole. Imipenem was the most active antibiotics with 96.37% susceptibility rates. Conclusions: Regular monitoring on the judicious use of antibiotics helps in preserving the effectiveness and emergence of further resistance of the sensitive antibiotics among the ESBL producing K. pneumonia.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae, susceptibility, ESBL producers , antimicrobial resistance
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod shaped bacterium found in the normal flora of the mouth, skin and intestines. In the recent years, klebsiella pneumoniae has become important pathogen in nosocomial infections. Klebsiella pneumoniae being the primary cause of respiratory tract infections, is most frequently recovered from clinical specimens and can cause a classic form of primary pneumonia. Klebsiella pneumoniae can also cause a variety of extrapulmonary infections, including enteritis and meningitis in infants, urinary tract infections in children and adults and septicaemia1. They are ubiquitously present and
reported worldwide. These bacteria have become important pathogens in nosocomial infections 2 which have been well documented in United States and India3. Epidemic and endemic nosocomial infections caused by Klebsiella species are leading causes of morbidity and mortality4. In the United States, Klebsiella accounts for 3-7% of all nosocomial bacterial infections, placing them among the eight most important infectious pathogens in hospitals. Klebsiellae have a tendency to harbour antibiotic resistant plasmids; thus, infections with multiple antibiotic-resistant strains can be anticipated.1
Multidrug resistant bacteria cause serious nosocomial and community acquired infections that are hard to eradicate by using available antibiotics. Moreover, extensive use of broad-spectrum antibiotics in hospitalized patients has led to both increased carriage of Klebsiella pneumoniae and the development of multidrug-resistant strains that produce extended–spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL). The first ESBL producing strain discovered in Germany was Klebsiella pneumoniae in 1980s. Outbreaks of ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae infections have increased worldwide 5. Recently, World Health Organization also warned the community that multidrug resistant bacteria are emerging worldwide which is a big challenge to healthcare. If we don’t take immediate action then antibiotics may lose their power to cure diseases caused by this bacteria6.
Area-wise studies on antimicrobial susceptibility profiles are essential to guide policy on the appropriate use of antibiotics. The present study was conducted to find out the prevalence of ESBL producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in respiratory samples of patients with respiratory tract infections along with their antimicrobial susceptibility pattern at our hospital. The information would be useful in establishing empiric therapy guidelines to prevent the emergence of further resistance and to contribute data to larger more extensive surveillance programs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The present study was conducted in the department of Microbiology, GSL Medical College and General Hospital, Rajahmundry, Andhra Pradesh, India. Patients having symptoms of respiratory tract infections diagnosed provisionally in different IPDs and OPDs whose respiratory samples (sputum / throat swab / bronchial washings) were sent for culture and sensitivity prior to starting of any antibiotics, during the period from January 2012 to June 2013 were included in the study . Informed consent was taken from the patient and ethical clearance was obtained from the institute.
400 respiratory samples received during that period were inoculated in MacConkey’s agar, Blood agar and Nutrient agar media and routine standard operative procedures are followed in the laboratory in isolating and identifying the organisms from the sputum samples. Klebsiella pneumoniae was identified by typical mucoid, lactose fermenting colony, Gram stain morphology, motility test, oxidase test, urease production test, IMViC reaction, fermentation of sugars like glucose, lactose, sucrose, mannitol with production of acid and gas.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was done by Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method in Mueller Hinton agar media and results are interpreted according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines 7. Standard antibiotics like ampicillin (10 mcg), amoxyclav (20/10 mcg), piperacillin/tazobactum (100 /10 mcg), ceftriaxone (30 mcg), cefotaxime (30 mcg), ceftazidime (30 mcg), cefepime (30 mcg), imipenem (10 mcg), aztreonam (30 mcg), ciprofloxacin (5 mcg) , levofloxacin (5 mcg) , co-trimoxazole (1.25/23.75 mcg) gentamycin (10 mcg), amikacin (30 mcg) and erythromycin (15 mcg)8 were tested (HIMEDIA, MUMBAI, INDIA)
Detection of ESBL
All Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates showing resistance to 3rd generation cephalosporins like cefotaxime, ceftazidime and ceftriaxone were screened initially for probable ESBL producing strains which were followed by the phenotypic confirmatory test for confirmation of ESBL producing isolates. The double-disk synergy test was used to confirm ESBL strains. In brief, ceftazidime (30 mcg), cefotaxime (30 μg) and ceftriaxone (30 μg) were placed at a distances of 30 mm from center to center and around a disk containing amoxicillin (20 μg) plus clavulanic acid (10 μg). The results were interpreted as positive when the difference in zones of inhibition of isolates was > 5 mm in combination with clavulanic acid than to ceftazidime, cefotaxime or ceftriaxone alone. Enhancement of the inhibition zone toward the amoxicillin-plus-clavulanic acid disk is suggestive of ESBL production. 9,10,7
The data obtained in this study was summarized by counts and percentages. Antibiotic Susceptibility rates were presented with the respective 95% confidence interval values.
RESULTS
Out of a total 400 respiratory samples (sputum and broncho-alveolar lavage) received in our central laboratory during the period from January 2012 – June 2013, 140 (35%) Klebsiella pneumoniae were isolated. Among the 140 K. Pneumoniae isolates, 38 ( 27.14 % ) were ESBL producing strains as confirmed by double disk synergy test and 102 ( 72.86 % ) were non ESBL strains; among them 107 (76.43%) were from male patient and 33 (23.57 %) were from females whereas 131 ( 93.57 % ) isolates were obtained from In Patient Dept. and 9 ( 6.43 %) were from OPDs; The distribution of ESBL and Non ESBL strains , sex wise and IPD / OPD wise are shown in Table – 1 . There was no significant age specificity noted in our study . Over all male to female ratio was 3.25 : 1 whereas the male to female ratio of ESBL producing isolates was 1.7 : 1 .
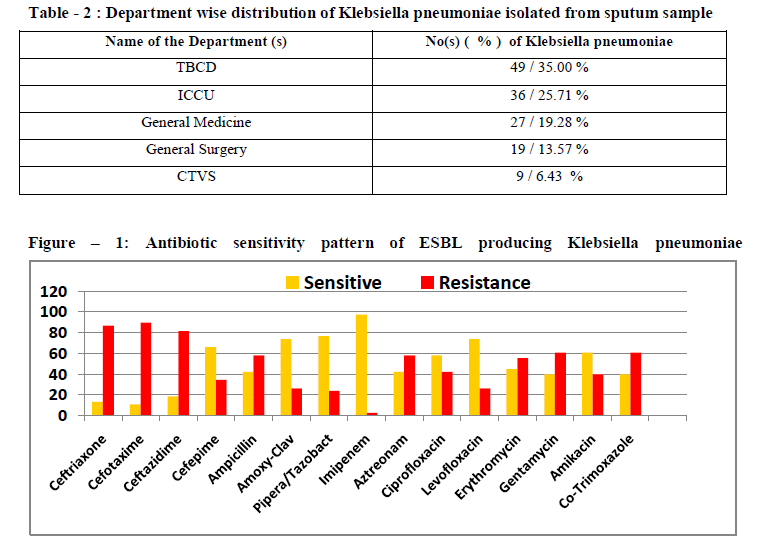
Most of the Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from respiratory samples were received from the TBCD department ( 49 / 35.00 % ) followed by ICCU (36 / 25.71 % ) , General Medicine (27 / 19.28 % ) , Surgery (19 / 13.57 % ) and lowest from CTVS department ( 9 / 6.43 % ) ( Table – 2 ) .
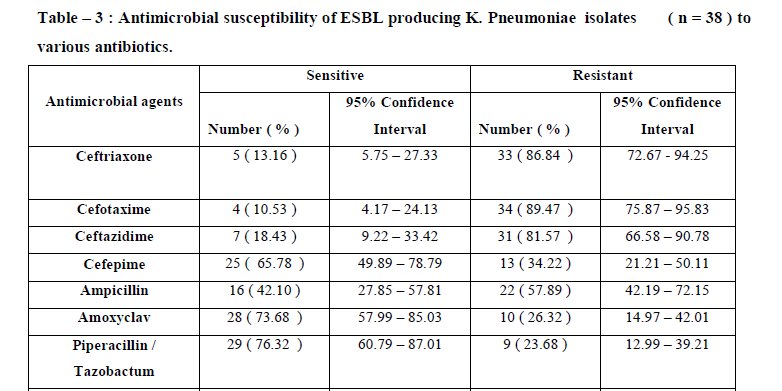
The results of antimicrobial susceptibility of ESBL producing strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae to various antibiotics tested in this study are shown in Figure - 1 and Table – 3 . 95 % confidence interval data are also presented. Imipenem was the most active antibiotics with 96.37% susceptibility rates . The next best were Piperacillin plus Tazobactum Amoxyclav, Levofloxacin and Cefepime. Apart from the high resistance to all 3rd generation cephalosporins, they were also resistant to common antibiotics like Ampicillin , Aztreonam , Gentamycin , Erythromycin and Co-trimoxazole .
DISCUSSION
The present study reveals that the ESBL producing strains of K. pneumoniae is highly prevalent
(27.14 %) in respiratory isolates from mostly hospitalized patients / IPDs which once again proves them to be an important cause of infection in hospitalized patients . The admitted patients were the majority in contributing the ESBL producing K. pneumoniae as seen in 25.72 % IPD versus 1.42 % OPD patients among overall K. pneumoniae isolates from respiratory samples. The high rate of ESBLs among hospitalized patients is a global problem. It is generally thought that patients infected by an ESBL producing strains are at increased risk of treatment failure.
The prevalence of ESBL producers varies across continents and countries and also within hospitals11,12 . In India, the prevalence rate varies in different institutions from 28 to 84% 13. In our study the prevalence of ESBL producing K. pneumoniae in respiratory isolates was 27.14 %. Subha et al. in the study of various clinical isolates in Chennai from South India, found ESBL
production in 25.8 percent isolates 14. A study on ESBL producing K. pneumoniae in Kashmir by S. Ahmed et al showed a 16.7% prevalence of the same in samples from respiratory tract infection 15. Hadi Mehrgan et al showed that ESBL production was more often seen in K. pneumoniae isolated from respiratory specimens 16 .
The male to female ratio of ESBL producing isolates was 1.7 : 1 which was supported by a study at Gulbarga by Renuka R. et al revealing slightly higher prevalence in males than among females 17.
Other than the 3rd generation cephalosporins, the ESBL producing strains of Klebsiella pneumonia showed higher resistance with commonly used antibiotics like Gentamycin (60.53%), Co-trimoxazole (60.53%) , Aztreonam (57.89 %) , Ampicillin (57.89 %) and Erythromycin (55.26 %) . They were highly sensitive to Imipenem (97.36 %) followed by Piperacillin + Tazobactum (76.32 %) , Amoxyclav (73.68 %) , Levofloxacin (73.68 %) and Cefepime (65.78 %) . Among all ESBL producing K. pneumoniae , 64 % was multidrug resistance showing resistance to more than four drugs . All these observation are in tandem with various study by R. Rampure et al 18 , M. M. Faizabadi et al 19 , S. Ahmed et al 15 and A. Singh Sikarwar et al 20 .
The indiscriminate use of higher groups of antibiotics and plasmid mediated drug resistance are the probable contributors to the emergence of multi drug resistance strains of ESBL producing strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae. It has been discovered that the mutant gene for ESBL production also contributes for resistance to other drugs.
CONCLUSIONS
Incidence of respiratory tract infection caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae is increasing worldwide and is a common cause of primary pneumonia affecting all age group which is further complicated by rapidly emerging strains of multi drug resistant ESBL producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. The inadvertent and indiscriminate use of 3rd generation cephalosporins and other antibiotics has lead to the emergence of multi drug resistant ESBL producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Regular monitoring on the judicious use of antibiotics helps in preserving the effectiveness of the sensitive antibiotics.
Our study aims to guide clinicians on starting empirical treatment and appropriate use of antibiotics which not only reduces the morbidity and mortality in the patients infected with ESBL producing Klebsiella pneumoniae but also controls the emergence of further resistance to the still sensitive drugs .


References:
- R.Sarathbabu, T.V.Ramani, K.Bhaskara rao, Supriya Panda; Antibiotic susceptibility pattern of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from sputum, urine and pus samples ; IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSRJPBS) ISSN : 2278-3008 Volume 1, Issue 2 (May-June 2012), PP 04-09
- P. Nordamann, G. Cuzon and T. Naas “ The real threat of Klebsiella pneumonia carbapenemase - producing bacteria” , Lancet Infec Dis.,2009,9 (4):228-236.
- Archana Singh Sikarwar and Harsh Vardhan Batra ; Prevalence of Antimicrobial Drug Resistance of Klebsiellapneumoniae in India ; International Journal of Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics, September 2011: Vol. 1, No. 3,
- S.J. Cryz, R. Furer and R. Germanier “Protection against fatal Klebsiella pneumonia burn wound sepsis by passive transfer of anticapsular polysaccharide”, Infect. Immun., 1985, 45: 139-142.
- Bradford PA.; Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in the 21st century: characterization, epidemiology, and detection of this important resistance threat ; Clin Microbiol Rev ; 2001; 14 (4): 933- 51.
- S.Young Soo, WHO, Western Pacific region, press release , 7 April , 2011.
- Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute; Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne; 2012; 22nd Informational Supplement : 32(3).
- Betty A. Forbes , Daniel F. Sahm , Alice S. Weissfeld ; Bailey and Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology ; 12th edition ; 2007 : p- 210 .
- d'Azevedo PA, Gonçalves AL, Musskopf MI, Ramos CG, Dias CA. Laboratory tests in the detection of extended spectrum beta-lactamase production: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS) screening test, the E-test, the double disk confirmatory test, and cefoxitin susceptibility testing. Braz J Infect Dis 2004; 8 (5): 372- 7.
- Collee JG, Fraser AG, Barry P Marmion, Simmons A.;Mackie and McCartney Practical Medical Microbiology ;14th Ed. Churchill Livingstone, London .1996 : 169
- 8. Babini GS, Livermore DM. Antimicrobial resistance amongst Klebsiella spp. collected from intensive care units in Southern and Western Europe in 1997-1998. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000;45:183–9. [PubMed: 10660500]
- Paterson DL, Bonomo RA. Extended-spectrum betalactamases: A clinical update. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18:657–86.[PMCID: PMC1265908] [PubMed: 16223952].
- Das A, Ray P, Garg R, Kaur B. Proceedings of the Silver Jubilee Conference. New Delhi: All India Institute of Medical Sciences; 2001. Extended spectrum beta-lactamase production in Gram negative bacterial isolates from cases of septicemia.
- Shubha S, Ananthan S 2002. Extended spectrum betalactamase (ESBL) mediated resistance to third genretion cephalosporins among Klebsiella pneumoniae in Chennai. Indian J Med Microbiology, 20: 92-95.
- Ahmad S. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Extended-spectrum β- Lactamase- producing klebsiella pneumoniae at a Microbiology Diagnostic Center in Kashmir. RMJ. 2009; 34(1): 68-71.
- Hadi Mehrgan , Mohammad Rahbar , Zohreh Arab-Halvaii ; High prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a tertiary care hospital in Tehran, Iran ; J Infect Dev Ctries 2010; 4(3):132-138.
- Renuka Rampure, Ravindranath Gangane, Ajay Kumar Oli , Kelmani Chandrakanth. R; Prevalence of MDR-ESBL producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from clinical Samples ; J. Microbiol. Biotech. Res., 2013, 3 (1):32-39.
- Reuka Rampure , Ravindranath Gangane, Ajay Kumar Oli , Kelmani Chandrakanth R.; Prevalence of MDR – ESBL producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from clinical samples ; J. Microbiolo. Biotech. Res.; 2013; 3 ( 1 ) : 32-39 .
- Mohammad Mehdi Feizabadi , Gelavizh Etemadi , Marveh Rehmati , Samira Mohammadi Yeganeh , Shiveh Shabanpur , Soroor Asadi ; Antibiotic resistance patterns and genetic analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from the respiratory tract; Tanaflos; 2007 ; 6 ( 3 ) : 20-25 .
- Archana Singh Sikarwar, Harsh Vardhan Batra; Prevalence of antimicrobial drug resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae in India; International Journal of Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics; Sept, 2011 : Vol. 1 , No. – 3.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License