Welcome to IJCRR
Indexed and Abstracted in: Crossref, CAS Abstracts, Publons, Google Scholar, Open J-Gate, ROAD, Indian Citation Index (ICI), ResearchGATE, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, WorldCat (World's largest network of library content and services)
CASE REPORT
Patient 1: An 81-year-old hypertensive woman with cerebral infarct leading to right sided hemiplegia was admitted to Medicine ICU. As per medical records she was a diabetic and hypertensive, not on any sort of immunosuppressive medication and was HIV seronegative. On admission the patient was catheterized immediately and put on intravenous ceftriaxone therapy and placed on mechanical ventilation. Her hospital course was subsequently complicated by upper respiratory infection with Acinetobacter baumannii, which was treated with ceftazidime followed by imipenem.
Patient 2: A 52-year-old woman having accidental insecticide poisoning was admitted to Medicine ICU. After four days of stay in the intensive care unit, her general condition was deteriorated and she had pyrexia of 102o F. Her blood parameters were as follows: Haemoglobin (Hb) 6.8 g/dL, Total leucocyte count (TLC) 12,840/mL (neutrophil 78%, lymphocyte 14%, monocyte 8% and eosinophil 0%). Serum urea 48 mg/dL, serum creatinine 2.1 mg/dL. Routine examination of urine, revealed pus cells in clumps and leucocyte esterase was positive. Her blood culture and urine culture was sent to Microbiology laboratory.
Patient 3: A 45-year-old man with a history of Noninsulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) was admitted to Trauma ICU following an accident. The patient was also catheterized on admission. On physical examination his general condition was found satisfactory but he had pyrexia of 1010F. His blood parameters were as follows: Hb 12.8g/dL, TLC 8700/mL (Neutrophil 54%, Lymphocyte 40%, Monocyte 02%, Eosinophil 04%). Serum urea 36 mg/dL, serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dL, Plasma Glucose level fasting was 230 mg/dl and serum electrolytes (Na+ 137 mmol/L and Cl 92 mmol/L).
Patient 4: A 73-year-old man with a history of NIDDM, hypertension, and ischemic heart disease was admitted to Medicine ICU in a comatose state following cerebellar hemorrhage and placed on mechanical ventilation along with IV fluids infusion and catheterization. On physical examination he was found to be severely ill, dyspnoeic at rest, anaemic and had pyrexia of 102o F. His haemoglobin was 7.2 gm/dL, leucocyte count 9800/mL, platelets 41000/mL. The patient’s
blood culture was sent and serological tests for Dengue were done which was negative.
As a routine, on 7th day of ICU stay all those three (no.1, 3 and 4) patients’ urine sample was sent for routine microscopical examination and culture andsensitivity tests. The 2nd patient’s urne sample was sent to Microbiology laboratory on 4th day of ICU stay for the same tests. Under microscopical examination all the 4 patients’ urine sample showed plenty of pus cells and budding yeast like cells. Hence, urine samples were inoculated on blood agar, MacConkey’s agar, Sabouraud’s dextrose agar (SDA) with chloramphenicol and cycloheximide and Hi chrome Candida agar and the plates were incubated at 370 C. Another SDA plate was incubated at 220 C also.
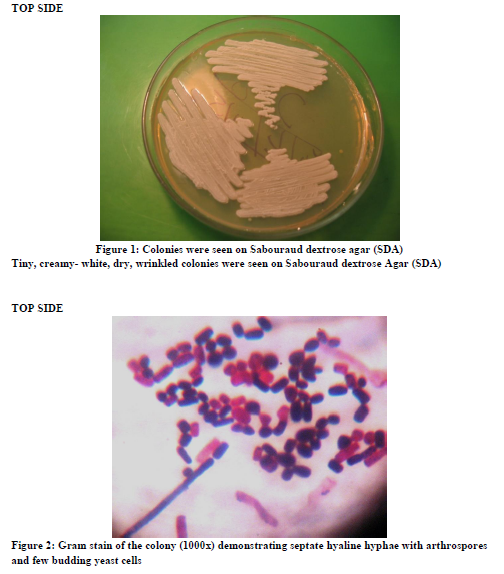
After overnight incubation, on Blood agar, tiny creamy white colonies were observed and on MacConkey’s agar there was no growth. On SDA plates (at 220C and 370C) tiny creamy white, wrinkled yeast like colonies were grown [Figure-1]. On 5th day deep furrow was observed in the colonies grown on SDA plates. On chrome agar dry wrinkled colonies which were light blue in colour was observed. Gram’s staining of the colony grown on all the plates were done which revealed Gram positive budding yeast cells with septate hyphae and arthrospores [Figure 2]. The diagnosis of Trichosporon sp was established by demonstration of yeast forms in the microscopical examination of urine and budding yeast cells and arthroconidia in the cultures.
The species identification of Trichosporon asahii was based upon verification of its salient diagnostic morphological and physiological characteristics, employing the standard techniques [12]. Slide culture on 2% malt agar showed budding yeast like cells and true hyphae forming abundant rectangular arthroconidia. The isolates were also tested for (i) resistance to 0.1% cycloheximide, (ii) growth at 37oC, and 45oC on SDA. (iii) Diazonium blue B colour reaction (iv) urease activity on Christensen’s urea medium, (v) carbohydrate and nitrogen assimilation profiles as determined by the Vitek 2 (BioMerieux, France) yeast identification system [13].
The VITEK ID-YST card consists of 64 wells with 47 fluorescent biochemical tests. They comprise 20 carbohydrate assimilation tests: adonitol (ribitol), D-trehalose, D-cellobiose, dulcitol, D-galactose, D-glucose, lactose, D-maltose, D-mannitol, D-melibiose, D-melezitose, palatinose, D-raffinose, L-rhamnose, sucrose, salicine, L-sorbose, D-sorbitol, D-L-lactate, and succinate. The six organic acid assimilation tests are N-acetyl-glucosamine, methyl- a-D-glucopyranoside, citrate, D-galacturonate, D-gluconate, and mono-methylester- succinate. The eight substrates for the detection of the oxidases are coupled with 4-methylumbelliferone (4MU).
The isolates were grown in presence of 0.1% cyloheximide, hydrolysed urea, Diazonium blue B reaction positive and grown at 370 C but not at 450C (2). Slide culture on 50% glucose peptone agar showed thick walled structure resembling chlamydoconidia.
Trichosporon species differ from Candida species in several respects that they do not produce a germ tube, as does Candida albicans; they can form both hyaline septate hyphae as well as pseudohyphae; and they produce arthroconidia [14]. It is very important that Trichosporon and Geotrichum species both can produce arthroconidia. But Trichosporon sp. differ from Geotrichum sp. that Trichosporon sp. can hydrolyse urea but Geotrichum sp. cannot [15].
Two more consecutive urine samples of the patients were obtained and analyzed. Isolation of Trichosporon asahii in these two consecutive urine samples with a significant number of pus cells (15-20/HPF) and absence of any bacteria isolated established Trichosporon asahii as an etiological agent of UTI in these patients. All the 4 patients’ blood culture was sterile. Out of these 4 patients, 3 patients recovered after antifungal treatment.
DISCUSSION
The source of superficial and deep-seated Trichosporon infections is still the subject of considerable debate. The mode of transmission increase in profoundly immunocompromized patients. Trichosporon spp. is one of the emerging mycoses, and Urinary tract infections by Trichosporon asahii may also occur, especially in patients with urinary tract obstruction or those undergoing catheterization and on prolonged antibiotic therapy. These infections represent a challenge for clinicians, as there are no clear and specific indications for the clinical interpretation of Trichosporon spp. Recovery in urine, although unusual, renal damage and aggravation of renal dysfunction may occur [16]. To the best of our knowledge this is the first report from India implicating Trichosporon asahii as an agent of urinary tract infection in catheterized patient. Isolation of the same yeast in three consecutive urine samples and the fact that no bacteria was isolated, establishes Trichosporon asahii as an etiological agent of urinary tract infection in those patients. The fact that there was clearance of organisms from the urinary tract with recovery of three patients following antifungal treatment strongly associates the fungi as a cause of UTI.
Factors that enhance mucosal colonization and subsequent invasion of Trichosporon spp. include morphological switching, the ability to adhere to abiotic surfaces by biofilm formation around the catheter, thermotolerance, the expression of cell wall components, enzyme production and broad spectrum antibiotic treatment, breaks in mucosal barriers etc. [17]. All the 4 patients exhibited risk factors such as low immune status, presence of indwelling catheter and prolonged use of broad spectrum antibiotics etc.
Trichosporon spp. are occasionally a part of normal flora of human skin. In fact this yeast has been documented on intact perigenital skin in 12.4% of the population in one study [18]. Therefore, it is possible that the organism colonized the catheter from the human flora during catheterization and subsequently progressed towards invasive trichosporonosis. Nosocomial urinary tract infection due to Trichosporon asahii has been reported from Chile also [19].
Trichosporonosis is usually an insidious disease but it can present as an acute opportunistic infection in susceptible persons. Clinicians, therefore, need to have an increased awareness of this organism and to note that trichosporonosis may appear similar to disseminated candidiasis both in its clinical and histopathologic appearance and in the type of patient infected. Treatment at this time appears to be less effective, and the mortality rate is high. Its diagnosis is likely to be missed particularly in developing countries, because of a general lack of awareness and lack of acquaintance with the salient diagnostic features of the etiological agent.
CONCLUSION
We hereby conclude, that as a Clinical Microbiologists we must be aware that Trichosporon asahii is an emerging pathogen to cause Nosocomial or Health Care Associated Infection (HAI) which is difficult to treat and can only be detected if specific tests are done to differentiate it from Candida species.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are thankful to The Director of Anandalok Sonoscan center Pvt. Ltd. Siliguri, West Bengal, for allowing them to use Vitek2 compact system for this work.
References:
Indexed and Abstracted in






Antiplagiarism Policy: IJCRR strongly condemn and discourage practice of plagiarism. All received manuscripts have to pass through "Plagiarism Detection Software" test before forwarding for peer review. We consider "Plagiarism is a crime"
IJCRR Code of Conduct: To achieve a high standard of publication, we adopt Good Publishing Practices (updated in 2022) which are inspired by guidelines provided by Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE), Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association (OASPA) and International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE)
Disclaimer: International Journal of Current Research and Review (IJCRR) provides platform for researchers to publish and discuss their original research and review work. IJCRR can not be held responsible for views, opinions and written statements of researchers published in this journal.
International Journal of Current Research and Review (IJCRR) provides platform for researchers to publish and discuss their original research and review work. IJCRR can not be held responsible for views, opinions and written statements of researchers published in this journal
148, IMSR Building, Ayurvedic Layout,
Near NIT Complex, Sakkardara,
Nagpur-24, Maharashtra State, India
editor@ijcrr.com
editor.ijcrr@gmail.com
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
Copyright © 2026 IJCRR. Specialized online journals by ubijournal