IJCRR - 5(20), October, 2013
Pages: 41-46
Date of Publication: 02-Nov-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS AS AN INITIAL PRESENTATION OF TYPE-1 DIABETIC CHILDREN IN ASEER REGION OF SAUDI ARABIA
Author: Mohammad A. Al Qahtani, Ayed A. Shati, Ali M. Alsuheel, Fuad I. Abbag
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: This study aimed to determine the frequency of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) as initial presentation among patients with type-1 Diabetes Mellitus (DM-1) following in Aseer Diabetes Center of Aseer Region, Southwestern of Saudi Arabia. Patients and Methods: Retrospectively we reviewed and analyzed medical records of type-1 DM children who were less than 15 years and diagnosed with DKA at initial presentation, over period of 7 years from February 2006 till January 2013. Results: Out of 508 diabetic patients, 244 (48%) patients had DKA at the initial presentation. The mean age was 8.5 years. 120 (49.1%) with DKA were males and 124 (50.9%) females. Six patients with type-1 DM were less than one year and 5 (83.3%) of them were in DKA, compared with the 239 patients (47.6%) of the remaining 502 patients beyond this age. Generally, frequency of DKA among patients from (1-5) year was 51.7% (N=176) and more than 5 years was 46.9% (N=153). No death, renal failure or permanent neurological damage was reported at the initial presentation. Conclusion: A significantly high percentage of children with newly diagnosed DM-1 still have DKA at the onset of DM. This calls for health education and awareness of the parents / public and primary health care physicians through continuous medical education and mass media to achieve early diagnosis of type-1 DM before the development of DKA.
Keywords: Type-1 DM, Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), Cerebral edema, Autoimmune, Beta-cells.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Worldwide, diabetes mellitus (DM) is currently a major health problem. Type-1 DM is the most common type of diabetes in children and may present initially as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Patients with type-1 DM are more susceptible to develop DKA than those with type-2 DM. DKA is a metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia, acidosis and ketosis which occur in the presence of low levels of circulating insulin. The underlying cause of type-1 DM is insulinopenia (low or absolute zero levels of insulin) due to either autoimmune destruction of pancreatic B-cells or idiopathic1,4. This type of diabetes and its association with DKA carries high rate of morbidity, mortality and health cost5,6. WHO DIAMOND project group and other studies have clearly mentioned that type-1 DM or insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) is the most prevalent and common chronic childhood disease in industrialized countries7,8. DKA as initial presentation in type-1 DM has been reported worldwide with varying prevalence as high as 67% and also up to 80% have been reported9,12. High rate of DKA, morbidity, and complications are due to the fact that most of the families are unaware of the symptoms of DKA. Parents and public awareness of these symptoms will lead to timely diagnosis of DM and prevention of DKA which is considered as acute complication of DM-1. The classic symptoms at initial presentation of type-1 DM are usually gradual, and include polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia and weight loss. The symptoms of DKA may be mild starting with vomiting, polyuria and dehydration symptoms. DKA in severe cases may present with abdominal pain mimicking acute appendicitis or pancreatitis and sometimes presents with rapid breathing and Kaussmaul’s breathing followed by obtundation of consciousness and ultimately coma. In Saudi Arabia, families with inadequate knowledge about diabetes, especially in pediatric age groups, fail to recognize symptoms of DM. Hence, their children may persist to suffer from the disease and fail to seek medical advice until they present with DKA. Furthermore the primary health care providers may miss these symptoms especially in the presence of common acute infections such as URTI, GE or UTI. This is alarming as DKA carries high risk and complications if not timely diagnosed13,15. There are few studies from Saudi Arabia (Northwest and Madina Regions) and also Gulf Region for DKA at initial presentation16,19. However, there are no large scale studies at tertiary care diabetes center from Aseer Region of Saudi Arabia. So, we aimed from this study is to review the patients in Aseer Region who presented with DKA as an initial presentation of type-1 DM.
METHODS
This is a retrospective analytical study done in Aseer Diabetes Center of Aseer Central Hospital which is the largest tertiary care diabetes center in Aseer Region (Southwestern) of Saudi Arabia. Diabetic patients from all primary health care centers (PHCCs) are usually referred to Aseer Diabetes Center (ADC) for follow up after initial diagnosis. ADC has catchment area of 20 secondary care hospitals and 285 primary health care centers. ADC is equipped with all modern health care facilities.
In this 7 year study, retrospectively we reviewed and analyzed the records of diabetic patients seen regularly in Aseer Diabetes Center, from February 2006 till January 2013. The study was approved by the hospital research committee.
Only type-1 DM children (aged <15 years) were included in the study. Patients who were considered to have DKA if they had a random blood sugar (RBS) greater than 300 mg/dl, pH less than 7.3, bicarbonate less than 15, glucosuria and ketonuria20,22 or if the patient had medical report from referring hospital documented with DKA as initial presentation (according to the above mentioned criteria). Patients with incomplete data for DKA were excluded from the study. Patients’ data were categorized for DKA presentation as less than 1 year, 1-5 years and more than 5 years of age.
RESULTS
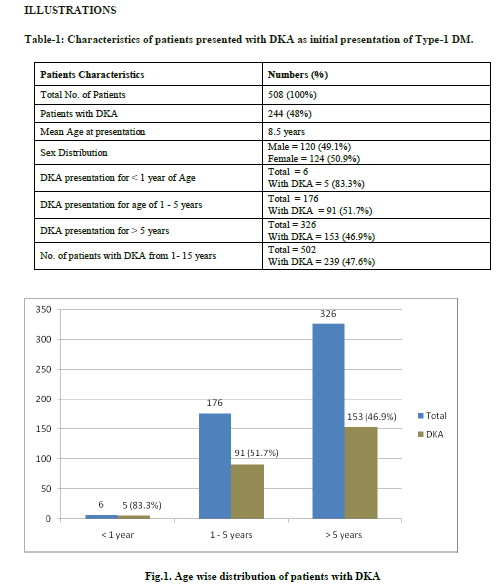
The medical records of 508 patients with type-1 DM were reviewed. Of these 508 patients, 244 patients (48%) had DKA at initial presentation of illness while 264 patients did not present with DKA. Out of 244 patients, 120 patients (49.1 %) were males. The mean age was 8.5 years. In the patients with DKA, those who are less than one year have higher chance to present with DKA comparing with other age groups, 5 patients of 6 patients (83.3%) in comparison with 239 patients (47.6%) beyond that age. The frequency of DKA in children 1-5 years of age is 51.7% (91 out of 176) compared with 46.9% (153 out of 326) in older children as demonstrated in table 1 and figure 1. There was no mortality, permanent neurological or renal damage.
DISCUSSION
Type 1 DM represents about 5% of all types of DM22. The frequency of DKA at onset of diabetes varies by geographic location9,12,16,19. In well-developed countries such as the United States, around 25% of type-1 DM will first present in DKA23. By reviewing the other international studies, we found that it ranges between 16-80%24,28.
In our study, we found that 48% of our patients presented initially in DKA which is considered relatively high and may reflect a delay in diagnosing DM. This figure is similar to a previously reported figure (55%) from other region of Saudi Arabia16, 17, and from Kuwait which was 49%19. Although this percentage is alarming, none of our patients with DKA developed permanent neurological damage, renal failure or mortality. However, it is known that a delay in the diagnosis of DKA may result in cerebral edema with its complications such as renal failure, hypokalemia or hypekalemia, arrhythmias and/or other electrolyte abnormalities. It will also necessitate admission to the pediatric intensive care unit and prolong the hospital stay. The younger the child at the onset of DM, the higher the chance of having DKA at initial presentation; this may be explained by the fact that infants have non-specific symptoms such as excessive crying, irritability and excessive diaper changes29,30, which may be interpreted as being secondary to infections, particularly urinary tract infection. Furthermore, dehydration and acidosis develop quickly in young children which may explain the high frequency of DKA30.
In our data, there were 6 patients with age less than 1 year and 5 of them (83.3%) developed DKA. The remaining one patient did not develop DKA and was diagnosed early because the family was already aware about the symptoms of DM and the patient’s brother was previously diagnosed as type 1 DM.
Although inadequate knowledge of DM among the family members play a role in delaying the diagnosis which leads to high frequency of DKA at onset. Other factors should be considered for example, symptoms of DM may be overlooked by the primary care physician as well. The presentation with symptoms and signs of coexisting common childhood infections like gastroenteritis, otitis media, flu-like illness, respiratory infections and urinary tract infections may mask the DM symptoms leading to a delay in the diagnosis of type-1 DM or DKA31. In such cases, diagnosis of type-1 DM can be judged simply by the lower serum C-peptide level in infants suggesting a more aggressive beta-cell destruction26.
Although DKA related mortality used to be high over 50 years ago, it has decreased significantly over the last few decades6. The reported mortality rate in Ontario (Canada) was 0.18% for all DKA admissions32, in comparison with 0.31% in UK13. In our study, no mortality was encountered which is in correlation with other reports from the gulf region19 and from the West11. This should not be overestimated as these rates reflect mortality for DKA admissions, and do not include DKA mortality outside the hospital; this consideration is particularly important in developing countries where DKA mortalities outside the hospital are undiagnosed. Diabetic children are missed and might be attributed to common infections like enteritis, viral influenza or encephalitis. The leading cause of mortality is cerebral edema accounting for 57-87% of DKA deaths13. The mortality from cerebral edema might be diminished by early diagnosis and management.
The relatively high frequency of DKA at initial presentation necessitates further studies to uncover other possible causes. Since the incidence of DM in general is increasing worldwide, we should emphasize the need for more public health education programs using the media and schools, beside evaluation of the children health care system; interventional measures like refreshing courses, workshops and training of medical and paramedical staff in the primary health care units are highly needed33, 34. Physicians should be aware of high index of suspicion of type-1 DM symptoms especially in infants.
CONCLUSION
Among type-1 DM patients from above study and data were obtained, DKA carries a high risk of morbidity and mortality. As type-1 DM represents lower percentage than type-2 DM which could lead to late diagnosis among junior doctors and parents. In particular, the early detection of symptoms of type-1 DM by parents / public and health care physicians is required at primary care levels to reduce hospital admissions, complications and the cost of health care, especially in young age group. The awareness and education of public and general practitioners are still highly recommended through continuous medical education and mass media to decrease the occurrence of DKA in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetic children.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The Authors of this study would like to thank Dr. Kamran Mahmood Ahmed, Diabetologist at Aseer Diabetes Center, for his valuable advises and suggestions for the improvement of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References:
- Nerup J, Andersen OO, Bendixen G, Egeberg J, Gunnarsson R, Kromann H, et al. Cell - mediated immunity in diabetes mellitus. Proc R Soc Med 1974; 67: 506 – 513.
- Schranz DB, Lernmark A. Immunology in diabetes: an update. Diabetes Metab Rev 1998; 14: 3 – 29.
- Bottazzo GF, Dean BM, McNally JM, MacKay EH, Swift PG, Gamble DR. In situ characterization of autoimmune phenomena and expression of HLA molecules in the pancreas in diabetic insulitis. N Engl J Med 1985; 313: 353 – 360.
- Knip M, Siljander H. Autoimmune mechanisms in type 1 diabetes. Autoimmun Rev 2008; 7: 550 – 557.
- Edge JA, Ford-Adams ME, Dunger DB. Causes of death in children with insulin dependent diabetes 1990–96. Arch Dis Child 1999; 81:318–396.
- Scibilia J, Finegold D, Dorman J, Becker D, Drash A. Why do children with diabetes die? Acta Endocrinol 1986; 279 (Suppl):326–333.
- WHO Multinational Project for Childhood Diabetes. WHO DIAMOND Project Group. Diabetes Care 1990; 13:1062-1068.
- LaPorte, RE, Cruickshanks KJ. Incidence and risk factors for insulin-dependent diabetes. In Diabetes in America. Washington, DC, Dept. of Health and Human Services, 1985 (NIH publ. no. 85-1468)
- Usher-Smith JA, Thompson M, Ercole A, Walter FM. Variation between countries in the frequency of diabetic ketoacidosis at first presentation of type 1 diabetes in children: a systematic review. Diabetologia 2012; 55:2878–2894.
- Mbugua PK, Otieno CF, Kayima JK, Amayo AA, McLigeyo SO. Diabetic ketoacidosis: clinical presentation and precipitating factors at Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi. East Afr Med J. 2005; 82 (12 Suppl): S191-6.
- Neu A, Willasch A, Ehehalt S, Hub R, Ranke MB. DIARY Group Baden-Wuerttemberg. Ketoacidosis at onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children – frequency and clinical presentation. Pediatr Diabetes 2003; 4(2): 77-81.
- Levy-Marchal C, Patterson CC, Green A. Geographical variation of presentation at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in children: the EURODIAB study. European and Diabetes. Diabetologia 2001; 44 Suppl 3: B75-80.
- Dunger DB, Sperling MA Acerini CL, Bohn DJ, Daneman D, Danne TP, et al. ESPE/WPES Consensus statement on diabetic ketoacidosis in children and adolescent. Arch Dis Child 2004; 89:188-194.
- Scibslin J, Finegold D, Dotman J, et al. Why do children with diabetes die?. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (copenh) 1986; 279: 326-333.
- White NH. Diabetic ketoacidosis in children. Endocrinol Metab Clinic North Am 2000; 29 (4): 657-682.
- Habib HS. Frequency and clinical characteristics of Ketoacidosis at onset of childhood diabetes mellitus in Northwest Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J 2005; 26(12): 1936-1939.
- Al Magamsi MS, Habib HS. Clinical presentation of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus in the Al-Madina region of Saudi Arabia. Pedatr Diabetes 2004; 5(2): 95-98.
- Abdul-Rasoul M, Al-Mahdi M, Al-Qattan H et al. Ketoacidosis at presentation of type 1 diabetes in children in Kuwait: frequency and clinical characteristics. Pediatr Diabetes 2010; 11:351–356.
- Al Khawari M, Shaltout A, Qabazard M et al. Incidence and severity of ketoacidosis in childhood-onset diabetes in Kuwait. Kuwait Diabetes Study Group. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1997; 35:123–128
- Wolfsdorf J, Craig M, Daneman D et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2009 Compendium: diabetic ketoacidosis in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2009; 10:118–133.
- Sperling M. Diabetes Mellitus. In: Pediatric endocrinology. Saunders; 2002. p 323-66.
- Norris AW and Wolfsdorf. Diabetes mellitus. In: Brook’s Clinical Pediatric Endocrinology. Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2005. p.436-473.
- Clinical Practice Guidelines Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Children and Adolescents 2005; by the Australasian Pediatric Endocrine Group for the Department of Health and Aging; p. 102-104.
- Pinkey JH, Bingley PJ, Sawtell PA, Dunger DB, Gale EA. Presentation and progress of childhood diabetes mellitus: a prospective population based study. The Barts-Oxford Study Group. Diabetologia 1994; 37(1): 70-74.
- Smith CP, Firth D, Bennett S, Howard C, Chisholm P. Ketoacidosis occurring in newly diagnosed and established diabetic children. Acta Paediatr 1998; 87(5): 537–541.
- Komulainen J, Lounamaa R, Knip M, Kaprio EA, Akerblom HK, et al. Ketoacidosis at the diagnosis of type1 (insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus is related to poor residual beta cell function. Arch Dis Child 1996; 75(5): 410–415.
- Rodacki M, Pereira JR, Nabuco de Oliveira AM, Barone B, Mac Dowell R, Perricelli P, et al. Ethnicity and young age influence the frequency of diabetic ketoacidosis at the onset of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res Pract 2007; 78(2): 259-262
- Quinn M, Fleischman A, Rosner B, Nigrin DJ, Wolfsdorf JI. Characteristics at diagnosis of type 1diabetes in children younger than 6 years. J Pediatr 2006; 148 (3):366-371.
- Hekkala A, Knip M, Veijolia R. Ketoacidosis at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in children in Northen Finland. Diabetes Care 2007; 30 (4): 861-866.
- Alqahtani MA, ElAwwad ME. Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus associated with other anomalies: experience from the Southern Region of Saudi Arabia. Pediatric ME 2008; 13(2): 32-37.
- Bui H, To T, Stein R, Fung K, Daneman D. Is diabetic ketoacidosis at disease onset a result of missed diagnosis? J Pediatr 2010; 156:472–477
- Curtis JR, To T, Muirhead S, Cummings E, Daneman D. Recent trends in hospitalization for diabetic ketoacidosis in Ontario children. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 1591-1596.
- Vanelli M, Chiari G, Ghizzoni L, Costi G, Giacalone T, Chiarelli F. Effectiveness of a prevention program for diabetic ketoacidosis in children. An 8 year study in schools and private practices. Diabetes Care 1999; 22:7–9
- Vanelli M, Chiari G, Lacava S, Iovane B. Campaign for diabetic ketoacidosis prevention still effective 8 years later. Diabetes Care 2007; 30:e12
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License