IJCRR - 7(10), May, 2015
Pages: 79-86
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
DIAGNOSTIC CHALLENGES IN ASSESSMENT OF REACTIVE SOFT TISSUE LESIONS OF ORAL CAVITY
Author: Farhat Kazmi, Wajiha Alamgir, Muhammad Mumtaz
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Objective: The study emphasizes on the features which lead to diagnostic complexities of localized reactive hyperplastic lesions (LRHL) in clinical settings thus making histolopathological examination imperative for definite diagnosis. Materials and Methods: A total of 314patients presenting with reactive hyperplastic lesions in out-patient department of University College of Dentistry from June 2012 to January 2015 were included in the study. After provisional diagnosis, lesions were excised and specimens were submitted for definite histopathological diagnosis. Descriptive statistics and Chi-square test was applied using SPSS version 20.0. Results: Most common age group was 30-39 years (n=147, 50.6%) with male to female ratio of 1:3. Most affected site was maxillary gingivae (n=140, 49.3%) while poor oral hygiene (n=152, 52.4%) was most frequent aetiological factor. Provisional diagnoses included pyogenic granuloma (PG) with maximum number of cases (n=141, 45%) followed by focal fibrous hyperplasia(FFH) (n=118, 37%), peripheral giant cell granuloma(PGCG) (n= 34, 11%) and peripheral ossifying fibroma (POF) (n=21, 7%). After definite diagnosis, the order of occurrence of LRHL remained the same but the number of cases of each individual lesion carried a significant discrepancy with 157 histopathologically proven cases of PG (50%) followed by FFH (n=111, 36%), PGCG (n=29, 9%) and POF (n=17, 5%) respectively. Conclusion: Variations in subjective assessment of LRHL could be lessened if histopathological examination is incorporated as a mandatory component in diagnostic protocol. Oral hygiene maintenance may also significantly improve the status of oral health
and diminish possible chances of development of pathologies.
Keywords: Hyperplastic lesions, Pyogenic granuloma, Focal fibrous hyperplasia, Peripheral giant cell granuloma, Peripheral ossifying fibroma
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
A collection of reactive hyperplastic lesions presenting as gingival and mucosal localized overgrowths pose a diagnostic tight spot to clinician due to closeimitationin their clinical appearance. In such circumstances, histopathologists provide an aid to clinicians to rule out the possibility of these lesions being malignant in nature and therefore establishing a definite diagnosis.1,2 Chronic trauma subjected to oral cavity can induce inflammation that leads to formation of granulation tissue along with endothelial cells, chronic inflammatory cells and later fibroblasts which proliferate and manifest as an overgrowth called ‘Reactive hyperplasia’3 . Localized factors which can lead to chronic local traumatisation include; calculus, food impaction, restorations with irregular margins and iatrogenic factors 4 . Underlying systemic disease, drug-induced stimulus or endocrine hormonesmay also play a contributing role in development of LRHL 5,6,7. Several investigators have classified reactive lesions on histopathological basis as fibrous, vascular or hemorrhagic and giant cell types1,2,7-9. Some others claim that all these entities represent same lesion at different developmental stages4,5,7. Currently, accepted classification of reactive lesions is given by Neville pertaining to four categories: 1. Focal fibrous hyperplasia (FFH) 2. Pyogenic granuloma (PG) 3. Peripheral ossifying fibroma (POF) 4. Peripheral giant cell granuloma (PGCG) 4,5,7,10. The prevalence of these lesions as reported in the literature is rather most common with focal fibrous hyperplasia comprising 56-61% followed by pyogenic granuloma (19-27%), peripheral ossifying fibroma (10-18%) and peripheral giant cell granuloma (1.5 – 7%) 10-12. These LRHL share many similarities on clinical examination that makes physician indecisive in making a definite clinical diagnosis. Table 1 elaborates intimately mimicking clinical features of LRHL of the gingiva.13-16 FFH represents the most common localized, reactive proliferation of oral soft tissues in response to injury or local irritation 13,14 followed by PG representing as an exuberant tissue response 10,13. Researchers have divided PG in two types namely lobular capillary hemangioma (LCH type) and non – LCH type which differ in their histological picture 17. LCH type is currently categorized as vascular tumors under the classification scheme of international society for the study of vascular anomalies 13. Among pregnant females, 5% develop PG which regress after delivery, indicating a definite role of female sex hormones in the etiology of this lesion 2,17,18. POF has mostly solitary occurrence, multicentric lesions have also been reported in the literature18.Current studies refer this le Current studies refer this lesion as POF (WHO type) and it is recognized separately from POF of gingiva 7,10. In 1953, Jaffe proposed the term “giant cell reparative granuloma” to distinguish PGCG from giant cell tumor 20. This term was used to show the association of development of this lesion to chronic irritation 21.Development of POF and PGCG in children has also been reported in the literature 19,22. In present study, emphasis is made on the features which lead to diagnostic complexities of LRHL in clinical settings thus making histolopathological examination imperative for definite diagnosis. Moreover, focus is made on the etiological factors involved in the development of these lesions especially those which are related to oral hygiene status of the patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study was conducted in Oral Diagnostic, Oral pathology and Oral Surgery department of University College of Dentistry, University of Lahore, Pakistan between June 2012 to March 2014 after approval from the ethical review committee (Approval No. 101/UCD/2012). A total of 314 patients presenting with exophytic hyperplastic lesions were examined in Oral Diagnostic department. Clinical data including age, gender, chief complaint at the time of presentation, etiology, site and size of the lesion, lesion attachment, surface and color was gathered and provisional diagnosis was made after clinical examination. Further referral was made to Oral Surgery department and biopsy was taken after making written informed consent from the patients. Biopsy specimens were submitted to Oral Pathology department. Microscopic evaluation for definite diagnosis was done by two oral pathologists to minimize the inter-observer bias.
Statistical analysis was done using SPSS software version 20.0. Descriptive statistics were employed to report the findings. Chi-square test was applied for evaluation of differences in frequencies among groups. P- value<0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
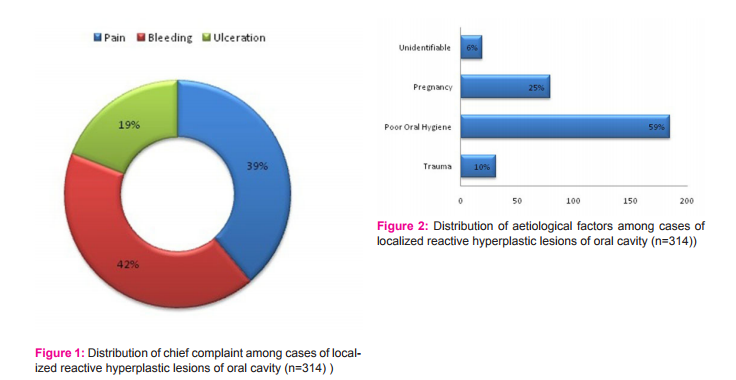
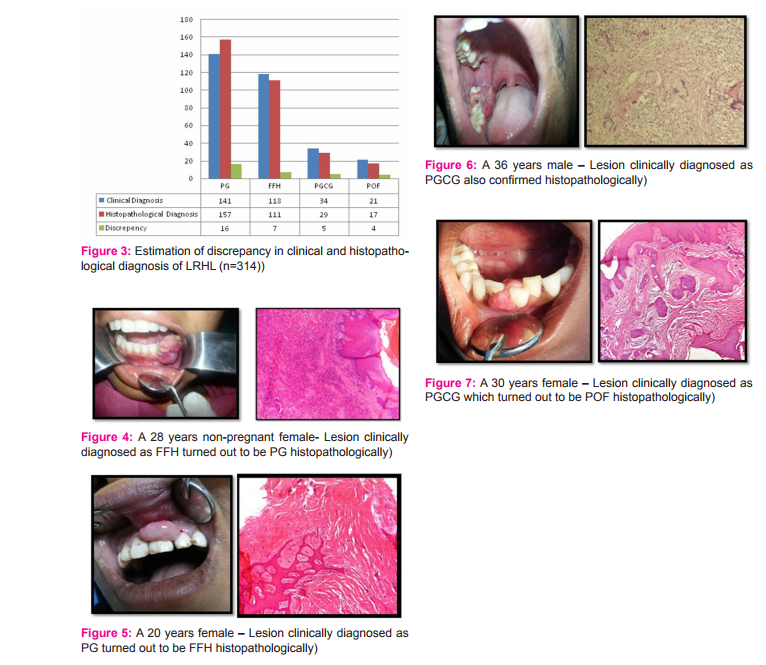
After clinical examination of 314 patients presenting with LRHL, provisional diagnoses made included (Figure: 1) pyogenic granuloma with maximum number of (n=141, 45%) followed by focal fibrous hyperplasia which comprised of 118 cases (37%). Peripheral giant cell granuloma with 34 cases (11%) and peripheral ossifying fibroma with 21 cases (7%) were next in the order. The diagnosis was based upon parameters mentioned in the previous section. Among socio- demographic parameters, most common age group was 30-39 years comprising of 157 cases (50%) followed by 20-29 years age group that counted 125 cases (40%)(p=0.000)(Table:2). Females were most commonly affected than males with a count of 241 (77%) yielding a male to female ratio of 1:3 (p=0.000)(Table 2). Most frequently involved site was maxillary gingiva with 155 cases (49%) followed by mandibular gingiva (n=142, 46%) (p=0.000). Majority of the patients presented with the chief complaint of bleeding (n= 132, 39%, p=0.000) followed by pain (n=122, 39%, p=0.000) and ulceration (n=60, 19%, p=0.000) (Figure: 1). Greater part of the lesions measured <1cm in size (n=260, 83%)(p=0.193) with majority having sessile base (n=224, 71%)(p=0.155). The most common surface appearance (p=0.000) of the lesions was smooth constituting 193 cases (61%) followed by ulcerated surface with 89 cases (28%) (Table 3). Large proportion of lesions were red in color comprising of 197 cases (62%) (p=0.000)(Table: 3). Evaluating the etiology of the lesion, (Figure:2)the greatest number of lesions was associated with poor oral hygiene with 185 cases (59%) while in small proportion of the cases aetiology could not be identified (n=19, 6%)(p=0.000). Detailed description of data recorded for each individual lesion is shown in Table: 2 and Table: 3. After excisional biopsy and histopathological review of cases of LRHL, a discrepancy rate of 10% (n=32) was observed between provisional diagnosis based on clinical examination and definite diagnosis which was made after microscopic examination. (Figure: 3). After definite diagnosis, the order of occurrence of LRHL remained the same but the number of cases of each individual lesion carried a significant difference with 157 histopathologically proven cases of PG (50%) followed by FFH (n=111, 36%), PGCG (n=29, 9%) and POF (n=17, 5%) respectively (Figure: 4 – Figure: 7)
DISCUSSION
An extensive research of the literature revealed that present study is the first attempt to document shortcomings of clinical evaluation and diagnosis of LRHL of oral cavity. Considerable discrepancy exists between visual assessment and histopathological appraisal of these lesions. Therefore, overlap in clinical appearance of these lesions led to subjective interpretation of histological specimens and their clinical correlation which led to contradictory results. Furthermore, the investigation also focuses on the frequency of different etiological factors associated with development of LRHL of oral cavity. Patients in of Oral Diagnostic department were provisionally diagnosed for different types of LRHL of oral cavity. The clinical information was based upon patient’s demographics such as age, gender, chief presenting complaint and etiological factors as well as diagnostic inspection points; location, size, surface, color and attachment base of the lesion. Out of total 314 lesions, most prevalent lesion figured out was PG (45%) followed by FFH (37%), PGCG (11%) and POF (7%) respectively. These results were in agreement to those demonstrated by Shahsavari et al as well as to some other studies which showed PG as most commonly occurring entity 2,7,23. On contrary, many of the global studies showed FFH as the most commonly found lesion as well as cases of POF exceeding to those of PGCG 3-5. Striking difference in the results was reported by Naderi et al demonstrating PGCG as most frequently found lesion 1-7, 20-24. Females turned out to be more affected than males with a male to female ratio of 1:3. This finding was concurrent with most of the studies conducted worldwide 1-5, 7, 23. Conversely, distribution of oral reactive lesions shown by Naderi et al in males outnumbered to that of in females with male to female ratio of 1.4:124. In current study, a conspicuous finding is the involvement of only females in cases of PG with no male patient affected by this entity. This finding was in accordance to majority of the studies conducted worldwide but all of them showing considerable involvement of males as well 2-7. On the other hand, in an Iranian study, Aghbali et al showed equal involvement of both genders among cases of PG25. In present study, 30-39 years age group was most commonly affected among all lesions(n=157, 50%). This result was exactly in concordance with that shown by Ramu and Rodrigues who also demonstrated the greatest prevalence of reactive lesions in thesame age group5 . Many other studies depicted the same finding in terms of mean age7,24,25. However, Shahsavari et al reported 4th to 6th decade as more prevalent age group in patients with reactive softtissue lesions of oral cavity9 . The difference in the results may be attributed to ethnic or demographic factors as well as differences in lifestyle and oral hygiene awareness among different populations. In current study, most frequent site of involvement was maxillary gingiva with 155 cases(49%). The finding was in agreement to many other studies showing the similar site predominance 2,4,25. However, Ramu andRodreigus5 as well as Zarei et al 6 showed a mandibular preponderance in their results. In present study, cases of PG were most commonly found involving maxillarygingiva (n=75, 53%). This finding was concurrent to many wide-reaching studies 4-8,25. Only a few researchers like Kashyap et al demonstrated large proportion of cases with PG occurring in anterior mandible7 . In current research, greater frequency of FFH cases was found involving maxillary gingiva with a count of 61 (52%). Al- Rawi showed the same results in his study while few other studies showed opposing results with preference of mandibular involvement2,5,6. The aforementioned result in enduring study was followed by mandibular involvement (n=40,34%) and buccal mucosa (n=17, 14%) respectively. In literature, buccal mucosa alongbite line is the site which is considered most vulnerable for the development of FFH 13,16. In accordance to this concept, Kashyap et al revealed buccal mucosa as the most frequently involved site7 . At the same time, Buchner et al 4 and Pour et al 8 depicted equal involvement of maxilla and mandible with cases of FFH. In present study, cases of PGCG were found more involving mandibular gingiva than maxillary gingiva (n=23, 68%). This result was in agreement to a wide range of studies conducted worldwide 4-6,8,20. To our knowledge, till now no single study covering up PGCG revealed mandibular dominance for the lesion. However, Kashyap et al in their findings demonstrated equal occurrence of PGCG in both maxilla and mandible7 . Site preponderance for POF in current study is same to that of PGCG with majorityof cases found in mandible ( n=13, 62%). This finding was parallel to various studies 2-5while some others mentioned opposing results in their studies 5,6. In present study, an enormous percentage of reactive hyperplastic lesions (n=248, 85.5%) measured 1cm15. Likewise, Effiom et al demonstrated a large proportion of the lesions measuring >1cm23. However, a quite different size range of 8mm to6cm was showed by A mirchaghmaghi et al in their study26. In enduring study, a major bulk of the localized reactive hyperplastic lesions turned outhaving sessile base attachment to the underlying bone (n=211, 72.7%). These results were in agreement to those revealed by Amirchaghmaghi et al showing majority of the lesionsexhibiting sessile base26. Among different studies which were overviewed in reference topresent one, none demonstrated lesions with pedunculated base attachment in majority. In current study, a major proportion of the lesions had smooth surface (n=188, 64.8%). This was followed by ulcerated surfaced lesions with 79 cases (27.2%) and polypoid lesions with23 cases (7.9%) respectively. These results were in accordance to those showed by Amirchaghmaghi et al 26. In present study, maximum number of cases with PG (n=85, 64.8%) and with FFH (n=102, 91%) exhibited smooth surface. These findings were exactly concurrent with those depicted by Zarei et al6 . Majority of the cases with PGCG (n=25, 86.2%) and POF (n=13, 72.2%) exhibited ulcerated surface in present study. These explorations too were precisely in agreement to those demonstrated by Zarei et al 6 . In present study, greater frequency of the lesions displayed red surface hue (n=197, 62%).Among these lesions, majority of cases with PG (n=104, 73%) exhibited red color. This outcome was similar to that demonstrated by Kashyap et al7 and Peralles et al 15.The later showed 28 cases of PG with red surface appearance while 14 with pink color. Likewise Peralles et al 15 showed greater proportion of cases with FFH having red surface color, the finding that was consistent with the cases of FFH (n=65, 55%) in present study. Among cases of POF, current study demonstrated greater part displaying pinkish white appearance (n=14, 66.6%). However Peralles et al showed more cases of POF with erythematous surface color15. In this study majority of the cases with PGCG (n=19, 62%) exhibited red surface color. This finding is quite usual for the lesions diagnosed as PGCG. However, no studies could be found during the work up of present study containing series of PGCG cases expressing clinical data regarding color of lesion. Though in a case reported by Flaitz regarding PGCG in children the lesion was shown to have reddish-purple appearance22. Among etiological factors poor oral hygiene turned out to be the most frequent factor (n=185, 59%) in current study. These results were in accordance to those reported by Peralles et al 15. This finding is also well reported in many of the world’s retrospective literature regarding development of hyperplastic lesions and denoting them as ‘reactive’ in response to chronic trauma 5,6,10. This outcome also signifies the fact of more female involvement by these reactive lesions due to the poor compliance of female patients towards dental care in our part of world 3 . In present study, most common etiological factor among cases of PG turned out to be pregnancy ( n=77, 55%). Ramu and Rodrigues reported an association between incidence of PG and serum concentrations of estrogen and progesterone in pregnant women5 .It was speculated in few studies that the two hormones render gingival tissue more susceptible to chronic irritation caused by plaque and calculus 17,18. In enduring study, poor oral hygiene was also figured out as etiological factor in majority of the cases of FFH (n=85, 72%) and PGCG (n=20, 59%), a finding that is validated in many wide-reaching studies 7,14,20. Conversely, in current study majority of the cases with POF demonstrated trauma as more prevalent etiological factor in this entity (n=13, 62%). However the possible causative factors for POF reported in literature depict a multitude of calculus, plaque, dental appliances, ill-fitting prostheses and microorganisms 19. In present study, most common chief complaint explored was bleeding with 132 cases (42%) followed by pain (n=122, 39%) and ulceration (n=60, 19%) respectively. Zarei et al in their study reported an equal prevalence of both bleeding and ulceration among reactive hyperplasticcases6 . Amirchaghmaghi et al mentioned swelling as chief complaint in majority of cases (76.2%) followed by burning sensation (8%), pain (5.7%) and ulceration (3.3%)26. Observation inpresent study led to conclusion that ulceration of overlying mucosa causes the exposure of nerve ending present in submucosa later on leads to development of burning sensation. Although this is a little reported finding in the world’s widespread literature, but it was presented as a noticeable clinical data in our region. After histopathological diagnosis, a significant disparity of 5% was seen among cases of PG with 157 (50%) of cases as compared to 141 (45%) which were diagnosed clinically. However an average discrepancy of 2% was seen among cases of FFH (n=111, 36%), PGCG (n=29, 9%) and POF (n=17, 15%). To our knowledge, so far no single study has been done based upon disagreement between clinical and histopathological diagnosis of LRHL. However, Prasanna and Sehrawat identified the diagnostic dilemmas of these lesions which mimic diverse groups of distinct pathological processes 27. Moreover, Krahl et al also emphasized the need of scrutinizing these lesions clinically and histologically from potentially malignant and neoplastic lesions28. Histopathological examination must be a mandatory part of clinicopathological evaluation which later on aids in appropriate therapeutic management of these lesions. The need of this practice is important particularly in elderly patients where biopsy and histopathological examination provide more accurate distribution of oral diseases especially when considering premalignant and malignant lesions 29.
CONCLUSION
This investigation summits variations in subjective assessment of LRHL on clinical grounds. This inter-observer variability could be lessened if histopathological examination is incorporated as a mandatory component in diagnostic protocol. Moreover, most common age range encountered in present study is 30-39 years which is crucial for the development of many pathologic processes which bear close resemblance to LRHL. Therefore, a careful diagnostic approach imparts a critical role in therapeutic management of the patients and elimination of anticipated dento-alveolar complications. Patient education regarding oral hygiene maintenance may also significantly improve the status of oral health and diminish possible chances of development of pathologies. Conflict of interest: None Source of funding: Self - funded Authors contribution Farhat Kazmi contributed with histopathological review, classification of cases and compilation of results. Wajiha Alamgir made the literature research, reviewed the cases and made the whole writing. Muhammad Mumtaz worked on clinical data and results. Moghees A. Baig guided in making necessary amendments in write up and final review.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are grateful to authors/ editors/ publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Bataineh A, Nawaf Z. Localized lesions of oral tissues: A clinicopathological study. J Contemp Dent Pract2005; 6: 1-8.
2. Al-Rawi NH. Localized reactive hyperplastic lesions of the gingiva: A clinicopathological study of 636 lesions from Iraq. Internet Journal of Dental Science2008; 7.
3. Reddy V, SaxenaS, Sexena S, Reddy M. Reactive hyperplastic lesions of the oral cavity: A ten year observational study on North Indian population. J Clin Exp Dent2012; 4: e136- 40.
4. Buchner A, Shnaiderman-Shapiro A, Vered M. Relative frequency of localized reactive hyperplastic lesions of the gingiva: a retrospective study of 1675 cases from Israel. J Oral Pathol Med2010;39: 631-8.
5. Ramu S, Rodrigues C. Reactive hyperplastic lesions of the gingiva: A retrospective study of 260 cases. World J Dent2012; 3: 126-30.
6. Zarei MR, Chamani G, Amanpoor S. Reactive hyperplastic lesions of the oral cavity in Kerman Province, Iran: a review of 172 cases. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2007;45: 288-92.
7. Kashyap B, Reddy PS,Nalini P. Reactive lesions of oral cavity: a survey of 100cases in Eluru, West Godavari. Contemp Clin Dent 2012; 3: 294-7.
8. Pour MAH, Rad M, Mojtahedi A. A survey of soft tissue tumor-like lesions of oral cavity: A clinicopathological study. Iranian Journal of Pathology2008;3: 81-7.
9. Shahsavari F, Khourkiaee SS, Moridani SG. Epidemiologic study of benign softtissue tumors of oral cavity in Iranian population. Journal of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology, Pathology and Surgery 2012; 1: 10-15.
10. Rossmann JA. Reactive lesions of the gingiva: Diagnosis and treatment options. The Open Pathology Journal2011;5: 23- 32.
11. Buchner A, Calderon S, Ramon Y. Localized hyperplastic lesions of the gingiva: A clinicopathological study of 302 lesions. J Periodontol1977;48: 101-4.
12. Kfir Y, Buchner A, Hansen L. Reactive lesions of the gingiva: A clinicopathological study of 741 cases. J Periodontol1980;51: 655-61.
13. Sudarshan R, Vijayabala GS, Kumar KSP. Inflammatory hyperplasia of oral cavity. Archives Medical Review Journal 2012; 21(4): 299-307.
14. Kale TA. Focal fibrous hyperplasia: a reactive lesion. Int J dent Clinics.2013;5: 29-30.
15. Peralles PG, Vianaa PB, Azevedo ALdR, Pires FR. Gingival and alveolar hyperplastic reactive lesions: clinicopathological study of 90 cases. Braz J Oral Sci 2006;5: 1085-9.
16. Akinyamoju AO, Adeyemi BF, Kolude B. Localized reactive lesions of the oral cavity: A review of 246 cases in Ibadan. The Internet Journal of Dental Science 2013; 12(1).
17. Jafarzadeh H, Snatkhani M, Mohtasham N. Oral pyogenic granuloma: a review. J Oral Sci2006; 48: 167-75.
18. Eversole LR. Pregnancy tumor: an anlysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol(1991;72: 196-9.
19. Kohli K, Christian A, Howell R. Peripheral ossifying fibroma associated with aneonatal tooth: case report. Pediatr Dent1998;20: 428-9.
20. Motamedi MHK, Eshghyar N. Peripheral and central giant cell granulomas of thejaws: a demographic study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral RadiolEndod2007;103: e39- e43.
21. Krahl D, Altenburg A, Zouboulis CC. Reactive hyperplasia, precancerous andmalignant lesions of the oral mucosa. J DtchDermatolGes2008;3: 217-30.
22. Flaitz CM. Peripheral giant cell granuloma: a potentially aggressive lesion in children. Pediatr Dent2000;22: 232- 33.
23. Effiom OA, Adeyemo WL, Soyele OO. Focal reactive lesions of the gingiva: Ananalysis of 314 cases at a tertiary health institution in Nigeria. Niger Med J2011;52: 35-40.
24. Naderi NJ, Eshghyar N, Esfehanian H. Reactive lesions of the oral cavity: A retrospective study on 2068 cases. Dent Res J2012;9: 251-5.
25. Aghbali AA, Hosseini SV, Harasi B, Janani M, Mahmoudi SM. Reactive hyperplasia of the oral cavity: A survey of 197 cases in Tabriz, Northwest Iran. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects 2010;4: 87-9.
26. Amirchaghmaghi M, Mohtasham N, Mozafari PM, Dalisrani Z. Survey of reactive hyperplastic lesions of the oral cavity in Mashhad, Northeast Iran. J Dent Res Dent Clin DentProspects2011;5: 128-31.
27. Prasanna JS, Sehrawat S. Fibroepithelial hyperplasia: Rare, Self-limiting condition – Two case reports. J Adv Oral Research 2011; 2(3):63-9.
28. Karhl D, Altenburg A, Zouboulis CC. Reactive hyperplasia, Precancerous and Malignant lesions of the Oral mucosa. JDDG 2008; 3(6): 217-32.
29. Correa L, Moreira ML, Frigerio A, Cantanhede S, de Sousa OM, Noveli MD. Oral lesions in elderly population: a biopsy survey using 2250 histopathological records. Gerodontology 2006; 23(1): 48-54.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License