IJCRR - 7(21), November, 2015
Pages: 66-71
Date of Publication: 11-Nov-2015
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EVALUATION OF PERINATAL OUTCOME IN PRETERM LABOUR
Author: Gulshan Akhter, Syed Masooma Rizvi, Syed Imtiyaz Hussain, Farhat Ali, Asifa Ali
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Preterm labour is a common complication that contributes significantly to high perinatal morbidity and mortality. Premature babies are physiologically and metabolically immature. As a consequence, preterm infants are at higher risk than are term infants of developing many immediate and long term complications. Objectives: To compare morbidity and mortality of preterm infants to those born at term. Appropriate intervention, institutional deliveries and good neonatal care back up facilities. Methodology: The present prospective, randomized, comparative study was conducted over a period of 18 months and a total of 200 patients were selected and allocated in two groups. Study group who were in preterm labour and control group who were in full term labour. Perinatal outcome was measured by birth weight, gestational age, Apgar score at 1 and 5 minutes, admission in intensive care unit, respiratory morbidity, neonatal sepsis, need for emergency section and neonatal deaths. All babies were followed up for a period of 7 days after delivery. Results: Preterm infants were at significantly higher risk for over all morbidity and mortality than term infants. Out of 100 preterm infants 43 had low birth weight, 70 had respiratory morbidity, 68 had sepsis, 83 required ICU admission and 35 had early neonatal death while the corresponding figures for term infants were 10, 0, 4, 6 and 5 respectively. The mean Apgar score at 1 and 5 minutes of cases was 5.54 and 6.47 respectively. The mean Apgar score at 1 and 5 minutes of controls was 7.16 and 7.64 respectively. Emergency caesarean section was required in 39 cases and 27 controls which was statistically non-significant. Conclusion: Compared with term infants, preterm infants are at high risk of overall morbidity and mortality. Clinical suspicion, early detection and correction of risk factors, institutional delivery and good neonatal care back up facilities can improve the outcome of preterm labour.
Keywords: Perinatal, Preterm labour, Apgar score, Caesarean, Clinical suspicion
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Preterm labor is defined as occurrence of regular uterine contractions (three or more in ten minutes) with cervical changes (effacement more or equal to 80% and dilatation more or equal to 1 centimeter) in women with intact fetal membranes and gestational age less than 37 weeks1 . In India its incidence is 10 to 15% and accounts for about 75 % of perinatal deaths2 . Preterm labor is the leading cause of neonatal morbidity in developed countries.50 to 60% of preterm births occur following spontaneous labor 30 % due to PROM and rest are iatrogenic termination for maternal or fetal benefit.1,3 Preterm labor is one of the syndromes characterized by premature activation of final path way of parturition. Preterm labor may either be a physiological process that has occurred too soon or pathological process following an abnormal stimulus. The etiology of preterm labor may be multi-factorial. The earlier the onset of labor the more likely is that a pathological process is implicated.4
RISK FACTORS
PAST HISTORY
• Previous preterm birth
Second trimester losses
• Habitual abortions
• Uterine anomalies
• Conization of cervix
ANTEPARTUM
• Threatened abortion.
• Young or advanced maternal age.
• Poverty.
• Short stature.
• Vitamin C deficiency.
• Occupational factors such as prolonged walking or standing, strenuous working conditions and long weekly work hours.
• Inter pregnancy interval 59 months.
• Bacterial Vaginosis6 .
• Twins, triplets (51% and 91% chance of preterm delivery respectively)7
• Preterm rupture of membranes
• Polyhydramnios
• Antepartum haemorrhage
• Intra-abdominal surgery
• Urinary tract infection
• Tobacco or cocaine use
• Serious maternal infection
• Physical/emotional trauma.
DIAGNOSIS7
SUGGESTIVE EARLY SYMPTOMS
• Low abdominal pain and/or cramps and/or pelvic pressure
• Low backache
• Increased vaginal discharge
• Bleeding/spotting/show
DEFINITIVE SIGNS8
Regular uterine activity (contractions of 3 in 10 minutes or 8 in 60 minutes) accompanied by cervical effacement (80% or more) and dilatation (>1 cm)
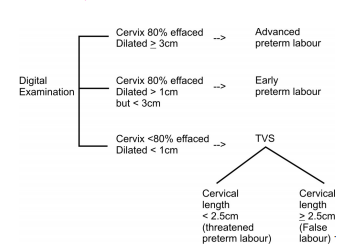
Preterm infant can be
• Late preterm -->33-36 weeks
• Moderate preterm --> 28-32 weeks
• Extreme preterm -->20-27 weeks
Preterm infants are physiologically and metabolically immature.9 As a consequence, preterm infants are at higher risk than are term infants of developing medical complications that result in higher rates of mortality and morbidity during the birth hospitalization.10.
Premature babies are at risk of many immediate and long term complications. Immediate (short term) neonatal mobidity includes respiratory distress syndrome, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, jaundice, intraventricular haemorrhage, necrotizing enterocolitis, broncho-pulmonary dysplasia, sepsis and patent ductus arteriosus. Long term morbidity includes cerebral palsy, mental retardation and retinopathy of prematurity.11 Residual mental and motor handicaps are the major deterrents to the optimal development of preterm infant12.
AIM OF STUDY
1. To compare morbidity and mortality of preterm infants to those born at term.
2. Appropriate intervention, institutional deliveries and good neonatal care back up facilities.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Study Design: Prospective, comparative study.
Source and Data Collection: The patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria were selected for the study. The study was conducted in the Postgraduate Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, Lalla Ded Hospital, which is the sole tertiary care hospital in the valley and an associated hospital of Government Medical College, Srinagar, for a period of 18 months from March 2013- September 2014.
Inclusion Criteria
• Primigravida and multigravida.
• Gestational age 28 weeks.
• Spontaneous onset painful regular uterine contraction occurring at least 3 per 10 minutes each lasting 40 seconds.
• Progression in cervical score in the form of effacement > 80% and dilatation > 3cm.
• Presence of show or bag of membranes.
• Singleton pregnancy
• Vertex presentation
Exclusion Criteria
• Congenital fetal abnormalities.
• Multiple pregnancy.
• Gestation age >40 weeks and < 28 weeks.
• Patients with false labor pains.
• Presentation other than vertex.
• Pregnancy complicated by preterm premature rupture of memranes and maternal complication
METHOD
About 200 patients were selected for the study. The study group was comprised of 100 women admitted in Preterm Labor and the comparative group was comprised of 100 women in full term Labor.
Following considerations were given to patients in preterm labor.
1. Close observation with monitoring of uterine contractions and serial examinations (after every 4 hrs under all asceptic precautions) were done to assess cervical changes and labor progression.
2. Close monitoring of fetal heart rate and timely intervention at early signs of fetal distress.
3. For pregnancies less than 34 weeks corticosteroids were given for enhancement of fetal lung maturity (2 doses of betamethasone 12mg each 24 hour apart).13
4. A broad spectrum antibiotic (ceftriaxone 1g i/v bid) was given for prevention of neonatal infections.
5. Pediatrician was available at the time of delivery.
6. Babies were transferred to premature baby care unit for neonatal care and perinatal outcome was analyzed.
Gestational age was assessed by maternal last menstrual period or by first trimester ultrasound scan. Perinatal outcome was measured by birth weight, gestational age, APGAR score at 1 and 5 minutes, admission in special care baby unit (SCBU), assessment of indication of admission in SCBU, Respiratory morbidity, neonatal infection, need for emergency caesarean section and neonatal deaths. All babies were followed up for a period of maximum 7 days after delivery.
RESULTS AND OBSERVATIONS
The present study included 100 patients (Group A) in preterm labor and 100 patients (Group B) in full term labor.
DISCUSSION
Gestational Age of Group A and Group B
In the present study, the minimum gestational age of Group A was 28 weeks and maximum gestational age was 36 weeks with mean of 33.19 weeks and SD 2.53. While in Group B, the minimum gestational age was 37 weeks and maximum gestational age was 40 weeks with mean 38.2 weeks and S.D. 1.12.
Respiratory Morbidity
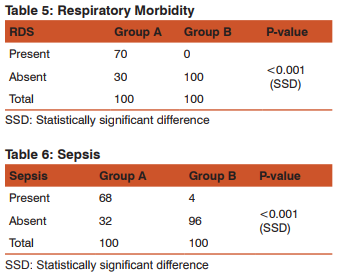
Twenty four studies published between 2000-2009 consistently revealed that infants born at 32-36 weeks experience Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Transient Tachypnea of Newborn, pneumonia and pulmonary hypertension of the newborn at higher rates than term infants75. Subsequent studies delivered similar conclusion. The rate of respiratory compromise in US hospitals was 10.5% of late preterm and 1.13% of term infants14. Broadly et al15 concluded that clinically significant respiratory morbidities are least common at 39-40 weeks. In the present study all forms of respiratory morbidity and overall respiratory failure decreased significantly with gestational age until 40 weeks. One study of all California singleton live births who survived to 1 year of age found that infants born at 34-36 weeks gestation were 3-9 times more likely to require mechanical ventilation than infants born at 38 weeks gestation.
Sepsis
Preterm infants are more likely to develop severe infections such as sepsis, meningitis and pneumonia than term infants. In a large retrospective population report, McIntire and Leveno16 found an increased risk of sepsis in late preterm versus term infants. The rate of sepsis in moderate preterm infants has also been shown to be almost double than in late preterm infants. In a twin population, Refuerzoet al17 found 5% of sepsis in moderate versus 2.2% in the late preterm infants.
Need for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
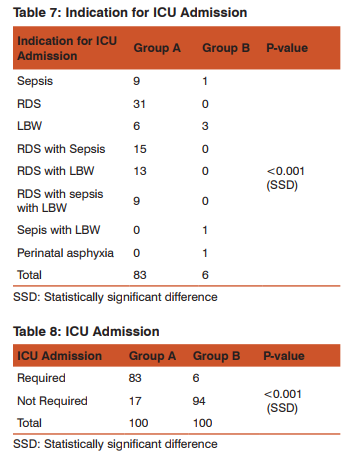
Admission Preterm infants are more likely than term infants to have longer initial hospital stays and to be admitted to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit18 One large cohort study found that 88% of infants born at 34 weeks gestation, 54% of infants born at 35 weeks gestation, 25% of infants born at 36 weeks gestation, 12% of infants born at 37 weeks gestation and 2.6% of infants born at 38-40 weeks gestation were admitted to a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. In the present study Neonatal Intensive Care Unit admission was required in 83% of preterm infants (< 36 weeks) 6% of term infants (> 37 weeks – 40 weeks).
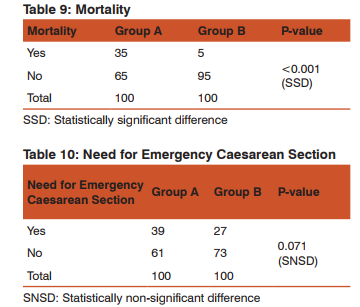
Mortality
Preterm infants have high neonatal mortality rate than term infants. Larroque et al19 reported the results of EPIPAGE study on the survival of preterm infants born between 27-32 weeks in a geographically defined population of France in 1997, stratified by gestational age. The survival rate between 22 and 32 weeks was 67% of all births (including still births). 85% of live births and 89% of infants admitted to neonatal intensive care units. Survival increased with gestational age. 31% of all infants born alive at 23 weeks survived to discharge 78% at 28 weeks and 97% at 32 weeks. Survival among live births was lower for Small for gestation age infants. Vidyadhar B. Bangal et al20 conducted a study of perinatal outcome in preterm labor at tertiary hospital. He observed that perinatal mortality in the study group was 42.4%. Roberta De Luca et al21 similarly found that mortality and morbidities had strong gestational age related trend with the lowest incidence consistently found between 38 and 40 weeks of gestation. Need for Emergency Caesarean Section and Mode of Delivery The main finding in this study is that caesarean delivery did not enhance the neonatal survival of preterm infants nor did it decrease the morbidity in these infants. This is further supported by the work of Malloy et al and others22.
APGAR Score at 1 minute and 5 minutes
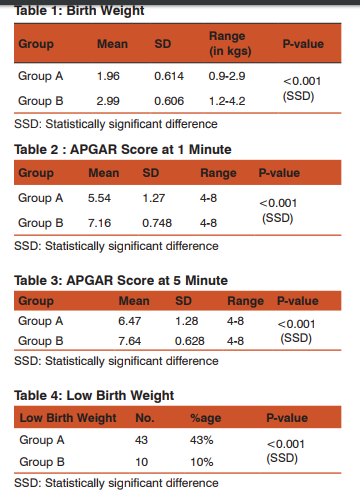
In the present study, it was found that there is a direct relationship between low APGAR score, gestational age and neonatal mortality in preterm infants. APGAR score in preterm infants at 1 minute was found to range from 4-8 with mean being 5.548 SD 1.27 while in term infants it ranged from 4.8 with mean being 7.16 and APGAR score at 5 minutes in preterm infants ranged from 4-8 with mean of 6.47 and SD 1.28 while in term infants it ranged from 4-8 with mean of 7.64 and SD 0.628. Henry Chong Lee, Mohammad Subeh and Jeffrey B. Gould23 conducted study on low APGAR score and mortality in preterm neonates born in the United States where they found that distribution of APGAR score depended on gestational age, the youngest gestational age having higher proportions of low APGAR score. Median APGAR score ranged from 6 at 24 weeks to 9 at (30-36 weeks) gestation. The RR of death was significantly higher at APGAR score 0-3 versus 7-10.
Low Birth Weight
The present study showed that preterm infants are at high risk of low birth weight than term infants and the low birth weight adversely affects the mortality of these preterm infants. Laurie S. Pulver, et al24 conducted a study on weight for gestational age affects the mortality of preterm infants being small for gestation age substantially increases the already higher mortality of preterm infants. This increased risk cannot be fully explained by an increased prevalence of lethal congenital conditions among small for gestation age preterm new borns.
CONCLUSION
Preterm onset of labor is a heterogeneous condition with multifactorial etiology. Clinical suspicion, from the past obstetric history, early detection and correction of risk factors like Group B of blood pressure in preeclampsia, correction of anaemia, treatment of cervicovaginal infections and asymptomatic bacteriuria, abstinence, use of tocolytics in over distended uterus, cervical circlage in proven cases of cervical incompetence can prevent preterm onset of labor and hence decrease the mortality and morbidity burden due to preterm births. Use of injectable progesterone in idiopathic threatened Preterm Labor can reduce the incidence of Preterm Labor. Maternal Betamethasone in Preterm Labor helps in enhancing the fatal lung maturity and reduces the incidence of Respiratory Distress Syndrome in newborn babies. Deliveries in the institution having facilities for neonatal care will improve the perinatal outcome in Preterm Labor. The rate of morbidity and mortality declines continuously when gestational age increases upto 39 weeks. There is a particular need to educate health care providers and parents about the vulnerability of infants born between 28-36 weeks gestation. From the present study and the literature, it is clear that preterm group is significantly more vulnerable when compared with the term group. This study will lead to review of care for preterm group and help optimize care for this cohort of infants. Reorganization of services and increased resource allocation to provide better clinical support to this group may be needed in most settings. The findings of this study may also affect antenatal counseling regarding delivery in preterm gestation. Based on the findings of the present study, it is concluded that caesarean delivery does not improve the outcome in preterm babies. Mode of Delivery does not influence mortality and morbidity in preterm infants, if there are no obstetric indications favoring a particular mode. Caesarean section cannot be recommended as the routine Mode of Delivery for preterm babies unless there are other recognized maternal / fetal indications. Preterm infants are physiologically less mature and have limited compensatory responses to the extra-uterine environment compared with term infants. An immature baby should be conveyed to an intensive care nursery as soon as possible in a portable incubator, if it is not immediately possible baby should be kept warm. It loses heat very easily and it should be supported by hot water bags, care should be taken to prevent burns which happen very easily and quickly. The ambient temperature may have to be about 320 C to maintain rectal temperature of 35.50 C. Understanding morbidity risk among preterm infants is not only important helping newborn care providers to anticipate and to manage potential morbidity during birth hospitalization and earlier follow up after hospital discharge, but also may possibly assist in guiding non-emergency obstetric intervention decisions. The present study is an attempt to obtain data in pattern of early neonatal morbidity and mortality to compare it with term neonates.
Conflict of interests The author(s) have not declared any conflict of interests.
Source of funding There is no source of funding.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Goldenberg RL. The management of preterm labor. Obstet Gynecol 2002; 100(5): 1020-37. 2. Fuch F. Prevention of prematurity. Am J Obstetric and Gynaec.1976; 12: 809.
3. Leitich H. Controversies in diagnosis of preterm labor. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 2005 March; 112 (suppl.): 61-3.
4. Sumana G, Renu Misra. Preterm labor. In: Ian Donald’s Practical Obstetric Problems. Sixth Edition: Page 398.
5. Creasy, R. and Resnik, R (1999). Maternal-Fetal Medicine, 4th Edition.
6. Cunningham, Leveno, Bloom Hauth, Rouse, Spoug Antecedents and contributing factors of preterm Labor In, Williams Obstetrics 23rd edition 2010; 36 : 811-814.
7. Fermendo Arias, Shirish N Daffary, Amarnath G Bhcte. Preterm Labor. In: Practical Guide to High – Risk Pregnancy and Delivery. 3rd Edition 2008; 8:221.
8. Wang ML, Dorer DJ, Fleming MP, Catlin EA. Clinical outcomes of near – term infants. Pediatrics. 2004; 114:372 – 376.
9. Kramer MS, Demissie K, Yang H, Platt RW, Sauve’ R, Liston R. The contribution of mild and moderate preterm birth to infant mortality. Fetal and Infant Health Study Group of the Canadian Perinatal Surveillance System. JAMA. 2000; 284: 843 – 849.
10. Devi PK. The problem of prematurity and low birth weight. J Obstet Gynecol India 1974; 1: 24. 11. Lubchenco CO, Searis DT. Epidemiology and causes of preterm labor. Paediatrics 1972; 47: 81 – 84.
12. American college of Obstetrician and Gynaecologists. Antenatal corticosteroid therapy for fetal maturation. Committee Opinion No.419. Obstet Gynecol 2008; 112: 963-965.
13. Colin AA, McEvoy C, Castile RG. Respiratory morbidity and lung function in preterm infants of 32 to 36 weeks gestational age. Pediatrics 2010 July; 126(1): 115-28.
14. Consortium on Safe Labor, Hibbard JU, Wilkins Sun L et al. Respiratory morbidity in late preterm births. JAMA 2010 July 28; 304(4): 419-25.
15. Yoder BA, Gordon MC, Barth WH. Late preterm birth: does the changing obstetric paradigm alter the epidemiology of respiratory complications. Obstet Gynecol 2008; 111: 814-22.
16. McIntire DP, Leveno KJ. Neonatal mortality and morbidity rates in late preterm births compared with births at term. Obstet Gynecol 2008; 111: 35-41.
17. Michael Cohen – Workoweiz, Moran C, Benjamin DK et al. Early and late onset sepsis in late preterm infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2009; 28: 1052-6.
18. Larroque B, G. Breast, M. Kaninski et al. The EPIPAGE Study Group. 2004. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 89: F139-F144.
19. Epidemiology of neonatal acute respiratory disorders. Biol Ne – Onate. 1998:74:7- 15.
20. Vidyadhar B. Bengal, Kunnal K. Shinde, Gayatri K. Khanwerkar, Neha A Patil. A study of risk factors and perinatal outcome in preterm labor at tertiary care hospital. International Journal of Biomedical Research 2012; 3(3): 147-150.
21. Luca RD, Boulvain M, Irion O, Berner M, Pfister RE. Incidence of early neonatal mortality and morbidity after late preterm and term caesarean delivery. Pediatrics 2009; 123: 1064-71.
22. Malloy MH, Onstad L, Wright E. The effect of caesarean delivery on birth outcome in very low birth weight infants. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Obstet Gynaecol 1991; 77: 498-503.
23. Henry Chong Lee, Mohammad Subeh, Jeffrey B. Gould. Low APGAR score and mortality in preterm neonates born in the United States. Acta Pediatr 2010 Dec; 99(12): 1785-1789.
24. Laurie S. Pulvr, Ginger Guest-Warnick, Gregory J. Stoddard, Carrie L. Byington, Paule Young. Weight for gestational age affects the mortality of late preterm infants. Pediatric 2009; 123: 1072-7.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License