IJCRR - 10(16), August, 2018
Pages: 16-25
Date of Publication: 27-Aug-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Profile of Metal Accumulation in Aquatic Macrophytes
Author: Rolli N. M., Hujaratti R. B., Gadi S. B., Mulagund G. S., Taranath T. C.
Category: Life Sciences
Abstract:Industrial development coupled with population growth has resulted in the over exploitation of natural resources. Life support systems viz; water, air and soil are thus getting exposed to an array of pollutants especially heavy metals released by anthropogenic activities. Tolerant species of aquatic plants are able to survive and withstand the pollution stress serves as pollution indicators and as tool for phytoremediation of heavy metals is an environment clean up strategy in which green plants are employed to remove toxic contaminants and operates on the principles of biogeochemical cycling.
The aquatic plants viz; Salvinia molesta and Pistia stratiotes were used for its toxicity and profile of metal accumulation (Cadmium \?Cd) from synthetic media. The test plants were cultured in a modified Hoagland solution supplemented with cadmium nitrate Cd (NO3)2. The present study focuses on Cd toxicity on morphology, biochemical parameters and bioaccumulation potential of Salvinia and Pistia. The laboratory experiments were conducted for the assay of morphological index parameters (MIP), biochemical parameters, and profile of cadmium accumulation in test plants at various concentrations viz, 0.1 ,0.5 ,1.0,1.5 and 2.0
ppm at 4 days regular intervals for 12 days exposure. The test plants show visible symptoms, like withering of roots, chlorosis, necrosis and in particular, at higher concentrations (2.0 ppm) lower leaves gets decayed. However, the lower concentrations i.e. 0.1 ppm shows normal growth. The estimation of biochemical parameters viz total chlorophyll, protein and carbohydrates of test plants showed significant increased at lower concentrations i.e. 0.1 ppm of Cd. The biochemical constituents decreased with increase in exposure concentrations i.e.0.5 to 2.0 ppm. The toxic effect Cd was directly proportional to its concentrations and exposure durations. The profile of metal accumulation by both test plants was maximum at 4 days exposure irrespective concentrations and gradually decreases at subsequent exposure concentrations and duration.
Keywords: Biochemical parameters, Cadmium, Toxicity, Accumulation, Aquatic plants
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Heavy metal pollution is a major environmental problem facing the modern world (1, 2). The global heavy metal pollution is increasing in the environment due to increases of human activities. However, it is gaining importance day by day due to its obvious impact on human health through the food chain (3). As a result of rapid growth in the industrial sectors, India is now encountering several environmental problems, especially contamination of heavy metals in water. The danger of heavy metals is aggravated by their almost indefinite persistence in the environment because they cannot be destroyed biologically but are only transformed from oxidative state or organic complex to another. In addition, they are highly toxic for both aquatic flora and fauna. The heavy metal, cadmium, is selected as toxicant for the present study because they are used in several industries in India and they are highly toxic to animals, humans and plants. Biological treatment of waste water through aquatic plants have a great potential for its purification which are effectively accumulates heavy metals (4). Aquatic macrophytes accumulates considerable amount of toxic metals and make the environment free from the pollutants. Thus, play significant role in cleaning up of environment and make the environment free from many pollutants. Many aquatic plants have been successfully utilized for removing toxic metals from aquatic environment (5). Similarly algae were also used to remove heavy metals from aquatic systems as they have capacity to accumulate dissolved metals (6, 7). The metal tolerance of plants may be attributed to different enzymes, stress proteins and phytochelatins (8). The accumulation of metals at higher concentration causes retardation of growth, biochemical activities and also generation of –SH groups containing enzymes (9).
In the present investigation Salvinia molesta Mitchell and Pistia stratiotes L, a common aquatic floating macrophytes are used to study the effect of different concentrations of cadmium on morphology, biochemical constituents and accumulation of Cd from the experimental pond under laboratory conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Salvinia molesta and Pistia stratiotes, free floating aquatic plants from unpolluted water bodies is maintained in cement pots (1 m diameter) under natural conditions at a temperature 28-300 C. About 20 g of young healthy Salvinia and Pistia were acclimatized for two weeks in Arnon and Hoagland nutrient solution maintaining pH between 7.1-7.4. The concentrations of Cd in the polluted water are in the range of 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 mg/l and tap water as a control. Morphological Index parameters (MIP) viz, root length, leaf length and breadth were observed for
12 days at interval of 4 days. Photographs of Salvinia and Pistia which were taken by using Canon’s Power Shot G2 digital camera were treated with different concentrations of copper. For the further study the plants were harvested at the end of 4, 8 and 12 days exposure and are thoroughly washed with distilled water and used for the estimation of total chlorophyll, protein and carbohydrate and also for morphological observations. Plants harvested after 48 hrs were dried at 800 C for 2 days for metal extraction.
The fresh test plant samples of 1g is macerated in 100 ml of 80% (v/v) chilled acetone by using pestle and mortar. The centrifuged and supernatant was used for the estimation of total chlorophyll by standard method (10) using 652 nm against the solvent (80% acetone as a blank). The protein was estimated by Lowry’s method (11) using Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a standard, using 660 nm and carbohydrates by phenol sulphuric acid method (12) using glucose as standard at 490 nm. Morphological characters were identified with the help of photographs, using Canon’s Power Shot G2 -digital camera.
The estimation of metal Cd in the test plant was carried out by using standard method (13). The dried and powdered 1 g plant material was digested by using mixed acid digestion method in Gerhardt digestion unit. The digested samples were diluted with double distilled water and filtered through Whatman filter paper No-44. The estimation of Cd was done by AAS (GBC 932 Plus Austrelia) with air acetylene oxidizing flame and metal hollow cathode lamp at 217.00 nm wavelength. Working standards (SISCOP-Chem-Bombay Lab) were used for the calibration of instrument.
Statistical analysis:
Data are presented as mean values ± SE from two independent experiments with three replicates each. Data were subjected to Two - way ANOVA to know significance between concentrations and between exposure duration for the accumulation of heavy metal (Cd). Further, Dunet’s test is also applied for multiple comparisons between control and other concentrations. Two – way ANOVA test is also extended to know the significance between concentration and duration for biochemical parameters.
RESULTS
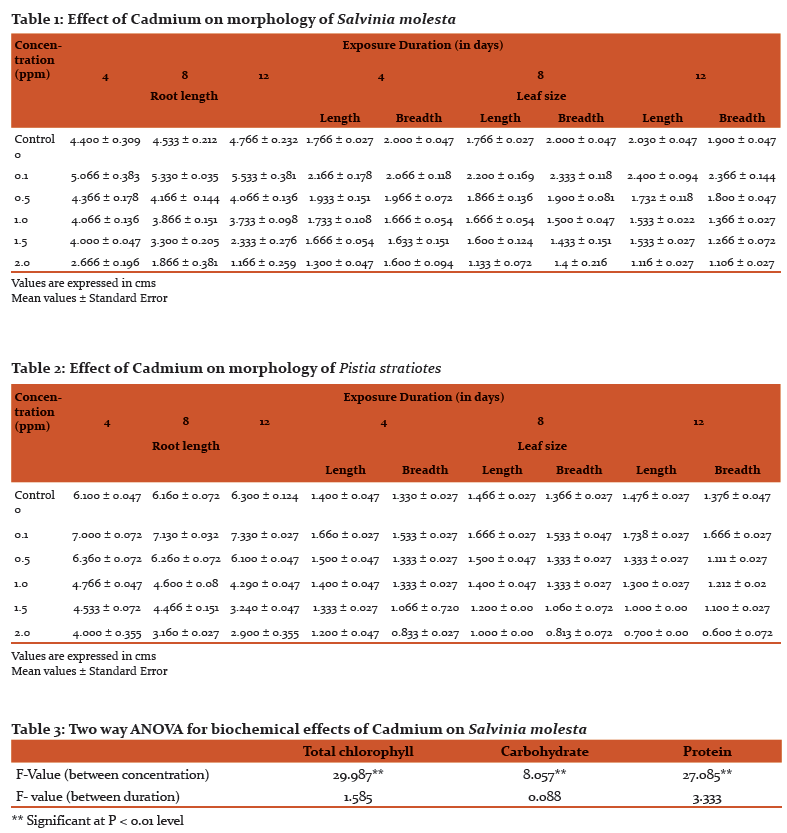
Toxicity effect of cadmium on morphology. The test plants showed luxuriant growth, shows increase in the laminal length and breadth at low concentration (0.1 ppm) in both test plants. In Salvinia at 0.1 ppm of Cd was found to promote laminal length by 2.166 ± 0.169, 2.200 ± 0.169 and 2.400 ± 0.094 and breadth by 2.066 ± 0.118, 2.333 ± 0.118 and 2.366 ± 0.144 at 4,8 and 12 days exposure duration. Similarly root length by 5.066 ± 0.383, 5.330 ± 0.0356 and 5.533 ± 0.381 in Pistia at the same concentration (0.1 ppm) shows increase in laminal length by 1.660 ± 0.027, 1.666 ± 0.027 and 1.738 ± 0.027 cm and breadth by 1.533 ± 0.027, 1.666 ± 0.047 and 1.666 ± 0.027 at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure durations respectively. Similarly, the root length by 7.000 ± 0.072, 7.130 ± 0.032 and 7.330 ± 0.027.at the same exposure duration.
However, in Pistia at 2.0 ppm Cd severely inhibit laminal length by 1.200 ± 0.047, 1.000 ± 0.000 and 0.700 ± 0.000 and breadth 0.833 ± 0.027, 0.813 ± 0.072 and 0.600 ± 0.072 at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure duration. Similarly root length inhibition by 4.000 ± 0.355, 3.160 ± 0.027 and 2.900 ± 0.355 at the same exposure duration.
Salvinia also shows at 2.0 ppm concentration severe inhibition of laminal length by 1.300 ± 0.047, 1.133 ± 0.072 and 1.116 ± 0.027 and laminal breadth by 1.600 ± 0.094, 1.4 ± 0.216 and 1.106 ± 0.027 at 4, 8 12 days exposure duration. Similarly root length inhibition by 2.666 ± 0.196, 1.866 ± 0.881 and 1.166 ± 0.259 cm at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure duration.(Table. 1 and 2).
Toxicity effect of Cadmium on biochemical parameters
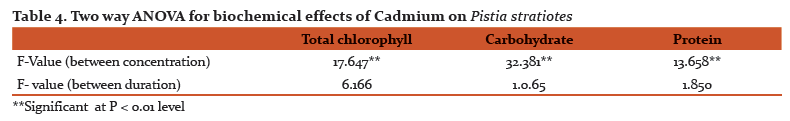
The total chlorophyll content was very sensitive to heavy metal (Cd) toxicity. The results found that Cd at 0.1 ppm found to augment chlorophyll synthesis and was directly proportional to concentration and exposure duration in both the test plants. In Salvinia the chlorophyll content was increased by 3.65% (0.602 mg/g), 4.06 % (0.615 mg/g) and 4.56% (0.645 mg/g) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days compared to control pond. Similarly in Pistia the chlorophyll content was increased by 0.79% (0.382 mg/g), 1.04 % (0.385 mg/g), 1.30% (0.389 mg/g) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days compared to control pond.
However, the higher concentration of Cd found to inhibit the chlorophyll synthesis in both the test plants. The inhibition at 2.0 ppm Cd by 20.05% (0.303mg/g), 31.49% (0.261 mg/g) and 39.58 % (0.232 mg/g) significant at P > 0.95% in Pistia and the inhibition at 2.0 ppm Cd by 24.09% (0.441 mg/g), 29.61% (0.416 mg/g) and 34.52% (0.402 mg/g) in Salvinia.
Two way ANOVA represents biochemical toxicity to the test plants, concentrations were significant at P > 0.01 level but duration is not significant (Table. 3 and 4).
The increase in carbohydrate content of Salvinia at 0.1 ppm Cd by 3.44% (30.0 mg/g), 12.88% (36.0mg/g) and 13.88% (43.0mg/g ) respectively. Similarly, in Pistia the carbohydrate content increases marginally at 0.1 ppm concentration of Cd exposure by 8.82% (37.0 mg/g), 11.42% (39.0 mg/g) and 13.15% (43.0 mg/g) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure. However, the severity of inhibition is more pronounced in Pistia at 2.0 ppm of Cd by 47.05% (18.0 mg/g), 62.85% ( 13.0 mg/g) and 74.35 % (10.0 mg/g) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure (fig. ). The 2.0 ppm of Cd found to inhibit carbohydrate synthesis by 27.58% (21.0 mg/g), 43.75% (18.0 mg/g) and 65.78% (13.0 mg/g) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure in comparison to control (Fig. 1 and 2).
The protein synthesis at 0.1 ppm of Cd was promotive irrespective of exposure duration in both test plants. However, the protein content decreased at subsequent concentration and inhibition was directly proportional to the exposure duration. The 0.1 ppm of Cd promoted the protein synthesis by 2.38% (4.3 mg/g), 4.65 % (4.5 mg/g) and 6.81 % (4.7 mg/g) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure duration. Similarly for Pistia at 0.1 ppm shows promotive by 2.22% (4.5 mg/g), 8.33% (5.2 mg/g) and 12.24% (5.5 mg/g) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure duration (Fig. 1 and 2).
The reduction in content was observed with progressive in Cd concentration in both the test plants. The inhibition of protein content increase viz, 35.7% (2.7 mg/g), 44.18% (2.4 mg/g) and 59.09% (1.8 mg/g) was noticed in Salvinia at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure. Similarly in Pistia also at 2.0 ppm inhibition by 3.4 mg/g (24.44 %), 2.6 mg/g (45.83%) and 2.0 mg/g (59.18%) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure duration (Fig. 1 and 2).
Application of two-way ANOVA, it is found that the biochemical responses of test plants species with respect to their concentrations were significant at P > 0.01 level. However, exposure durations are not statistically significant (Table. 3 and 4).
Profile of metal accumulation
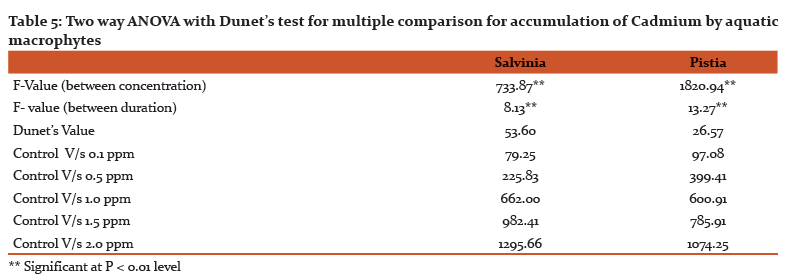
Fig.3 shows the concentration of Cd accumulation in Salvinia and Pistia and was directly proportional to its concentration and exposure duration. The Salvinia grown in experimental pond containing 0.1 ppm found to accumulate 112.050 µg/g, 130.75 µg/g and 133.75 µg/g. Similarly Pistia also shows metal accumulation at the same concentration by 112.50 µg/g, 130.75 µg/g and 133.75 µg/g at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure duration (Fig. 3).
However, at higher concentration (2.0 ppm) accumulation in Pistia by 1060.50 µg/g,1104.50 µg/g and 1125.00 µg/g and rate of accumulation in Salvinia also by 1270.0 µg/g, 1375.25 µg/g and 1381.00 µg/g during 4, 8 and 12 days exposure duration respectively (fig. 3).
Two way ANOVA showed that both concentration and exposure duration were significant at P < 0.01 level in both test plants and further Dunet’s test was applied for the multiple comparison between control and different concentration treatments of test plant. From the statistical analysis it is clear that concentrations treatments are significantly differ with control (Table. 5).
DISCUSSION
Toxicity effect of Cd on morphology
-
Morphological toxicity: Morphometric assay is one of the quantitative tools for the assessment of toxicants measured by using Morphological Index Parameter (MIP). The rate of inhibition in the root and leaf (fronds) is directly proportional to the concentration of cadmium in both the test plants. Two way ANOVA test states the concentrations are significantly toxic at 5% level but duration is not significant. MCA test also represent maximum deviation is at higher concentration compared to control (Table 1). Both the test plants showed normal growth at their respective lower concentrations (i.e. 0.1 ppm). Similar observations were made by (14) in Limnantherum cristatum at 1 ppm concentration of Pb, Zn and Cr. The higher concentration of Cd (0.5 to 2.0 ppm) exhibited toxicity symptoms like chlorosis and leaf fall were observed, then brownish was occurred being marked in old leaves, respectively at higher concentration 2.0 ppm in both the test plants. Our results of toxicity symptoms of Cd at higher concentrations observed were similar to (15) and (16) and also in Salvinia natans (2). Sobero et. al (17) confirmed root elongation of Cd in some members of lemnaceae was found at different concentrations of Cd. The heavy metal induces morphological abnormalities in algae also (18).
-
Toxicity effect of cadmium on biochemical parameters: A number of heavy metals required by plants as micronutrients and they act as co-factors of enzymes as a part of prosthetic groups and involved in a wide variety of metabolic pathway, but higher concentration of heavy metals are toxic and induces physiological and genetical changes in plants (19, 20).
In the present investigation the lower concentration of Cd promotes the synthesis of chlorophyll in Salvinia molesta and Pistia stratiotes. The enhancement of chlorophyll content from 0.602 mg/g to 0.642 mg/g in Salvinia and 0.379 mg/g to 0.384 mg/g in Pistia from 4 to 12 days exposure. The percent enhancement of chlorophyll is 4.56% in Salvinia and 1.56% in Pistia when compared to control (respective) during 12 days exposure. The stimulatory of Cd at lower concentration (0.01 to 0.4 mg/lt) was noticed in Ceratophyllum demersum (21). The phytochelatins (PCs) play an important role in cellular metal ion homeostasis and metal detoxification (22) and hence lower concentration of Cd shows stimulatory effect.
The Cd treatment at higher concentration decreases the chlorophyll content due to accelerated degradation of chlorophyll. In the present investigation, the inhibition varies from 0.441 mg/g to 402 mg/g in Salvinia and 0.303 mg g to 0.232 mg/g in Pistia. The inhibition is 34.52% in Salvinia and 34.58% Pistia at 12 days exposure compared to their respective control. The Cd found to inhibit general metabolic activities in many species of aquatic plants viz, Eichornia species (23) and in Salvinia natans (24). Inhibition activity of Cd is due to inhibition of haemobiosynthesis and chlorophyll formation by integrating with functional –SH group of enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of chlorophyll (25). Similar observation was made by (26) in Hydrilla verticillata at higher concentration of Pb at 20 ppm and Cd att 0.05 ppm. The decline in chlorophyll content in plants exposed to 2.0 ppm of Cd is due to i) inhibition of important enzymes associated with chlorophyll biosynthesis ii) peroxidation of chloroplast membranes resulting from heavy metal induced oxidative stress and iii) formation of metal substituted chlorophyll (27).
Carbohydrates acts as osmoregulaters which maintains water balance in plants (28). Lower concentration (0.1 ppm) of Cd increases the carbohydrate content from 30 mg/g to 36 mg/g in Salvinia and 37 mg/g to 43 mg/g in Pistia from 4 to 12 days exposure duration. The percent enhancement of carbohydrate at 12 days exposure is 13.88% in Salvinia and 13.55% in Pistia compared to respective control. However, higher concentration of Cd inhibits the synthesis of carbohydrate and vary from 21 mg/g to 3 mg/g in Salvinia and 18 mg/g to 10 mg/g in Pistia from 4 to 12 days exposure duration. The rate of carbohydrate at 2.0 ppm of Cd is 67.75% in Salvinia and 74.35% in Pistia during 12 days exposure compared to respective control. The reduction in carbohydrate content can be attributed to the reduced rates of photochemical activities. (18) and also succinic dehydrogenase (SDH) fall in cells indicate oxygen stress and energy crisis and mitochondria disturbances (29).
The lower concentration of Cd (0.1 ppm) enhance the rate of protein synthesis. The protein content vary from 4.32 mg/g to 4.7 mg/g in Salvinia and 4.6 mg/g to 4.7 mg/g in Pistia from 4 and 12 days exposure duration. The percent enhancement is 6.81% in Salvinia and 12.24% in Pistia during 12 days exposure when compared to their respective control. The stimulation of protein synthesis at lower concentration of Cd may be attired to the synthesis of stress proteins (30). The phytochelatins (PCs) are produced by Glutathione reductase (GR) and Phytochelatin Synthetase. These proteins bind and regulate the Cd and sequester the Cd toxicity and thus, plants shows metal tolerance (31).
However, the higher concentration of Cd inhibit protein metabolism in the plants. The protein content declines from 2.7mg/g to 1.8 mg/g in Salvinia and 3.4 mg/g to 2.0 mg/g in Pistia from 4 to 12 days exposure period. The percent inhibition is 59.09% in Salvinia and 59.18% in Pistia during 12 days exposure compared to respective at control. The Cd shows slight inhibitory effect 0.5 mg/lt and severe inhibition of algal growth at higher concentration in some algae ( 32, 18). The DNA and RNA were inhibited, rather due to blocking of _SH group or to the inactivation of RNA and DNA polymerase activity (18, 33).
Profile of metal accumulation
Heavy metal pollution of water is a major environmental concern , is increasing at alarming rate due to anthropogenic activities and is drawing attention and gaining paramanual importance due to its obvious impact on health through the food chain (1, 34). In the present investigation aquatic macrophytes viz, Salvinia and Pistia are used in accumulation.The plants exposed to concentration of cadmium, i.e 0.1 ppm found to accumulate maximum in Salvinia (133.75 µg/g) followed by Pistia (128.50 µg/g) during 12 days exposure duration. Similarly at higher concentration i.e 2.0 ppm of Cd during 12 days exposure duration shows 1381 µg/g in Salvinia and 1125 µg/g in Pistia.
Generally in our experiments it was found that the rate of accumulation is maximum at 4 days exposure irrespective of concentrations and exposure duration, however, at subsequent concentrations and exposure durations it is marginal. Similar observations were also made by (35) in Nastutium officinale and Mentha aquatic to the exposure concentrations of 0.1 and 0.5 ppm of Cd. Similar observation was made by (36) in the accumulation of Nickel in Hydrilla verticillata and Cd and Pb in Salvinia cuculata (24). The increase in the accumulation might be due to increased number of binding sites for the complexation of heavy metal ions, leading to the increased absorption, however, slow accumulation may be attributed to binding ions to the plants and establishment of equilibrium status between adsorbate and adsorbent (37, 38).
CONCLUSION
It is concluded from the findings that morphological, biochemical responses and profile of metal accumulation by Salvinia and Pistia were directly proportional to concentration of metal and maximum metal uptake was recorded at 4 days exposure and later it was marginal at subsequent concentrations and exposure durations Pistia stratiotes is found to be suitable candidate for toxicity evaluation. Salvinia molesta is the tolerant species and can be used for the remediation of heavy metals from aquatic ecosystem and environmental monitoring.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are thankful to the Principal, B.L.D.E.A’s Degree College, Jamkhandi (India), Research and Development centre, Bharthiar University, Coimbatore. Dept. of Botany, Karnatak University Dharwad for providing necessary facilities to carry out research work. Further, the author acknowledges the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The author is also grateful to authors / editors, publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been received and discussed.
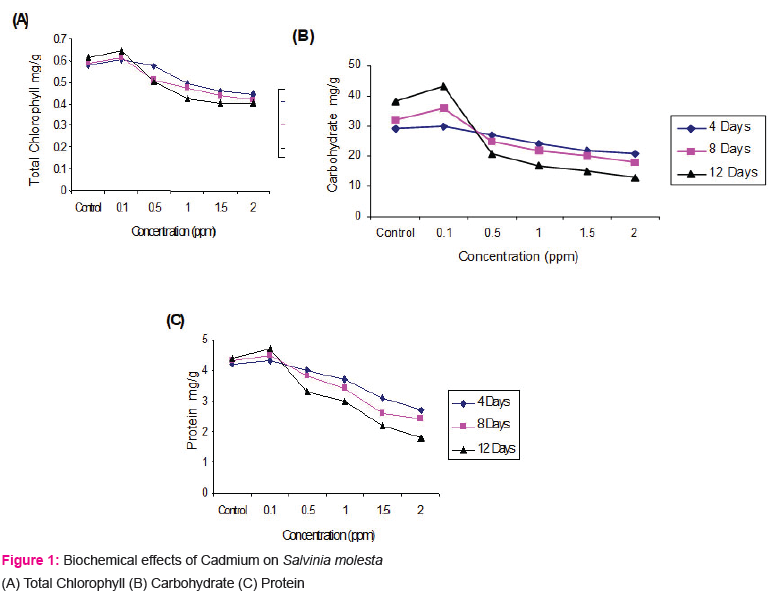
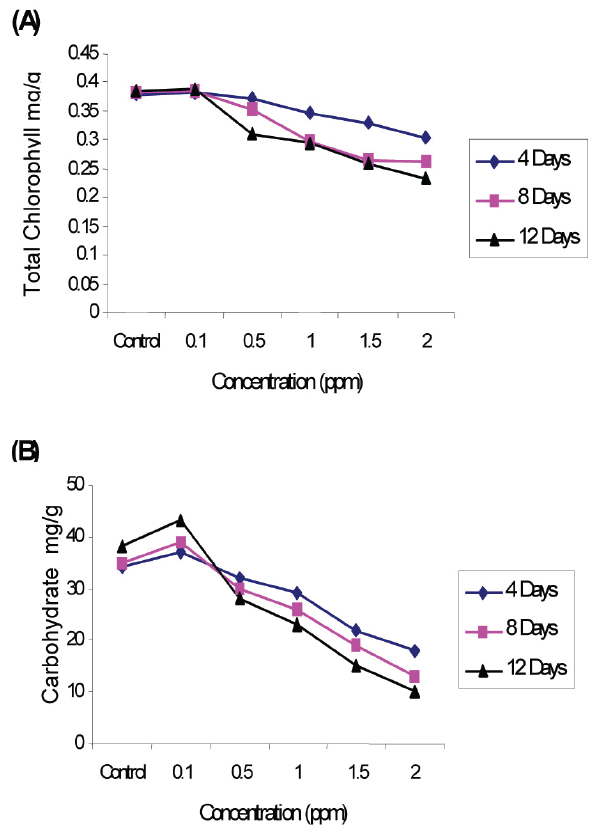
Figure 2: Biochemical effects of Cadmium on Pistia stratiotes.
(A) Total Chlorophyll (B) Carbohydrate (C) Protei
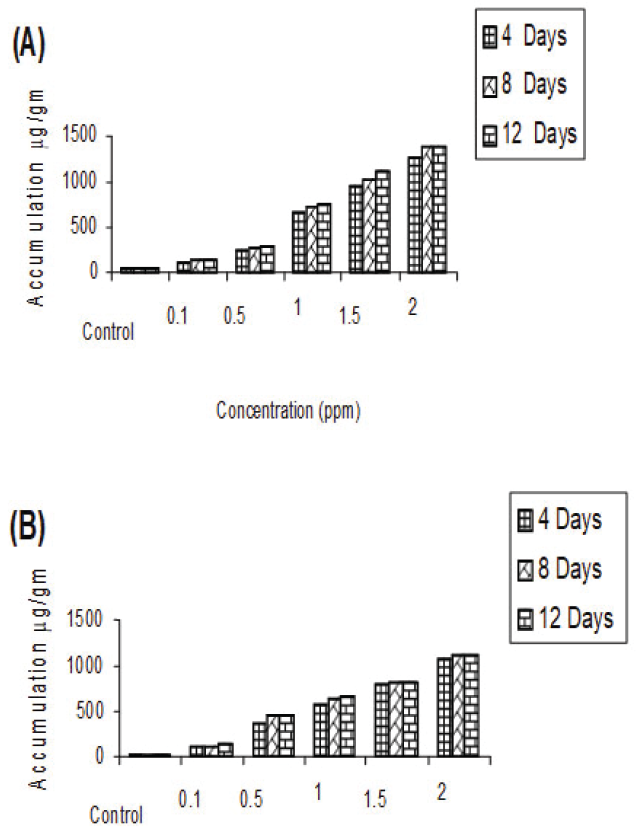

Figure 3: Accumulation profile of Cadmium by aquatic macrophytes.
(A) Salvinia (B) Pistia
References:
-
Dushenkov, V., Kumar, P.B.A.N., Motto, H. and Raskin, I. 1995. Rhizofiltration the use of plant to remove heavy metals from aqueous streams. Environ. Sci. Tech. 29:1239-1245.
-
Yongpisanphop, J., Chue, M. K. and Porethitiyook, P. 2005. Toxicity and accumulation of Lead and Chromium in Hydrocotyle umbellate, Journal of Environmental Biology. 26(1):79-89.
-
Prasad, M.N.V. 1997. Inhibition of maize leaf chlorophyll carotenoids and gas exchange functions by Cd. Photosynthetica. 31: 635-640.
-
Brix, H. and Schierup, H.H. 1989. The use of aquatic macrophytes in water pollution control. Ambio, 18: 100-107.
-
Satyakala, G. and Jamil, K. 1992. Cr-induced biochemical changes in Eichhornea crassipes (Mart) Solms and Pistia stratiotes L. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 48: 921-928.
-
Wilde, E. W. and Benemann, J. R. 1993. Bioremoval of heavy metals by the use of micro-algae. Biotech. Adv. 11:781-812.’
-
Brahmbhat, N., Patel, R. and Jasrai, R.T. 2013. Heavy metal accumulation in Oscillation sp. Induced biochemical response, Advances in Applied Science Research, 4(3):182-185.
-
Van Asche, F. and Clijsters, H. 1990. Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 13: 195-206.
-
Weckx, J. and Clijsters, H. 1996. Oxidative damage and deference mechanisms in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol. Plant. 96: 506-512.
-
Arnon, D.I. 1949. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplast Poly-phenol Oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol,24: 1-15.
-
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Randall, R. J. Farr, A. 1951. Protein determination by the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265-275.
-
Dubois, M., Gilles, K.A., Hamilton, J.K., Rebers, P.A. and Smith, F. 1956. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances.Annul. Chem. 28: 350-356.
-
Allen, S.E., Grimshaw, H.M., Parkinson, J.A.and Quarmby, C. 1974. Chemical analysis of ecological materials. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford.
-
Garg, P., Chandra, P. and Devi, S. 1994. Cr (VI) induced morphological changes in Limnanthemum cristatum Griseb: A possible biondicator. Phytomorphology. 44(3and4): 201-206.
-
Saygideger, S. and Dogan, M. 2009. Pb and Cd accumulation and toxicity in the presence EDTA Lemna minor L. and Ceratophyllum demersum L.Bull. Environ. Contam, Toxicol. 73: 182-189.
-
Koppitte, P.M., Asher, C.J., Koppitte, R.A. and Menzies, N.W. 2007. Toxic effects of Pb2+ on growth of cowpea (Vignaunguic-ulata).Environ Pollut 150: 280-287.
-
Sobero, M. C., Beltarano, J. and Ronco, A. E. 2004. Comparative responses of Lemnaceae clones to Cu (II), Cr (VI) and Cd (II). Toxicity. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 73:416-423.
-
Mathad, P., Angadi, S. B. and Mathad, R. D. 2004. Short and long term effects of exposure of microalgae to heavy metals. Asain Jr. of Microbiol. Biotech. Env. Sci. 6(1): 99-106.
-
Mudhakavi, J. P. and Narayana, B.V. 1997. Toxic heavy metals contamination of the soil and biota: Part II- environmental implications, IJEP. 18(2): 108.
-
Rajendra, J., Muthukrishnan. and Gunashekaran, P. 2003. Microbes in heavy metal remediation. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 41: 935-944.
-
Ornes, W. H. and Sajwan, K. S. 1993. Cadmium accumulation and bioavailability in coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum. L) Water, Air and Soil Pollution. 69:291-300.
-
Prasad, M.N.V. 2004. Metallothioneins, metal binding complexes and metal sequestration in plants. In: Prasad MNV (Ed), Heavy metal stress in plants: From biomolecules to ecosystems. Springer-Verlag. Heidelberg Narosa publishing House, New Delhi. 47-83.
-
Zhu, Y. L., Zayed, A. M., Qian, J. H., Souza, M. and Terry, N. 1999. Phytoaccumulation of trace elements by wetland plants. Water hyacinth, J. Environ. Qual. 28,339-344.
-
Phetsombat, S., Kruatrachue, M., Pokethitiyook, P. and Upatham, S. 2006 . Toxicity and bioaccumulation of Cadmium and Lead in Salvinia cucullata. Journal of Environmental Biology. 27(4) 645-652.
-
Heng, L.Y., Jusoh, K., Mui Ling, C.H. and Indris, M. 2004. Toxicity of single and combinations of Pb and Cd to cynobacteria Anabaena flos-aquae. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 72: 373-379.
-
Singh, A., Kumar, C.S. and Agarwal, A. 2011. Phytotoxicity of Cadmium and Lead in Hydrilla verticillata (L.F) Royle. Journal of Physiology3: 01-04.
-
Patsikka, E., Kairavuo, M., Seren, F., Aro, E.M. and Tyystjavi. 2002. Excess copper predisposes photosystem II to Photoinhibition in vivo by outcompetingiron and causing decrease in leaf chlorophyll. Plant Physiol 129: 1359-1367.
-
Mohan, B. S. and Hosatti, B. B. 1997. Potential phytotoxicity of Pb and Cd to Lemna minor grown in sewage stabilization ponds. Environmental pollution. 98:233-238.
-
Azharbaig, M. B., Joseph, K., Vijay Rao, K. and Jayantha. 1999. Heptachlor induced changes in the enzymes associated with carbohydrate metabolism in functionally different muscles of Chenna punctatus J. Ecotoxicol. Environ. 1:156-161.
-
Reddy, G. N. 1992. Cadmium induced biochemical changes in Scenedesmus quadricauda and Oryza sativa Ph. D Thesis submitted to the University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad.(India).
-
Steffens, J. C. 1997. The heavy metal binding peptides of plants, Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 41: 553-575.
-
Lasheen, M. R., Salwa, A., Sheata, Gamila, H. and Ali. 1990. Effect of Cadmium, Copper and Chromium (VI) on growth of nile water algae. Water, Air and Soil Pollution. 50:19-30.
-
Romero-Puertas, M.C., Corpas, F.J., Rodriguez-Seranno, M., Gornez, M., and Dei Rio, L.A. 2007. Differential expression regulation of antioxidative enzymes by cadmium in pea plants. J Plant Physiol164: 1346-1357.
-
Prasad. M.N.V. 1997. Trace metal In: Plant ecophyscology (Ed. Prasad. M.N.V) John Wiley and Son. New York. 207-249.
-
Aslan, M., Unlu, M. Y., Turkmen, N. and Yilmaz, Y. Z. 2003. Sorption of Cd and effects on growth, protein content and photosynthetic pigment composition of Nasartium officinale R. Br. and Mentha aquatica L. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 71:323-329.
-
Sinha, S. and Pandey, K. 2003. Ni induced toxic effects and bioaccumulation in the submerged plants, Hydrilla verticillata (L.F). Role under repeated metal exposure. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 71:1175-1183.
-
Rai, A.K. and Kumar, S. 1999. Removal of Cr (VI) by low cost dust adsorbents. Applied Microbiol. Biotechno. 39: 661-667.
-
Sibihi, K., Cherifi, O., Agarwal, A., Oudra, B. and Aziz, F. 2012. Accumulation of toxicological effects of cadmium, copper and zinc on the growth and photosynthesis of the fresh water diatom Planothidium lanceolatum (Brebison) Lange-Bertalot; A laboratory study. J Mater Environ Sci3: 497-506.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License