IJCRR - 10(8), April, 2018
Pages: 20-24
Date of Publication: 28-Apr-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Interplay between the Levels of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Nitric Oxide in Preeclampsia
Author: Mohit Upadhye, Aditya Tolat, Tanvi Karambelkar, Ankita Tikalkar, Shruti Mulgund, Rupali Pawar, Rahul Chaudhari, Subodhini Abhang
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Preeclampsia is a leading cause of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality all over the world. Endothelial dysfunction is the chief mediator of clinical manifestations of preeclampsia, which are hypertension and proteinuria. Asymmetric dimethylarginineis an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase that induces endothelial dysfunction by reversibly inhibiting nitric oxide production from l-arginine.
Materials and Methods: We conducted a prospective case-control study to estimate the levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine and nitric oxide in the maternal serum of pregnant women with and without preeclampsia. Pregnant women with non-severe preeclampsia (n=40) and healthy, normotensive women (n=40) admitted for normal vaginal delivery were enrolled in the study.
The serum levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine were estimated using ELISA and those of nitric oxide by Griess reaction.
Results: After analyzing the data we found that the levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine were significantly higher and those of nitric oxide significantly lower in cases. There was no significant correlation between the levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine and nitric oxide, suggesting a role of factors other than asymmetric dimethylarginine in the regulation of nitric oxide metabolism. Nitric oxide showed significant negative correlation with the systolic BP and mean arterial pressure of the cases whereas asymmetric dimethylarginine did not, which implies that nitric oxide is an important determinant of BP in preeclampsia.
Conclusion: The present study highlights the interplay between asymmetric dimethylarginine & nitric oxide and its role in the etiopathogenesis of preeclampsia. It is a complex, multifactorial interaction with no one-to-one relationship and can serve as the biochemical focus of the treatment of preeclampsia.
Keywords: Asymmetric dimethylarginine, Nitric oxide, Preeclampsia
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2018.10804
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
Preeclampsia, a hypertensive disease of pregnancy, is a major cause of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. Preeclampsia alone complicates about 3% of pregnancies whereas all hypertensive disorders together affect about 5 to 10% of pregnancies worldwide.(1) In India, the incidence of preeclampsia is reported to be 8 to 10% amongst registered pregnant women. Preeclampsia is defined as hypertension in pregnancy after ≥20 weeks of gestation with systolic blood pressure of ≥140 mmHg or a diastolic pressure of ≥90mmHg as measured twice, 4-6 hours apart and proteinuria ≥30mg per day (≥1+ on dip-stick) in a minimum of two random urine samples collected at least 4-6 hours, but not more than 7 days apart.(2)
During normal pregnancy, certain structural modifications take place in the myometrium and spiral arteries of the uterus. The villous cytotrophoblast invades into the myometrium and leads to the loss of endothelium and muscle fibres of the spiral arteries. This converts the spiral arteries into low resistance vessels.(3) Pre-eclampsia is caused by the defective invasion of the spiral arteries by cytotrophoblastic cells. This increases the resistance of spiral arteries leading to chronic placental ischemia. The ischemic placenta produces free radicals, oxidized lipids, cytokines, and serum soluble vascular endothelial growth factor leading to oxidative stress.(4)
All these factors cause severe endothelial dysfunction leading to the classical manifestations of preeclampsia that are hypertension and end-organ damage.(5) This adversely affects the fetal circulation causing intrauterine growth retardation or even intrauterine death of the fetus.(6)
Endothelial dysfunction leads to derangement in a number of biochemical parameters out of which asymmetric dimethyl arginine and nitric oxide are well-known factors.
Asymmetric dimethylarginine is one of the degradation products of methylated proteins. Its formation is catalyzed by the enzyme protein arginine methyltransferase type 1 and the methyl group is donated by S-adenosyl methionine.(7) Asymmetric dimethylarginine and other asymmetrically methylated residues are competitive inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase.(8) Asymmetric dimethylarginine is cleared by renal and non-renal routes such as pancreas, liver, brain and aorta in which it is degraded by the enzyme dimethyl arginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH) into citrulline and dimethylamine.(9)
Asymmetric dimethylarginine is a mediator molecule of endothelial dysfunction implicated in the pathogenesis of many cardiovascular diseases. This action is mediated by the inhibition of nitric oxide synthase enzyme as well as direct endothelial toxicity. Asymmetric dimethylarginine has been suggested as a strong and independent risk factor for total mortality and cardiovascular outcome.(10)
The endothelial cells are chiefly responsible for the vascular homeostasis. They respond to a variety of stimuli by elaborating a host of vaso-active agents, primarily nitric oxide, also known as the endothelium-derived relaxing factor.(11) A principal intracellular target for nitric oxide is guanylate cyclase, which, when activated, increases the intracellular concentration of cyclic guanosine monophosphate, which in turn activates protein kinase G.(12) Acting through this pathway, nitric oxide induces relaxation of vascular smooth muscle and inhibits platelet activation and aggregation.(13)
High concentrations of asymmetric dimethylarginine are associated with inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and obesity.(14)Asymmetric dimethylarginine and nitric oxide have been studied more extensively in cardiovascular diseases. There are conflicting remarks about their role in preeclampsia in the literature. Hence it was of interest to understand the interplay of these two molecules in preeclampsia.
MATERIALS & METHODS
We conducted a case-control study in the Department of Biochemistry of B.J. Govt Medical College and Sasoon General Hospital Pune, a tertiary care teaching hospital, during the period of February-March 2017. Ethical clearance was obtained from the institutional ethics committee.
The study comprised of 40 cases of preeclampsia and 40 normotensive, healthy pregnant women as controls, admitted for normal vaginal delivery in Sasoon General Hospital in the above mentioned time period. The samples were collected immediately after admission to the labour room.
The diagnostic criteria for preeclampsia were, having an onset at ≥20 weeks of gestation, systolic blood pressure of ≥140 mmHg or a diastolic pressure of ≥90mmHg as measured twice 4-6 hours apart and ≥30mg per day of proteinuria (≥1+ on dip-stick) in a minimum of two random urine samples collected at least 4-6 hours but not more than 7 days apart. Normal pregnant women in their third trimester of pregnancy were taken as controls.
The inclusion criteria for cases were: age 18-30 years, patients in the third trimester of pregnancy, bp ≥140/90 mmHg at the time of sample collection, ≥1+ proteinuria on dip-stick test at the time of sample collection. Bothprimi and multigravida patients were included.
The exclusion criteria for both cases and controls were the presence of any comorbidities other than preeclampsia, any history of infections including HIV, HBV or HCV, gestational age less than 28 weeks and peeclampsia with complications i.e. severe preeclampsia.
After explaining all the details, a written informed consent was taken from each patient. A detailed history of the patients was recorded on a preformed questionnaire. After taking proper aseptic precautions 5ml of blood sample was collected in a plain vacutainer from each patient. The serum was separated and was stored at -20?C.
Asymmetric dimethylarginine was measured by Human asymmetric dimethylarginine ELISA kit and nitric oxide by cadmium reduction method (Griess reaction).(15)
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Unpaired t-test was performed to compare all the parameters between cases and controls. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated to assess the correlation between asymmetric dimethylarginine, nitric oxide and blood pressure of the patients. Regression analysis was done for the parameters with a significant correlation.
RESULTS
The mean age in preeclampsia cases was 23.925±4.33 years and that in controls is 23.3±3.083 years. The mean systolic blood pressure of cases, being 153.75±11.55 mmHg, was significantly higher than that of controls i.e. 114.6±8.53 mmHg (P<0.0001). The mean diastolic blood pressure of cases, being 102.4±9.48 mmHg, was significantly higher than that of controls i.e. 79.65±8.20 mmHg (P<0.0001.) Similarly, the average mean arterial pressure of cases was 119.5167±8.95 mmHg, which was significantly higher than that of controls, being 91.3±7.242 mmHg (P<0.0001). (Table 1)
The mean asymmetric dimethylarginine concentration in cases was 0.7425±0.208 µmol/L and that in controls was 0.61755±0.1337 µmol/L. It was significantly higher in cases than in controls with P<0.0018. The mean nitric oxide concentrations in cases and controls were 24.7400±10.03 mmol/L and 57.7923±11.84 mmol/L respectively. It was significantly less in cases than in controls with P<0.0001. (Table 1)
In patients withpreeclampsia, we found that there was a significant negative correlation between nitric oxide and systolic blood pressure and also between nitric oxide and mean arterial pressure. There was no correlation between nitric oxide and diastolic blood pressure. (Table 2)
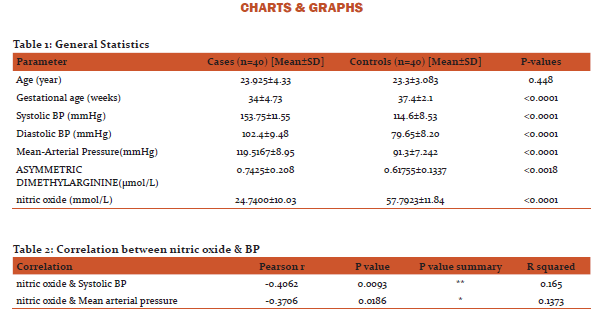
Regression analysis was applied for nitric oxide (X) vs. Systolic blood pressure (Y). At 95% confidence limit the slope of the line was -0.46775±0.34575 which was significantly non-zero with P=0.0093. The equation of the line was obtained as Y = -0.4678*X + 165.3. This implies that for a 10 mmol/L decrease in serum nitric oxide concentration the systolic blood pressure increase by 4.678 mmHg. (Graph 1)
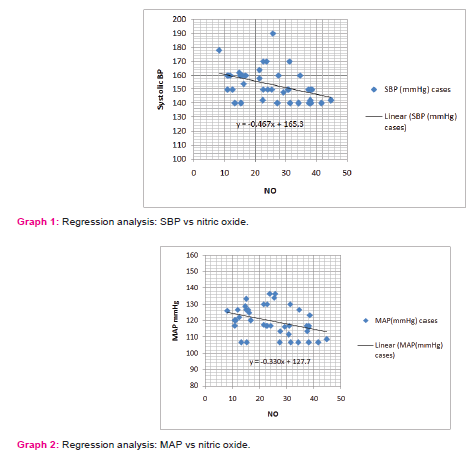
Similarly on applying the regression for nitric oxide (X) vs. MAP (Y), at 95% confidence limit the slope of the line was -0.330755±0.272345. The slope was significantly non-zero with P=0.0186. The equation of the line was obtained as Y = -0.3307*X + 127.7. This implies that for a 10 mmol/L decrease in serum nitric oxide concentration the mean arterial pressure increases by 3.307 mmHg. (Graph 2)
No correlation was found between asymmetric dimethylarginine and the systolic, diastolic and mean arterial pressures of patients with preeclampsia.
Even though there was a significant increase in the levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine and reduction in the levels of nitric oxide in patients of preeclampsia, no correlation could be demonstrated between the two parameters.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we found that there is a highly significant increase in the serum concentration of asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients of preeclampsia as compared to the normal pregnant women (Table 1, P<0.0018). This could be explained by chronic placental ischemia seen in preeclampsia which leads to oxidative stress. Oxidative stress diminishes the activity of the enzyme DDAH that normally degrades the asymmetric dimethylarginine, thus leading to its rise.(16) Similar findings were reported by Anders Pettersson, et al.(17)
Asymmetric dimethylarginine is a known cause of endothelial dysfunction. The endothelium of renal vasculature is also affected by the elevated asymmetric dimethylarginine levels leading to proteinuria in preeclampsia. A similar relationship between asymmetric dimethylarginine and proteinuria was shown by K. Caglar et al in their study.(18)
We also observed a very highly significant decrease in the serum concentration of nitric oxide in preeclampsia as compared to the normal pregnancies (Table 2, P<0.0001). As explained above, asymmetric dimethylarginineis a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase. Hence a rise in its levels could be the reason for the observed fall in nitric oxide levels. This is consistent with the findings of the study conducted by Duane T. Lowe.(19)
Taking into consideration the above observations, a negative correlation between asymmetric dimethylarginine (inhibitor) and nitric oxide (product) was expected but was not found statistically significant, which was contradictory to the findings of D Mao et al. who reported a significant negative correlation between the two.(20) This discrepancy may be due to multiple factors involved in the regulation nitric oxide synthesis one of which is the inhibitory effect of asymmetric dimethylarginine on nitric oxide synthase.
Previous studies have pointed out the role of nitric oxide in atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. The study conducted by Vincente Lahera et al described the role of nitric oxide in hypertension by its effects on the kidney (21), also Ji-Yeon Sim has studied its role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension.(22) In our study, we have tried to elucidate the role of nitric oxide in preeclampsia as the cause of hypertension.
On correlation analysis, nitric oxide showed a highly significant negative correlation with the systolic blood pressure (Table 2, r=- 0.4062) and a significant negative correlation with the mean arterial pressure in preeclampsia patients (Table 2, r=-0.3706). This suggests that nitric oxide is the chief determinant of blood pressure in preeclampsia and reduction in its levels can be the cause of hypertension in preeclampsia.
On applying regression analysis we found that a 10 mmol/L decrease in the serum concentration of nitric oxide increases the systolic blood pressure by 4.678 mmHg and mean arterial blood pressure by 3.307 mmHg.
Although asymmetric dimethylarginine, by inhibiting nitric oxide synthase reduces nitric oxide and can thus lead to the development of hypertension, no direct correlation was found betweenasymmetric dimethylarginine and the blood pressure parameters suggesting that factors other than asymmetric dimethylarginine must be playing a role in the regulation of nitric oxide production. The competitive inhibition of nitric oxide synthase by asymmetric dimethylarginine may be overcome by the substrate arginine and its bioavailability may affect the asymmetric dimethylarginine-nitric oxide relationship.
CONCLUSION
The present study demonstrates that the interplay between asymmetric dimethylarginine and nitric oxide may form the basis of the etiopathogenesis of preeclampsia. These interactions are multifactorial and do not demonstrate a one-to-one relationship. Further studies are required for a better understanding of this complex interplay as it can serve as a potential biochemical focus of the treatment of preeclampsia in future.
Limitation: The levels of arginine were not studied in this project.
References:
1. Hutcheon JA‚ Lisonkova S‚ Joseph KS. Epidemiology of pre-eclampsia and the other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2011 Aug 1;25(4):391–403.
2. Uzan J‚ Carbonnel M‚ Piconne O‚ Asmar R‚ Ayoubi JM. Pre-eclampsia: pathophysiology‚ diagnosis‚ and management. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2011;7:467.
3. LYALL F. Mechanisms regulating cytotrophoblast invasion in normal pregnancy and pre?eclampsia. Aust New Zeal J Obstet Gynaecol. 2006;46(4):266–73.
4. El-Sayed AAF. Preeclampsia: A review of the pathogenesis and possible management strategies based on its pathophysiological derangements. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Oct 1;56(5):593–8.
5. Poston L. Endothelial dysfunction in pre-eclampsia. Pharmacol Rep. 2006;58 Suppl:69–74.
6. Meng W‚ Li R. Association between asymmetric dimethylarginine level and preeclampsia: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2017;10(6):8720–7.
7. Spoto B, Parlongo RM, Parlongo G‚ Sgro’ E‚ Zoccali C. The enzymatic machinery for ADMA synthesis and degradation is fully expressed in human adipocytes. J Nephrol. 20(5):554–9.
8. Böger RH. Asymmetric dimethylarginine, an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase‚ explains the “L-arginine paradox” and acts as a novel cardiovascular risk factor. J Nutr. 2004;134(10 Suppl):2842S–2847S; discussion 2853S.
9. Sibal L, Agarwal SC, Home PD, Boger RH. The Role of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) in Endothelial Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2010;6(2):82.
10. Landim MBP‚ Filho AC‚ Chagas ACP. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) and Endothelial Dysfunction: Implications for Atherogenesis. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2009;64(5):471.
11. Tousoulis D‚ Kampoli A-M‚ Tentolouris C‚ Papageorgiou N‚ Stefanadis C. The role of nitric oxide on endothelial function. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2012;10(1):4–18.
12. Cary SPL‚ Winger JA‚ Derbyshire ER‚ Marletta MA. Nitric oxide signaling: no longer simply on or off. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Apr 1;31(4):231–9.
13. Radomski MW‚ Palmer RMJ‚ Moncada S. Characterization of the l-arginine: nitric oxide pathway in human platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct 1;101(2):325–8.
14. Jeyabalan A. Epidemiology of preeclampsia: Impact of obesity. Nutr Rev. 2013;71(0 1):S18-25.
15. Cortas NK‚ Wakid NW. Determination of inorganic nitrate in serum and urine by a kinetic cadmium-reduction method. Clin Chem. 1990 Aug;36(8 Pt 1):1440–3.
16. Nair N‚ Gongora E. Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Aging: Interaction Between NRF-2 and ADMA. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2017 Jul 11;13(3).
17. Pettersson A‚ Hedner T‚ Milsom I. Increased circulating concentrations of asymmetric dimethyl arginine (ADMA)‚ an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis, in preeclampsia. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1998 Jan;77(8):808–13.
18. Caglar K‚ Yilmaz MI‚ Sonmez A‚ Cakir E‚ Kaya A‚ Acikel C‚ et al. ADMA, proteinuria‚ and insulin resistance in non-diabetic stage I chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2006;70(4):781–7.
19. Lowe DT. Nitric Oxide Dysfunction in the Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia. Nitric Oxide. 2000;4(4):441–58.
20. Mao D‚ Che J‚ Li K‚ Han S‚ Yue Q‚ Zhu L‚ et al. Association of homocysteine, asymmetric dimethylarginine, and nitric oxide with preeclampsia. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2010;282(4):371–5.
21. Vicente Lahera Navarro-Cid Josefa Victoria Cachofeiro Joaquin García-Estañ Luis. Nitric Oxide‚ the Kidney‚ and Hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 1997;10(1):129–40.
22. Sim J-Y. Nitric oxide and pulmonary hypertension. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010 Jan;58(1):4–14.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License