IJCRR - 10(8), April, 2018
Pages: 15-19
Date of Publication: 28-Apr-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Lab Diagnosis of Extra Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Comparison of Histopathology, Cytology, ZeihlNeelsen stain and Light Emission Diode Microscopy with Culture and Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests
Author: Meenal Bagdia, Sanjay Bijwe, Nilma Hirani, Ameeta Joshi, Abhay Chowdhary, Manish Agrawal, Amitkumar Bagdia
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: To compare various diagnostic methods for diagnosing Extra Pulmonary Tuberculosis.
Methodology: A total of 173 extra pulmonary specimens depending on the site of infection were collected aseptically in sterile containers for tuberculosis (TB) culture and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)‚ and in formalin for the purpose of cytology and pathology. TB culture was performed using the MGIT 960 liquid system‚ after initial screening using Light Emission Diode (LED) microscopy and ZN staining‚ while all the samples were also processed by Gene Xpert .
Results: Gene Xpert showed a high sensitivity of 85.71% and negative predictive value (NPV) of 98.67% while LED-FM had a high specificity of 98%‚ which was the same as of ZN stain and a high positive predictive value (PPV) of 86.36%.
Discussion: Clinical presentation of Extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) is atypical; especially when the disease involves obscure occult sites and EPTB may not even be considered in the initial list of differential diagnosis. Diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis is challenging due to the paucibacillary nature as well as atypical clinical presentations. Definitive diagnosis of tuberculosis involves demonstration of M. tuberculi by microbiological‚ cytopathological or histopathological methods.
Conclusion: Extrapulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis should hence be made using more than one diagnostic methods. In our present study, Light Emission Diode- Fluorescent Microscopy (LED-FM) proves to be a sensitive‚ specific and cost effective method for diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis..
Keywords: Extrapulmonary, Paucibacillary, Gene Xpert
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2018.10803
Full Text:
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is the major cause of death worldwide. This disease usually affects the lungs, although other organs are involved in up to one-third of cases. If properly treated, TB is curable in virtually all cases. Early diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) in clinical samples becomes important in the control of tuberculosis both for the treatment of patients and for preventing disease transmission in the community.
FNA cytology is a simple and affordable procedure for diagnosis of tuberculosis compared with core-needle biopsy or excision biopsy. FNA offers a wider scope for diagnosis of organ and tissue involvement. Histopathological examination is easy, quick and affordable and provides characteristic findings of M. tuberculosis. But, as the infecting organisms are less in number in extrapulmonary tuberculosis, the sampled site may not represent the infected area and thus, the chances of missing the infected site are increased.
Direct microscopy is used for rapid diagnosis of TB and other mycobacterial diseases, as a relatively longer period of time is required for mycobacteria to be detected by bacteriological culture. For Tuberculosis case detection, microscopy is essential part because of its low cost, rapidity, simplicity of procedure and high specificity.1
Culture is a very sensitive diagnostic technique for tubercle bacilli, detecting as few as 10 to 100 bacilli per ml of sputum.2However, on solid media, the bacilli grow slowly and colonies appear in about two weeks and may sometimes take up to eight weeks.
The rapid detection of M. tuberculosis and drug resistance in infected patients is essential for disease management, because of the higher risk of transmission in community and emergence of MDR-TB (Multidrug resistant tuberculosis) and EDR-TB (Extensively drug resistant tuberculosis).
Molecular methods like Gene Xpert and Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) has been developed in last few years for rapid TB diagnosis.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique is highly emerging as of its high sensitivity and specificity but require more technical expertise and expensive lab. Also, several PCR-based molecular methods have been setup to detect resistance to rifampicin and isoniazid. Amongst the recent molecular diagnostic methods, two commercial DNA strip assays have been developed, the INNO-LIPA Rif TB (Innogenetics, Ghent, Belgium) and the Genotype MTBDR plus (Hain Life-Science, Nehren, Germany). Both the tests are based on reverse hybridization of amplicons (rpoB in the INNO-LIPA Rif TB and rpoB plus katG and inhAin the Genotype MTBDR plus) to immobilized membrane-bound probes, allowing the detection of mutations at the level of the most frequently mutated codons. The presence of a mutation is revealed by the absence of hybridization at the level of the wild-type probes (rpoB WT1 to WT8 for RIF and katG WT and inhA WT1 and WT2 for isoniazid), with a possible positive hybridization signal at the level of the mutant probes.3
Methods
The present study was carried out in the Department of Pathology in collaboration with Microbiology department, in a tertiary care hospital in Mumbai.
Study population and sample collection
A total of 173 patients were enrolled in this study over a period of 18 months. Patients suspected of extrapulmonary tuberculosis were included in the study while those with clinical impression of pulmonary tuberculosis were excluded.
In patients coming with mass, specimen was collected by aspiration. Aspiration was done using 23 gauze needle with attached 10 ml disposable syringe. Body fluids, coming to the department were also collected. The specimen collected was divided into three parts. One part was smeared onto slides, fixed immediately with 95% alcohol and stained by haematoxylin and eosin (H and E) for cytological examination. Second part was used to make another air dried slide for ZN stain, which was then followed by auramine stain. Last portion of the material was collected in Falcon tube and submitted to microbiology department, for PCR and culture.
Tissue samples were collected for histopathologic correlation, when ever biopsy was carried out. Tissue received was examined grossly for presence of exudates, appearance of caseous necrosis, miliary tubercles and matted appearance. Sections were taken and divided into two parts. One part was submitted in Falcon tube to microbiology section, for further procedures of Ziehl Neelsen (Z-N) stain, Fluorescent stain, Culture and Polymerase Chain Reaction(PCR). The other part of the tissue received was processed in an automatic tissue processor. After processing, the paraffin blocks were made. Five microns thick sections were cut on a rotary microtome and then stained with Haematoxylin & Eosin and Ziehl Neelsen (Z-N) stain. Tissue histology was said to be suggestive of TB, if evidenced by presence of granulomatous inflammation, consisting of epithelioid cells, Langhans giant cell and caseation necrosis, surrounded by a rim of lymphocytes. The bacilli appear as yellow to orange, slender, rod-shaped under fluorescent microscopy. In the smears stained by the Z-N method, bacilli appear bright red against the background material counterstained in blue.
All the above samples were collected and processed for LED microscopy and Gene Xpert. Following decontamination and concentration, samples were processed for liquid culture, using MGIT960 system (BD, India). Cultures positive by this system were then processed for Line Probe Assay (LPA).
The kit used at our center for LPA was Geno Type MTBDR Plus version 2.0 manufactured by Hain Life science, Germany which detects resistance to RIF and/or INH using culture isolates. The steps involved were
- DNA extraction from cultured isolates
- A multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- Reverse hybridization, where probes (reaction zones or bands) on the strips are used to interrogate the M. tuberculosis target DNA associated with RIF and INH resistance by detecting sequences complementary to the probes on the strip.
The molecular identification of rifampicin (RIF) resistance was accomplished by detecting the most significant mutations in the 81-bp (base pair) region of the rpoB gene (which encodes the β-subunit of RNA polymerase, the essential enzyme that is inactivated by RIF). High-level resistance to isoniazid(INH) is detected by screening for the most common mutations in the katG gene (which encodes catalase, the enzyme that activates INH). Low-level resistance to INH is detected by screening for mutations in the promoter region of the inhA gene (which encodes the NADH enoyl ACP reductase, involved in cell wall biosynthesis).
Procedure for Gene Xpert involved using an automated instrument which worked on the principle of
- Detection of the target sequences in simple or complex samples using real-time PCR and reverse transcriptase PCR.
- Nucleic acid amplification.
Statistical analysis:
The analysis of the results obtained by comparing various diagnostic tests, was done using open EPI software. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value were calculated using culture as gold standard.
Results
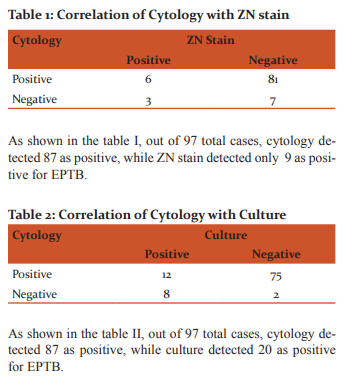
Sample detected positive by any of the diagnostic tests was considered to be positive for extrapulmonary tuberculosis in the present study. Out of the total 173 cases, 108 cases were found to be positive for extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) by one or the other method.
Distribution of 108 extrapulmonary tuberculosis specimens were as follows:
? Lymph node aspirates (49 cases) – Most common
? Fluids (43 cases)
? Histological tissue specimens (11 cases)
? Pus (5 cases)
Most of the site of lymph node aspiration among extrapulmonary tuberculosis cases was from cervical lymph nodes (39 cases out of total 49lymph nodes); other sites included axillary, inguinal, submandibular and supraclavicular lymph nodes. Fluids included pleural fluid, ascitic fluid, bronchoalveolar lavage, cerebrospinal fluid, pericardial fluid and peritoneal fluid,out of which pleural fluid accounted for the majority (25 cases out of 43). Out of the total 108 EPTB cases, 97 were subjected for cytology, which included lymph node aspirates, fluids and pus samples. 11 were subjected for histopathological examination. All 108 samples were subjected to Culture and LED-FM, while LPA was done on the 23 culture positive samples and Gene Xpert on 83 samples, of which 58 cases were positive for extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB). However as the Gene Xpert instrument was not available initially in our department, Gene Xpert could be performed in only 83 cases, out of which 58 cases were positive for extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
Given below are the findings showing comparison of various diagnostic modalities.
Discussion
The smear positivity for AFB on the conventional ZN method in our study was 9.28% while the positivity increased to 17.52% on the modified fluorescent method. In the study done by Vamseedhar Annam et al4, the positivity rates were 44.11% for the ZN method and 81.37% for the modified fluorescent method. The results showed that FM staining technique is more sensitive in the detection of AFB in EPTB samples compared to ZN stain.
In our study ZN smear positivity for AFB was 9.28%, while positivity by routine cytological examination was 89.7%. There are other various reports regarding the sensitivity of ZN smear for extra-pulmonary specimen ranging from as low as 0% to as high as 75%. This limitation has been reported to be due to inadequacy and paucibacillary nature of extrapulmonary specimen.5
In the present study, culture positivity was 20.61% and ZN smear positivity was 9.28%. This is in concordance with the study done by M. Kashif Munir et al5, where culture positivity of extra-pulmonary specimens was 18.46% and was considerably high as compared to the ZN smear positivity of 3.85%, thus proving that culture is a sensitive tool in the diagnosis of extra-pulmonary TB.
When cytology was compared with Gene Xpert out of 56 cases, cytology could detect 53 cases and Gene Xpert could detect 6. Gene Xpert detected 3 cases, which were negative by cytology. Out of these 3 cases, 2 were also negative by culture, ZN stain and LED microscopy.
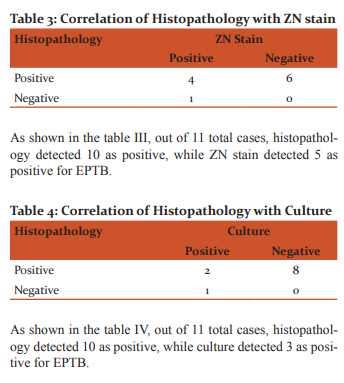
According to our study out of total 11 EPTB samples, Histopathology could detect 10 of them, while LED- FM, culture and ZN stain detected 5, 3 and 5 respectively. Thus positivity rate of Histopathology was 90.90% while of LED- FM and ZN was 45.45% and of culture was 27.27%. In study done by B.R. Maldhure et al6, 67.07% of cases were diagnosed as tubercular pleural effusion by biopsy as compared to our study where positivity rate of Histopathology was 90.90%. Thus histopathology remains one of the most important methods for diagnosing tuberculosis.
In our study, all of the 2 specimens positive for histopathology were also positive for Gene Xpert. In study carried out by SA Patwardhan et al7, PCR positivity was 69.2% and Histopath positivity was 80%. Thus PCR is a rapid and useful method for diagnosis of TB lymphadenitis and definitely increases the positive predictive value of a positive histopathology report.
In our study, positivity of ZN stain was 5.17% (3/58), FM microscopy was 10.34% (6/58), culture was 12.06% (7/58) and Gene Xpert was 15.38% (8/58). In the study done by Mohammed Abdul Mohi Siddiqui et al8, positivity by ZN stain was 5%, culture was 15% and PCR was 70%. Thus PCR as a diagnostic tool has more sensitivity to diagnose extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
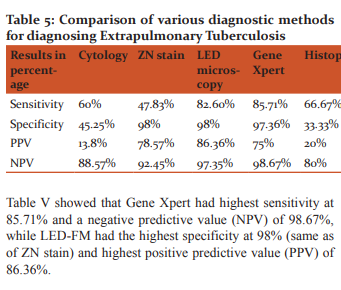
As per Table 5, sensitivity and specificity of FNAC was 60% and 45.25% respectively. In study done by Yohannes Derese et al9, the sensitivity and specificity of FNAC was 81% and 50% respectively. In general, cytopathological morphology in FNAC lacks specificity but has higher sensitivity because non-tuberculous granulomatous patients could also be diagnosed as TBLN. Therefore, relying on cytology alone could lead to false case reporting.
Sensitivity and specificity of Histopathology was 66.67% and 33.33% respectively in our study. In study conducted by SA Patwardhan et al7, the sensitivity and specificity of histopathology was 96% and 78.5% respectively. Histopathological examination is easy, quick and cheap and provides characteristic features of M. -tuberculosis. The presence of caseation necrosis and epithelioid cell granulomas is taken as diagnostic of tuberculosis on Histopathological examination. However, granulomatous lymphadenopathy has a wide differential diagnosis and many other clinical conditions can present the same histopathology as TB lymphadenitis, thus thus decreasing the specificity of histopathology.
ZN stain, in our study had sensitivity and specificity of 47.83% and 98% respectively. In study done by Yohannes Derese et al9, ZN stain for AFB had sensitivity and specificity of 22.9% and 92.4% respectively. The quality of the smear as well as the scanty bacilli found in the FNA could be the main factor for decreased sensitivity.
Sensitivity and specificity of LED-FM in our study was 82.6% and 98% respectively. Specificity of LED and ZN were highest in our study. In the study done by Gerardo Alvarez-Uria et al10, LED fluorescent microscopy has shown sensitivity of 84% and specificity of 98% against culture as the reference standard. The advantage of using the fluorescent staining method is that fluorescent-stained slides can be examined under low magnification allowing for much larger areas of the smear to be examined in a short period of time. The use of the fluorescent method greatly improves the diagnostic value especially in patients with a low density of bacilli that are likely to be missed on ZN-stained smears.
Sensitivity and specificity of Gene Xpert in our study was 85.7% and 97.36% respectively. Its sensitivity was the highest compared to other diagnostic tests in our study. In study done by Doris Hillemann et al11, Gene Xpert sensitivity and specificity was 77.3% and 98.2% respectively.
According to table 5, maximum sensitivity was of Gene Xpert, followed by LED microscopy and maximum specificity was of LED microscopy and ZN stain, followed by Gene Xpert. However, the cost of the Gene Xpert equipment is much higher (approximately 2000 INR in a subsidized laboratory) than LED microscopy, which is a major obstacle for its use in small scale laboratories. Although the Xpert assay does not require operator expertise or external quality controls and is able to provide information about rifampicin resistance, only four samples can be processed every two hours. The biggest limitation of DNA based molecular tests is that these tests can not differentiate between dead and live target organisms. So its relevance has to be judged in light of the overall clinical picture in cases where the patient has received anti-tubercular treatment recently.
Conclusion
Diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis is challenging due to the paucibacillary nature as well as atypical clinical presentations. Its diagnosis should hence be made by considering more than one diagnostic methods. In our present study, Light Emission Diode- Fluorescent Microscopy proves to be a sensitive, specific and cost effective method for diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
Acknowledgement
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Ethical clearance
Ethical clearance was taken from ethics committee.
Consent
Blanket consent was taken.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References:
1]. Singhal R, Myneedu VP. Microscopy as a diagnostic tool in pulmonary tuberculosis. International Journal of Mycobacteriology 2015; 4:1–6.
2]. Ananthnarayan and Panikar's. Mycobacterium I: Tuberculosis. In: Textbook of Microbiology, 9th edition, 2013. Pgs 345-358.
3]. Nu-LAMP TB kit insert.
4]. Annam V, Kulkarni MH, Puranik RB. Comparison of the modified fluorescent method and conventional Ziehl-Neelsen method in the detection of acid fast bacilli in lymph node aspirates. Cyto Journal 2009;6:13
5]. Munir MK, Shabbir I, Iqbal R, Khan SU. Comparison of AFB Smear Microscopy and Culture from Specimens Received for the Diagnosis of Extra Pulmonary Tuberculosis. P J M H S 2009;1(1):59-61.
6]. Maldhure BR, Bedarkar SP, Kulkarnl HR, Paplnwar SP. Pleural Biopsy and Adenosine Deaminase in pleural fluid for the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion. Ind. J. Tub 1994;41:161.
7]. Patwardhan SA, Bhargava P, Bhide VM, Kelkar DS. A study of tubercular lymphadenitis: A comparison of various laboratory diagnostic modalities with a special reference to tubercular polymerase chain reaction. Indian Association of Medical Microbiologists 2011;29(4):389-94.
8]. Siddiqui MAM, Anuradha PR, Nagamani K, Vishnu PH. Comparison of conventional diagnostic modalities, BACTEC culture with polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis. J Med Allied Sci2013;3(2):53-58.
9]. Derese Y, Hailu E, Assefa T, Bekele Y, Mihret A, Aseffa A, et al. Comparison of PCR with standard culture of fine needle aspiration samples in the diagnosis of tuberculosis lymphadenitis. J Infect Dev Ctries2012;6(1):53-57.
10]. Alvarez-Uria G, Azcona JM, Midde M, Naik PK, Reddy S, Reddy R. Rapid Diagnosis of Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis in HIV-Infected Patients. Comparison of LED Fluorescent Microscopy and the Gene Xpert MTB/RIF Assay in a District Hospital in India. Tuberculosis Research and Treatment 2012.
11]. Hillemann D, Gerdes SR, Boehme C, Richter E. Rapid Molecular Detection of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis by the Automated Gene Xpert MTB/RIF System. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2011;49:1202–5
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License