IJCRR - 10(2), January, 2018
Pages: 01-05
Date of Publication: 19-Jan-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Study of Biodegradation of Luffa Cylindrica/Poly(lactic) Acid Composites
Author: Swarnalata Tripathy, Chinmay Pradhan, Chhatrapati Parida
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Objective: The main objective of present research is to convert the agricultural waste Luffa cylindrica (LC) fiber into a valuable product.
Methodology and Results: By injection molding technique, biodegradable composites were fabricated using 2, 5 and 10 weight percent of natural fiber of LC in biodegradable polymer matrix poly lactic acid (PLA).The patterns of disintegration of the virgin PLA and its composites were studied for a period of 75 days in sand, soil and compost environment and for a period of 30 days in bacterial and fungal conditions. The biodegradation were evaluated by measuring weight loss of the composite samples with time at every interval of 15 days in the above mentioned environment. The probable outcome of the study presents that the PLAand the composites using LC fibers almost degrade completely in bacterial environment after 30 days. However,in fungal environment the degradation was found upto 4 %. Lastly the composite samples were unable to degrade in sand, soil and compost environment. Before reinforcement the LC fibers are treated chemically for enhancing fiber matrix adhesion. The thermal
degradation and the structural changes of the chemically treated LC fibers are studied by thermogravimetry analysis and X ray diffractometer.
Conclusion: The fiber parts were mostly consumed by microorganisms. High fiber loading provides larger surface area for the microorganisms as a result the degradation rate is found to be high. Thus, the degradation process is accelerated by the microorganisms.
Keywords: Biodegradation, Biocomposites, Poly(lactic) acid, luffa cylindrica
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2018.1021
Full Text:
Introduction
Increasing environmental concerns has motivated the researchers worldwide to develop and utilize materials that are compatible with the environment. Natural fibers have gained importance as they are cheaper, environment friendly and more sustainable than synthetic or man-made fibers like glass, kevlar, aramid, nylon, terylene etc. Natural or plant fibers are renewable and when they are burnt they leave very less residue and discharge less carbon dioxide in the environment. Thus composites made from natural fibers are environment viable. In the prevailing research, a common tropical fruit found in Odisha, India. luffa cylindrica (LC) also known as sponge gourd, vegetable sponge, wash sponge, gourd towel, dishcloth gourd, loofah gourd is chosen as reinforcement for fabrication of composite materials.It belongs to the family cucurbitaceae and is abundantly found throughout India as an agricultural waste. The LC fibers are composed of 60% cellulose, 30% hemicellulose and 10% lignin. The cellulose present in plant fiber consists of some identical units named as glucopyranoze unit. Each unit contains three hydroxyl groups, which are the active sites for strong bond formation. When the cellulose percent is high, the number of active sites are high leading to better adhesion between fiber and matrix. Such high percent of cellulose in the LCfiber is the motivating agent of our investigation.PLA is one of the most promising biopolymer which is completely biodegradable. It is obtained from natural feed stocks as well as agricultural wastes. It has a wide range of applications in various fields and possess various advantages such as biocompatibility and better thermal processibility. PLA is hydrophobic and LC fibers are hydrophilic. They are thermodynamically incompatible and it leads to poor fabrication of the composites. As the chemical nature of fiber and matrix are different, various treatments like chemical treatment, electron beam irradiation, gamma irradiation, plasma treatment, ultra violet exposure etc are given to the fiber before reinforcement to improve compatibility between LC fiber and PLA matrix. In this study the LC fibers are exposed to various chemical treatments like alkali treatment, bleaching and acid hydrolysis.
Biodegradation is the enzymatic breakdown of living organisms such as bacteria and fungi into their metabolic products. During the process of degradation, PLA gradually degrades to lactic acid which splits into CO2, H2O and biomass.Thermal analysis of composite material is an influential tool for understanding the structural property,heat resistance capacity,mass degradation etc. Thermogravimetric analysis(TGA) is the most important technique to study the thermal behaviour of materials. The information regarding thermal stability of composite materials are indispensible for proper use of these materials.
Kumar et alin 2010 investigated biodegradation of flax fiber reinforced PLA composites. They reported that different amphiphilic additives can be added for delaying and The study of biodegradation of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites have been carried out by many researchers. S.N Surip et. al., in 2016 studied the degradation of Poly lactic acid reinforced with kenaf fibers. The study revealed degradation PLA / kenaf fiber composites increased by 17% compared to degradation of only virgin PLA. A. Araujo et al in 2014 carried out biodegradation assessment of PLA and its nanocomposites in presence of organoclay. They reported that degradation rate of nanocomposites of PLA increased when the composites were exposed to ultra violet radiation. Also they revealed that the rate of degradation was affected by the presence of organoclay in the composites.
However, the study of biodegradation of composites involving PLA and LC fibers are scarce in literature survey. The present research deals with extensive study of biodegradation of PLA/LC fiber composites in soil, sand, compost, bacterial and fungal conditions.
Research Methodology -
Materials-
Polylactic acid (PLA) of grade 4042 D (molecular weight MW~6,00,000), was purchasedfrom Nature Works, USA. The LC fiber was collected from the local forest area. All chemicals such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), sodium hypochlorite (NaClO), sulfuric acid (H2SO4) of AR grade were purchased from E. Merck, India.
Chemical treatment of LC fiber-
Small pieces of LC fibers were cut of length around 2cm and then were washed thoroughly, in order to remove the impurities such as oil, dust etc. Then these were dried at 700C in vacuum oven for 20 minutes. Chemical treatments like alkaline treatment followed by bleaching and acid hydrolysis were done. The LC fibres were soaked in 5% sodium hydroxide solution at 800C for 1 hour for alkali treatment. The main drawback is hydrophillic nature of the natural fibres which causes poor adhesion between fiber and matrix. Therefore, such composites possess very poor mechanical properties in wet conditions. The LC fibers were treated with sodium hydroxide to improve interfacial bonding and to reduce moisture absorption. The hemicellulose and lignin were treated from the natural fibers during alkaline treatment. The number of hydroxyl groups present in the fiber are gradually reduced in order to increase the hydrophobicity of fibers that helps in strengthening the bond between fiber and matrix. Bleaching of alkali treated LC fibers was done with 2% sodium hypochlorite solution. Continuous stirring of the mixture was done at 800C for 2 hours. Bleaching increases the whiteness of the fibers. The bleached LC fiber/ water suspension was finally prepared andkept on an ice bath. Along with continuous stirring, sulphuric acid was added slowly to the suspension kept in an ice water bath till it reached the final concentration of 60% sulphuric acid. Under continuous stirring the obtained suspension was heated at 250C for 20C. The mixture was centrifuged in an ultracentrifuge for 20 minutes at 300C with 7000 rpm to remove excess acid. Isolation of micro and nano-fibers with a high degree of crystallinity was obtained by acid hydrolysis by removing the amorphous regions of the raw cellulose material. The degree of polymerization (DP) and the molecular weight of the bleached fibers decreases due to acid hydrolysis.
Processing and fabrication of composite -
Prior to use, the PLA pellets and the LC fibers were dried at 800C for 24 h under vacuum. In a micro-compounding moulding equipment (DSM Micro SSC Compounding System, DSM research, The Netherlands), the polymer and fiber were mixed at 1700C for 10 minutes at 100rpm.
The PLA pellets and LCfibers were mixed In different weight proportion to obtain B0, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5 and B6 samples. The virgin Poly lactic acid is B0. The LC fibers are in the weightratio 2%, 5% and 10% in B1, B2 and B3 samples respectively. In samples B1, B2, B3, the LC fibers are subjected to chemical treatments such as alkali treatment, bleaching and acid hydrolysis. The LC fibers are in the weight ratio 2%, 5% and 10% in B4, B5 and B6 samples respectively. But in B4, B5 and B6 samples, LC fibers were exposed to only alkali treatment and bleaching. Fibers were not subjected to acid hydrolysis.
Biodegradation of LC fibers in soil, sand and compost – The degradation of the samples were checked by weight loss over time (at an interval of 15 days) in soil-sand, sand-compost, soil-compost and soil-sand-compost. Samples were put in thermocol cups containing mixture of sand, soil and compost. These cups were kept at room temperature. Water was sprinkled on it every day. After every 15 days, samples were taken out, washed with water and then dried. Then the samples were weighed for evaluation.
Microbial degradation of LC fibers -
- Degradation by bacteria – 8.75 grams of nutrient broth was dissolved in 350 ml of distilled water. It was mixed thoroughly. 7 conical flasks were taken and in each flask, 50ml of nutrient broth was poured. The mouth of the flask was plugged with cotton and covered with brown paper. It was autoclaved for 45 minutes. The conical flasks were kept in laminar air flow under ultra violet light for 20 minutes. Then 20μL of bacterial strain (Bacillus subtilis) was added in each flask using sterilised micropipette and these flasks were kept in an incubator at 30ºC. After 24 hours, the samples of LC fibers were put in the flask. After 15 days the samples were taken out, washed and dried. Then the samples were weighed for evaluation.
- Degradation by fungus – 350 ml of potato dextrose broth was done by dissolving 7.4 gms of potato dextrose broth powder in 350 ml of distilled water. In 7 conical flasks, potato dextrose broth was poured, each flask containing 50ml of potato dextrose broth. The mouth of the conical flask was plugged with cotton and brown paper was wrapped over it. It was autoclaved for 45 minutes. The conical flasks were then placed in laminar air flow under ultra violet light for 20 minutes. Then 20μL of fungal strain (Fusariumoxysporum) was added in each conical flask and these flasks were kept in an incubator at 37ºC. After 72 hours, the samples were put in the flasks.
Result –
Biodegradation of composites
Biodegradation studies of neat pure PLA and PLA/ LC fiber composites were carried out in soil/sand, sand/compost, soil/compost, soil/sand/compost, and finally in bacterial and fungal environments. Ultimately, biodegradation depends on the nature of the materials. PLA biocomposites will expand further if the materials degrade faster after their end-uses.
Biodegradation of composites in soil/sand
The PLA and its composites are not affected by soil/sand composition which may be attributed to chemical nature of PLA.The degradation nature is closely related to the chemical component and bonding characteristics of the plastic.
Discussion
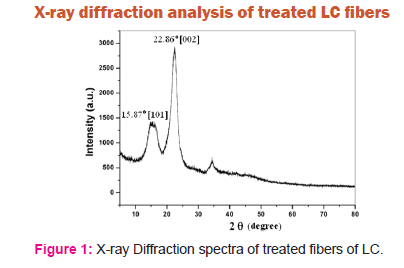
The figure 1 shows intense peaks at 15.87o and 22.86o. The peak at 15.87o corresponds to amorphous cellulose or cellulose II of [101] crystallographic plane. The peak at 22.86o correspond to crystalline cellulose [cellulose I] of[002] crystallographic plane. Natural fibers are composed of cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin.The presence of peaks at 15.87o and 22.86o confirms that when the LC fibers are treated chemically, hemicelluloses and lignin are removed and only cellulose is present after chemical treatment. Two different crystalline allomorphs have been identified by the characteristic X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of treated fiber viz. cellulose I and cellulose II. Cellulose I is the most abundant form found in nature. Cellulose II can be prepared by mercerization or alkali treatment.In other words, the chemical modification of LC fiber exposed large numbers of cellulosic hydroxyl groups which can increase the adhesion between the fiber and matrix. Removal of hemicelluloses and lignin decreases the hydrophilic nature of the fiber which attributes for increase of bio compatibility between fiber and matrix.
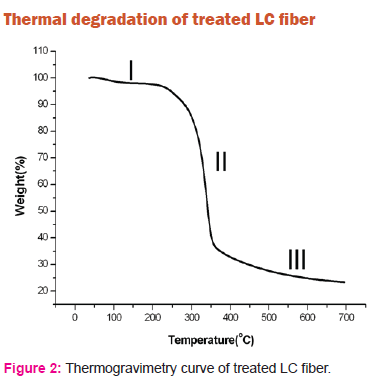
Natural fibers are hydrophilic in nature and absorb a lot of moisture. Thus when the fibers are heated there is loss of mass due to the moisture in the temperature range of 150oC. But when the LC fibers are treated with alkali, the hydrophilic nature is decreased due to removal of hemicellulose and lignin. This is evident from figure 2. When the chemically treated LC fiber is heated up to 200oC, there is only a marginal loss of mass of 2.37%. This is shown as stage I in the figure 2. In the second stage (II) in the temperature range 250oC to 350oC a rapid loss of mass of around 55% is observed. This loss of mass is due to degradation of amorphous cellulose present in the sample. In the third stage (III) beyond 350oC the degradation is due to decomposition of crystalline cellulose. There is a mass loss of 76% observed for treated LC fibers at 600oC compared to loss of only 61% in the composites with untreated LC fibers. The higher loss of mass of the cellulose fibers at high temperatures beyond 350oC may be attributed to removal of lignin and hemicellulose during the chemical treatment.
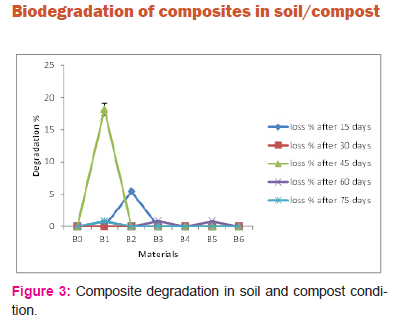
Figure 3 shows composite degradation in soil and compost. Here the sand was replaced by compost which initiated the bio degradation. Composites B1 (2%fiber) and B2 (5%fiber) samples degraded slightly. No biodegradation was seen in other composite samples. The moisture and heat present in the compost attacks the PLA chains and splits them apart leading to smaller polymer fragments, and finally, lactic acid. It can be suggested that microorganisms found in active compost consume the smaller polymer fragments and lactic acid as energy source. PLA degradability is driven by the hydrolysis and cleavage of the ester linkages in the polymer backbone. But when the fiber weight percentage increases as in composite sample B3 (10% wt reinforcement) biodegradation didn’t occur. It may be due to non-breakage of polymer chain by presence of excess fiber. Also no biodegradation was observed in composite sample B4, B5 and B6 where the fiber were exposed to only alkali treatment and bleaching. So it can be concluded that the fiber treated with alkali followed by bleaching and acid hydrolysis (sample B1, B2)are actively biodegraded.
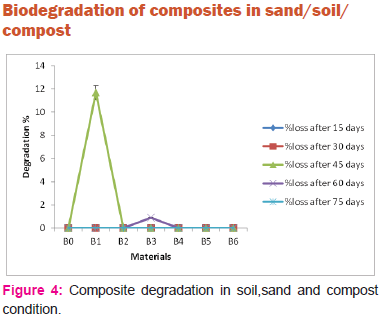
Figure 4 shows degradation in sand-soil-compost medium. Composite sample B0 (virgin PLA) does not degrade at all. However when the virgin PLA is reinforced by LC fibers the composite samples start degrading.Thus soil /compost/sand environment is further a better active medium for biodegradation as compared to sand/compost and soil/compost environment.
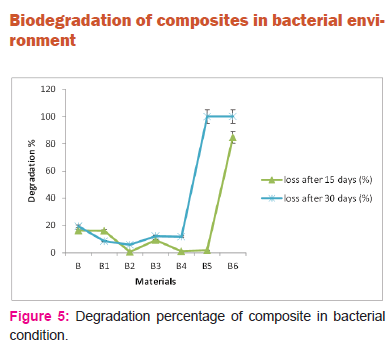
Figure 5 indicates degradation of composites in bacterial condition. Allthe composite samples degraded in bacterial environment unlike soil/ sand/compost environment where only composite samples B1 and B2 degraded. Thus the weight of LC fiber in composites play an important role in bio degradation in bacterial environment. However the rate of degradation in sample B4, B5 and B6 are observed to be more compared to sample B1, sample B2 and sample B3.Thus when the fibers are subjected to acid hydrolysis as in sample B1, sample B2 and sample B3 the degradation is low. This may be due to strong bonding between acid hydrolyzed fiber and PLA matrix. Thus degradation in bacterial environment is more prominent compared to soil/ compost/sand environment.
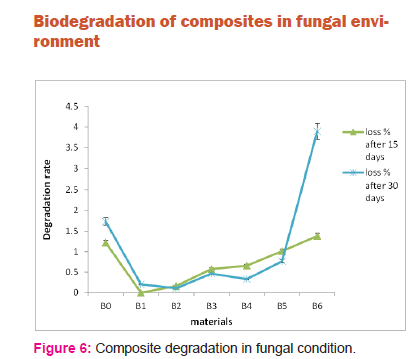
Figure 6 shows degradation of composites in fungal condition. Again the rate of degradation in sample B4, B5 and B6 are observed to be more compared to sample B1, sample B2 and sample B3 which shows better chemical bonding between acid hydrolyzed fiber and PLA matrix. However degradation in bacterial environment is more prominent compared to degradation in fungal environment.
Conclusion
The biodegradation of PLA/ LC fibers were carried out in sand, soil, compost and microbial (bacterial and fungi) conditions at room temperature. The composite did not degrade in sand, soil and compost. But the PLA composites degraded under bacterial and fungal conditions. This work effectively demonstrates the conversion of a waste product like LC fiber into a highly valuable product and its disposal under various environments.
Acknowledgement
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. Major research project funded by DST, Government of Odisha, 1184/ST-(BIO)-02/2017 Dt: 1/3/17
References:
- AraújoA., OliveiraM., Oliveira R., Botelho G., Machado A. V. ; `Biodegradation assessment of PLA and its nanocomposites’; Environ SciPollut Res (2014) 21:9477–9486
- Bhatia, A, Gupta, R, Bhattacharya, S, Choi, H. International Polymer Processing, vol.25 (1), 5-14(2010).
- Kumar R., Yakubu M.K., Anandjiwala R.D.; `Biodegradation of Flax Fiber Reinforced Poly lactic acid’; Express Polymer Letters Vol.4, No.7 (2010) 423-430
- S.N. Surip, W.N R Wan Jaafar, N.N. Azmi, N.A. Hassan.; `Biodegradation properties of polylactic acid reinforced kenaffibers’; Acta Physica Polonica A Vol.129, No.3 (2016) 835-837
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License