IJCRR - 9(23), December, 2017
Pages: 32-40
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Ontology Based Optimization with Adaptive Network Based Fuzzy Inference System Based Health Maintenance Systemv
Author: R. Jaya, C. S. Pillai, R. Jagadeesh Kannan
Category: Technology
Abstract:In late years, economic growth and globalization have driven significant modernization of Ayurvedic Medicine in India. According to Ayurvedic Medicine, human body is divided into three constitutions/tridoshas based on the hypothesis of Prakriti. The categories of Prakriti are written based on the philosophy of tridoshas namely Vata, Pitta and Kapha. Ayurvedic clinicians' records/documents the consultation of patient along with patient's Prakriti in a paper. This is neither exchanged nor made accessible to other clinicians'. Due to rapid advancement in electronic media, the necessity of digital Ayurvedic patient management systems could help in diagnosing the patient before the consultation of clinicians. Henceforth, an electronic health record system is proposed that uses ontology oriented procedure to compute the physical constitutions of a human body. Specifically, a rule based system is developed and evaluated using Particle Swarm Optimization - Adaptive Network based Fuzzy Inference system (PSO-ANFIS). The ontological inputs to the fuzzy interface includes Doshas, food and lifestyle recommendations, obtained from clinical and textual data. Automated system created using ontology oriented PSO-ANFIS interface supports food, herbs, diet and life style recommendation to the patients'. The proposed model is evaluated with different patient and the sample is tested with the clinicians. The results proved that the proposed method fits with better results than the conventional ones.
Keywords: Particle swarm optimization, Adaptive network based fuzzy inference system, ANFIS-PSO Markup Language
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2017.9237
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The core aim of data mining is to discover the meaningful knowledge from the data collection. The data mining theories are often represented in the form of models. Each model has its own process that builds the entire system. A reliable model holds the essence as specific formulation that may discover the knowledge from junk data. The model is designed in such a way that it acts as an interface between the human and machine world. Thus providing a model, a better understanding about the outer world. The certain models are designed strictly for production and diagnostic purpose [1] in the field of medicine. Data mining provides technical and practical solutions that provides better analysis of medical data. With such solutions, the construction of prediction models could be an easier task for diagnostic purpose [2].
Globalization in India has improve the evidence based research and the ingenuities required to regulate the procedure for Ayurvedic medicines. Ayurvedic not only considers the disease examination but also the patients and their diet, food, herbs and life style recommendation. The prominent method for examining the patient in Ayurvedic medicine is Prakriti. Prakriti represents the unique constitution, personality with the globe, represented in the form of three dimensions namely: Dhosas, Kapha and Vata. If the Prakriti of an individual are in correct proportion then the patient is considered healthy or vice versa. Clinicians assess the patients through Prakriti profile for customizing the treatment and its prior diagnosis. However, the Prakriti of a patient is recorded in a paper after the consultation. This is not usually exchanged between the clinicians [3].
The increased use of electronic devices further improved the interoperability of the health records in electronic format. This provided the use of electronic health system for prior diagnosis before consultation with the clinicians. The electronic records that posses the standards of Prakriti constituents and other associated datasets modernizes the Ayurvedic treatments. Clinicians analyzes the person health through their experience and skill, however, this is not available with all clinicians. Hence, an intelligence system for interpretation and analysis of health related issues is made precise with the available datasets. This combination of datasets could help in diagnosing the disease that is exact or precise in nature [4].
The aim of the research is to improve the degree of precision in diagnosing the ailments through the concept of fuzzy systems. The fuzzy rule base associated with logical systems represents the fuzziness of the input parameter. Further improvement in analyzing the ailments could be done through the concept of ontology. Ontology represents the knowledge in form of a tree with concept and its linked instances. To handle the vagueness and uncertainty of ontological data, fuzzy logic is combined with input dataset. However, to improve the matching pattern with more precise results, Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is used.
Since each individual is born with specific constitution, Ayurveda proposed three major Prakriti. The dominance of each constitution provides a particular Dosha to each individual according to which the body behaves. The present research works involves discovery of suitable Prakriti method that fits well in diagnosing the patient ailments. The solution to such ailments is provided through Prakriti constitutional medicine. Hence, an automated system is defined with strict rules that involves predefined ontological datasets in fuzzy rule base. The proposed method involves Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Interference System (ANFIS) to diagnose the diseases with defined rule pattern. To improve the training pattern of the ANFIS, Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is used. The Diagnosis is carried out after performing the rules based on the inputs given at the user end. The outputs purely depends on the rule selection from the predefined ontological datasets. This system helps well as a diagnostic tool in finding out the ailments of the patients and treating them with one of the constitutional medicine.
The other parts of the paper includes: section 2 deals with the related works, section 3 deals with the collection of data and the procedure of using ANFIS and PSO algorithm to handle the datasets and to improve the training pattern. Section 4 and 5 describes the evaluation of the proposed method and finally, section 6 concludes the entire paper with future direction.
- RELATED WORKS
Ranjit et al. [5] proposed fuzzy expert system on the physical constituents from human body namely Vatt, Pitt and Kapha [15]. The entire operations is carried out to assist the Ayurvedic diagnosis and treatment. Here fuzzy based expert system is used to calculate the three constituents. Begic et al. [6] proposed genetic algorithm based ANFIS expert system to predict the dermatological disease in human beings. Here, nine features are taken as inputs to the classifier for diagnosing the disease in real time. Farooque et al. [7] compared the performance of data mining algorithms like naïve bayes, knn classifier, logistic regression and decision tree for Ayurvedic Prakruti Temperament. However, Yim and Joo [8] used fuzzy logic designer to diagnose 8 constitutions in human body. This method is a Korean way of diagnosing the patients. The technique evaluated assist the physicians in determining the disease. The 8 constitution of human body is considered in the present research with more detailed parameters from [12]. Chattopadhyay [9] Mamdani’s Fuzzy logic controller (FLC) on a Feed Forward Multilayer Neural Net is used to diagnose the depression in human beings. Appaih et al. [10] used ANFIS for diagnosing the malaria disease. So, this proves how the ANFIS system is efficient in medical applications. However, to improve the effectiveness and computational capability can be improved with the addition of other meta-heuristic approaches. Karaboga and Kaya [11] proposed Ant colony optimization (ACO) algorithm to improve the training phase of ANFIS. Similar procedure is implemented in our proposed system but with PSO algorithm to improve the training phase using swarming procedure at every iterations. A ontology based automated clinical systems [13, 16, 17, 18, 22, 25, 26, 27, 29,30,31,32,33,34] has proved better in health care system and the association of fuzzy further enhanced the results [14, 20, 21, 23, 24, 28]. Hence the use of ontology is inbuilt in the proposed system with fuzzy logic for Prakriti ailments. The method in [19] uses PSO to build the ontological structure, however, the present system involves the use of PSO in improving the ANFIS training pattern.
- PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
A three categories of questions is prepared for determining the Prakriti in Ayurvedic medicine. These categories include anatomical, psychological and physiological questions of each individuals or patients. Suitable questionnaires are prepared and the scores related to each questions is calculated. Sample questionnaire is attached under appendix A.The patients are allowed to fill the questionnaire that includes parameters like season details and patient details. The Prakriti concept is unique from other medical concepts. Hence, Prakriti is determined with its associated parameters using proposed ontological datasets, easily. The entire process is carried out in PSO – ANFIS interface that helps in improved accuracy of the test datasets.
3.1 ONTOLOGY – HEALTH MAINTENANCE FRAMEWORK
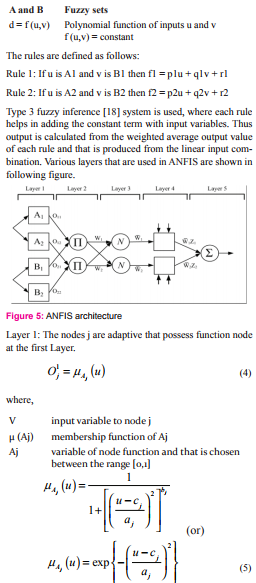
The health maintenance system is proposed with ontology rule based system that address the diagnostic problems using ontological representation. This includes the core principles of Ayurvedic medicine, Prakriti Doshas, Prakriti categories, herbs, diet, diseases, symptoms and diagnosis (Figure 1).
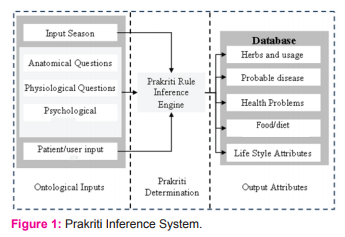
The figure represents the Prakriti system with input output interface that is controlled by a rule base system that involves ANFIS – PSO logic (Figure 3). The input parameters involves: user profile input, season input and determined anatomical, psychological and physiological Questions. These input ontology parameters is prepared through questionnaires, since it is not available in web resources, however, certain literatures related to Prakriti records the related resources. Depending on the Prakriti determination using ANFIS-PSO Markup Language (APML), the output parameters includes attributes like Food, Diet, Herbs and Lifestyle recommendation to the patients.
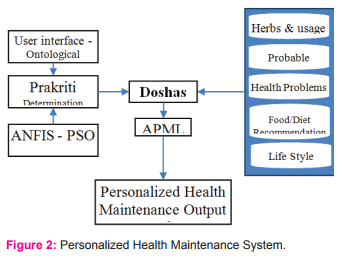
Database consist of set of different data related to the recommendation of user that is collected from various resources like questionnaires and from clinicians. A user interface is created via APML and delivers the Doshas from database that consist of herbs and usage, probable disease, health problems, food and diet style recommendation and life style. The output is delivered through the Prakriti determination through ANFIS-PSO system. The entire process is started upon the input from the user input interface. Here to improve the Prakriti determination in proposed method, the ontology is integrated with fuzzy logic for providing best recommendations to the user/patient. Fuzzy ontology generates ontology through fuzzy logic, fuzzy sets and variables. This predicts the uncertain things in an effective way and the knowledge extraction occurs based on the membership value of the variables.
The proposed system works in the following manner:
- User provides information about age, height, weight and sex.
- User enters his/her Prakriti type through recommended questionnaires.
- User/patient enters the current season.
- Fuzzy ontology is applied over the collected inputs from an individual.
- PSO is applied over the results of fuzzy trained patterns to improve accuracy.
- A fuzzy profile for the user is created.
- For the recommendation purpose, fuzzy ontology and the fuzzy profile ontology is created finally.
- Then the recommendations like: Food, Diet, Herbs and Lifestyle recommendation is suggested to the patients.
3.2 FUZZY ONTOLOGY
The Fuzzy ontology is similar to the procedure as mentioned in [20]. The fuzzy ontology system provides a semantic relationship between the associations of the same domain. A flexible fuzzy query searches the database contents and compares it with the domain ontology that represents the queried attributes in the domain. The ordering of resulting dataset is done through the degree of similarity calculated from the query subject and the database content in the ontology.
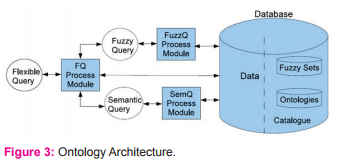
Input process divides the query and each subquery is sent to the corresponding process module according to the query attributes domain. Output processing combines the answers obtained from the different modules. Each row accomplishment degree in the resulting dataset should be higher than a user-given threshold [20].
3.3 Particle swarm optimization (PSO)
Particle Swarm Algorithm (PSO) solves the problem formulation iteratively by improving the solution w.r.t the given ontology. The optimization in PSO is carried out through n particles/individuals of candidate solution. The particles are moved around in the search space with specified mathematical formulation over its position and velocity. Here, each particle is assigned with random position in N-dimensional space. The position and velocity of the particle is denoted as xi and vi over solution space.
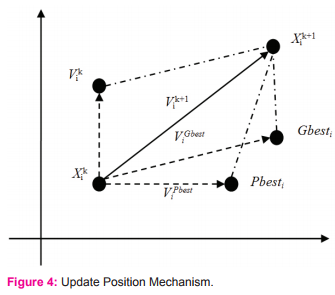
The movement of each particle is guided by its local best position to attain the best position in the search space. The position of previous best local or personal solution is denoted as Pbesti. The best positions are updated frequently to all the particles and move the swarm towards best solution in the search space. Similarly, the best global position is denoted as Gbesti. This is considered as the best particle among all particles in the search space. Here, each particle in search space is considered as a vector V that moves in the range of [-Vmax, Vmax]. The movement of particle in search space is controlled by the factor V that avoids excessive roaming. The velocity of the particle is updated using:
Vi(t+1) = ωVi(t) + Car1[Xi(t) - pi(t)] + Cbr2[Xi(t) – gd(t)] (1)
At each iteration the particle moves towards new position, hence, the range of particle should not exceed [min X, max X]. The position of the particle is thus updated using:
Xi(t+1) = Xi(t) + Vi(t+1) (2)
The process gets repeated until the stopping criterion is defined or reached and
ω = (ωmax – (ωmax–ωmin)/Imax)I
where,
|
i = 1,2,..., M
|
Total number of particles
|
|
d = 1, 2,..., D
|
Total dimension of particles the solution space
|
|
r1and r2 Î [0,1]
|
Random numbers distributed uniformly in the search space
|
|
Ca and Cb
|
Learning factors (value is taken as 2.0)
Ca represent individual cognition component that represents the particle’s ability in search space.
Cb represents social communication component that gets influenced from the social environment.
|
|
ω
|
Inertial component that limits the particle’s velocity in search space. The value of inertial component is 0.4
|
|
ωmax
|
Final inertial weights
|
|
ωmin
|
Initial Inertial weights
|
|
Imax
|
Total Iterations
|
|
I
|
Current Iteration
|
The algorithm for PSO in ontology evaluation is shown in following table.
|
Algorithm 1: Particle swarm optimization (PSO)
|
|
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
Step 5:
Step 6:
Step 7:
|
INITIALIZE the position and velocity, randomly to all the particles in the search space.
EVALUATE the xi and vi of each particle. The local (Pbesti) and global (Gbesti) position is evaluated
UPDATE the xi and vi of each particle using Eq.(1) and Eq.(2).
CALCULATE the xi and vi of each particle.
UPDATE Pbesti
For each particle
IF value of new position is better than that Pbesti,
THEN replace its Pbesti by new position.
UPDATE Gbesti
For each particle
IF value of new position is better than that Gbesti,
THEN replace its Gbesti by new position.
REPEAT the process until the maximum iterations
IF solution converges
THEN the value of Gbesti is considered as output
IF ELSE GOTO Step 3.
END
|
3.4 ADAPTIVE NEURO-FUZZY INFERENCE SYSTEM (ANFIS)
The ANFIS network is used to classify the Prakriti diagnosis with predefined set of rules. The ANFIS system possess fuzzy model with rules that formulates the input output datasets. The second model is the neural network model, which is integrated with Fuzzy model that improves the learning capability of nonlinear functions.
The ANFIS system consists of two inputs and a single output interface with if-then rule type. The rules are specified as follows:
If u is A and v is B then q = f (u,v) (3)
where,
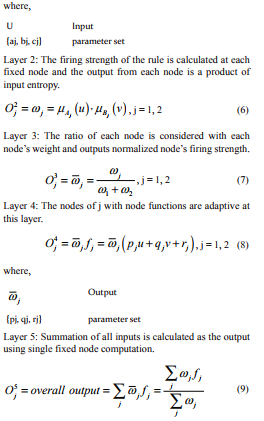
Depending on the input entropy results, the ANFIS predicts accurately the class of disease to which it belongs. As a result, if the value is greater than 0 then the patients are marked as diseased and vice versa.
3.5 ANFIS-PSO CLASSIFIER
The algorithm of ANFIS-PSO classifier is described stepwise. Here, the recombination of the predicted signals is carried out to find the suitable category of Prakriti.
Step 1: Form a matrix with Prakriti data set in columns matrix. The column array possess patients profile collected from real time datasets. In this first step, the matrix will contain seven columns (represents seven Prakriti constitutional types) corresponding to collected datasets of Prakriti determination.
Step 2: Select total columns in previous array represents the values of real input data.
Step 3: Train the ANFIS system using the input data that uses a combination of the least-squares and back propagation gradient descent method. Training allows the proposed method that adjusts its parameters as submitted inputs or outputs. The acquired knowledge through the process of training is then tested through a new dataset or the testing set. The ANFIS network generalize for its accurate output over the testing data. It is undesirable in order to over-train the proposed system, since it represents that it works only on training dataset and does not generalizes on training dataset. A large training datasets is thus avoided that over-trains the system during the process of learning. To obtaining better accuracy, PSO trains the membership function parameters of fuzzy system
Step 4: A vector of N-dimensions is created that equals the total membership functions. The vector contains membership function parameters that is optimized by PSO. The mean squared error is used for defining the fitness function.
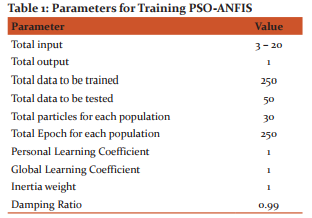
Step 5: The parameters of PSO is defined in Table.1. The Parameters are randomly initialized at first stage and gets updated using PSO. During each iteration, parameters are being updated and once the entire parameters gets updated, the initial parameter update is considered further and so on. The updated parameters are grouped in the form of vectors that gets updated during each iteration.
The PSO algorithm for optimizing the parameters/fuzzy membership functions is shown below:
- Initialization of the population position and speed in swarm. For each particle, there obtains a random initialization of particle position and velocity. The size of the vector is same as the problem size.
- Assess ability of each particle, Pbest. If the particle value is better than its present value, particle’s current position or Pbest is reset and individual value is updated. Location of best particles is made reset, if the best of all particles’ value is better than overall current Gbest value.
- Measure each particle’s fitness, Pbest and store the best fitness value of each particle Gbest.
- Modify the speed through the positions of Pbest and Gbest.
- Update the particles.
- End the process if the conditions are verified. When the current iteration reaches the maximum, then the iterations are stopped and the best solution is collected.
Sixth step: Extraction of the ANFIS output using the PSO parameters.
Seventh step: The final output provides the results of the predicted values of this approach.
IV.RESULTS
The proposed method is implemented over Jena framework that supports RDF, OWL and rule inference engine. Additionally, fuzzy logic with PSO training pattern is coded and applied over J7ena framework.
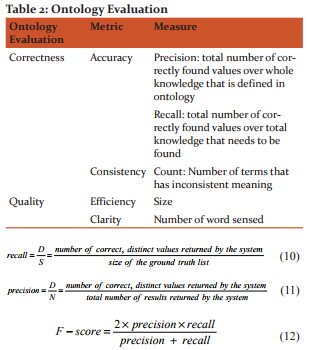
The evaluation of ontology depends on quality and correctness. Standard metrics like recall, precision and F-score is used for performance measurement. Let S – size of ground truth value, D – Number of correct values that is extracted by proposed system and N denotes the number of total values returned by the proposed system. The evaluation metrics is shown in table 2.
The results of the automated system is checked with a clinician to evaluate its correctness. Here, if the value of the prediction system is found to be 1, then the patient is said to have a specific disease and vice versa. Depending on the disease, the Prakriti type is found and it is divided into following class:
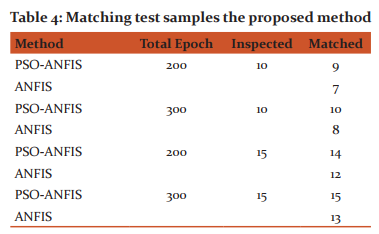
The set of test samples are tested after the system is trained by the PSO-ANFIS procedure. Initially, the epoch or the iterations of PSO algorithm is set as 200 and the total test samples for inspection is taken as 10. It is seen that the proposed PSO-ANFIS method has 9 matched samples which is higher than normal ANFIS [12] method with 7 samples. The total epoch is increased to 300 with other set of 10 samples. It is found that the proposed method has all the 10 samples matched and ANFIS has got 8 samples matched. Likewise, the test samples are increased for 15 over 200 and 300 iterations. From the test results, it is found that the proposed method attains 14 and 15 matched samples and the ANFIS method has12 and 13 matched samples respectively for 200 and 300 iterations.
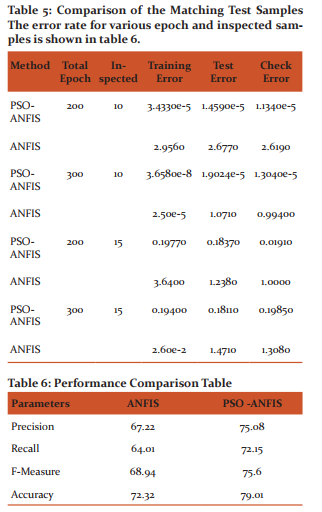
The test success of the proposed method with the existing ANFIS is tested to see the errors present during the training and testing process. Similar inspected and epoch pattern is carried out to find the training, testing and check error. It is found from the results that the error rate of training, testing and check error for the proposed PSO-ANFIS system produces less error than the ANFIS system. It could also be interpreted that the use of PSO algorithm over the training samples further improved the test performance than the existing ANFIS.
DISCUSSIONS
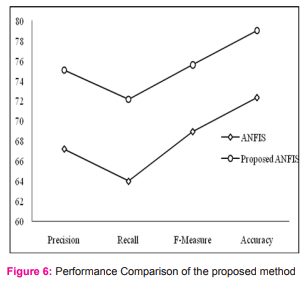
It is found from the table 5 that the results obtained has better improvements in all performance parameters than the conventional ANFIS system. This proves that PSO classifier helped in training the samples of the fuzzy ontology output. Specifically, the variations of parameters like recall and F-measure has a considerable impact than the existing system. Further investigations on performance through FMeasure value as a benchmarking point has carried forward that enables the system to perform well over the defects in existing system.. Finally, a drift in performance is found that shows that the accuracy of PSO-ontology-ANFIS is further improved than the conventional ANFIS type.
CONCLUSIONS
In the present research, comparisons are carried ou
References:
- Tang PN, Steinbach M, Kumar V. Introduction to Data Mining. Pearson Addison: Wesley Bostan; 2005.
- Bellazzi R, Zupan B. Predictive data mining in clinical medicine: Current issues and guidelines. International Journal of medical informatics. 2008; 77(2):81–97.
- Ranjit K, Vishu M, Prateek A, Kumar SS, Amandeep K. Fuzzy Expert System for Identifying the Physical Constituents of a Human Body. Indian Journal of Science and Technology. 2016 Jul 27;9(28).
- Shital, V., and Sambare, S. S. (2015). Study of Diet Recommendation System based on Fuzzy Logic and Ontology. International Journal of Computer Applications, 132(12), 20-24.
- Ranjit K, Vishu M, Prateek A, Kumar SS, Amandeep K. Fuzzy Expert System for Identifying the Physical Constituents of a Human Body. Indian Journal of Science and Technology. 2016 Jul 27;9(28).
- Begic FL, Avdagic K, Omanovic S. GA-ANFIS Expert System Prototype for Prediction of Dermatological Diseases. Studies in health technology and informatics. 2014 Dec;210:622-6.
- Farooque MM, Aref M, Khan MI, Mohammed S. Data Mining Application in Classification Scheme of Human Subjects According to Ayurvedic Prakruti–Temperament. Indian Journal of Science and Technology. 2016 Apr 18;9(13).
- Yim J, Joo J. Implementation of an Inference System to Classify Persons into Eight Constitutions. Indian Journal of Science and Technology. 2015 Oct 14;8(26).
- Chattopadhyay S. A neuro-fuzzy approach for the diagnosis of depression. Applied Computing and Informatics. 2014 Feb 4.
- Appiah R, Panford JK, Riverson K. Implementation of Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System for Malaria Diagnosis (Case Study: Kwesimintsim Polyclinic). International Journal of Computer Applications. 2015 Jan 1;115(7).
- Karaboga D, Kaya E. An adaptive and hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm (aABC) for ANFIS training. Applied Soft Computing. 2016 Dec 31;49:423-36
- http://ecmed.org/board/content.asp?bsNo=18andlng=en
- Kuziemsky, C. E., and Lau, F. (2010). A four stage approach for ontology-based health information system design. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 50(3), 133-148.
- El-Sappagh, S., Elmogy, M., and Riad, A. M. (2015). A fuzzy-ontology-oriented case-based reasoning framework for semantic diabetes diagnosis. Artificial intelligence in medicine, 65(3), 179-208.
- Stranieri, A., Butler-Henderson, K., Sahama, T., Perera, P. K., Da Silva, J. L., Pelonio, D., Manjunath, SS., and Raghavachar, D. (2016). A visual grid to digitally record an Ayurvedic Prakriti assessment; a first step toward integrated electronic health records. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine.
- Riaño, D., Real, F., López-Vallverdú, J. A., Campana, F., Ercolani, S., Mecocci, P., Annicchiarico, R., and Caltagirone, C. (2012). An ontology-based personalization of health-care knowledge to support clinical decisions for chronically ill patients. Journal of biomedical informatics, 45(3), 429-446.
- Saalmann, P., Zuccolotto, M., da Silva, T. R., Wagner, C., Giacomolli, A., Hellingrath, B., and Pereira, C. E. (2016). Application Potentials for an Ontology-based Integration of Intelligent Maintenance Systems and Spare Parts Supply Chain Planning. Procedia CIRP, 41, 270-275.
- Grandi, F. (2016). Dynamic class hierarchy management for multi-version ontology-based personalization. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 82(1), 69-90.
- Pancerz, K., and Lewicki, A. (2014). Encoding symbolic features in simple decision systems over ontological graphs for PSO and neural network based classifiers. Neurocomputing, 144, 338-345.
- Martínez-Cruz, C., Noguera, J. M., and Vila, M. A. (2016). Flexible queries on relational databases using fuzzy logic and ontologies. Information Sciences, 366, 150-164.
- Karthikeyan, N. K. (2016). Fuzzy service conceptual ontology system for cloud service recommendation. Computers and Electrical Engineering.
- Viale, P., Bora, J. J., Benegui, M., and Basualdo, M. (2016). Human endocrine system modeling based on ontologies. Knowledge-Based Systems, 111, 113-132.
- Liu, J., Zheng, B. J., Luo, L. M., Zhou, J. S., Zhang, Y., and Yu, Z. T. (2016). Ontology Representation and Mapping of Common Fuzzy Knowledge. Neurocomputing.
- Ali, F., Kwak, K. S., and Kim, Y. G. (2016). Opinion mining based on fuzzy domain ontology and Support Vector Machine: a proposal to automate online review classification. Applied Soft Computing.
- Medina-Oliva, G., Voisin, A., Monnin, M., and Leger, J. B. (2014). Predictive diagnosis based on a fleet-wide ontology approach. Knowledge-Based Systems, 68, 40-57.
- Koukias, A., and Kiritsis, D. (2015). Rule-based Mechanism to Optimize Asset Management Using a Technical Documentation Ontology. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 48(3), 1001-1006.
- Arch-int, N., and Arch-int, S. (2013). Semantic ontology mapping for interoperability of learning resource systems using a rule-based reasoning approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 40(18), 7428-7443.
- Ochs, C., He, Z., Zheng, L., Geller, J., Perl, Y., Hripcsak, G., and Musen, M. A. (2016). Utilizing a structural meta-ontology for family-based quality assurance of the BioPortal ontologies. Journal of biomedical informatics, 61, 63-76.
- Ying, H. (1998). Sufficient conditions on uniform approximation of multivariate functions by general Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems with linear rule consequent. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and Humans, 28(4), 515-520.
- Jaya R et al,Ontology based Decision Support System for Identifying the Physical Constituents of a Human Body, International Journal of Control Theory and Applications, Volume 9 • Number 51 • December 2016
- Jaya R et al, A Narrative Review of Research on Traditional Indian Medicine and Role of Prakriti in Lifestyle Recommendation, International Journal of Control Theory and Applications, Volume 9 • Number 51 • December 2016
- Jaya R,et al,Ontology Based Virtual Assistant for Diet Recommendation, IJCSMC, Vol. 6, Issue. 4, april 2017
- Jaya R et al, Implementation Of Clinical Decision Support System For The Ayurveda Medicine, , IJCSMC ,Vol. 5, Issue. 9, September 2016, pg.29-33
- Jaya R et al ,Ayurveda Medicine Roles in Healthcare Medicine, and Ayurveda Towards Ayurinformatics, IJCSMC, Volume 4 Issue 12, ISSN 2320-088X














 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License