IJCRR - 9(17), September, 2017
Pages: 32-36
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effect of Gingival Crevicular Fluid Volume in Smokers
Author: Aishwarya A.S., Jaiganesh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:The association between smoking and periodontal disease has been proven by many epidemiological evidences. This article reviews the recent studies and compiles the effect of smoking on Gingival crevicular fluid volume. Many studies support the fact that tobacco smoking affects the periodontium through different pathways like microcirculatory, host immune systems, connective tissue and bone mechanisms.
Keywords: Smoking, Periodontal disease, Gingival crevicular fluid
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2017.9175
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
Periodontal disease is defined as inflammatory destruction of periodontal tissue and alveolar bone supporting the teeth. [5] Smoking is accepted as a risk factor for periodontal disease and detrimental to periodontal tissues. Many investigations suggest negative periodontal effects among smokers in comparison with non smokers. Smokers tend to have greater numbers of deeper periodontal pockets and probing depth. Studies show that cigarette smokers are 2 to 6 times more likely to develop severe periodontitis than in non-smokers [31,32]. Several epidemiological studies indicate that smoking has harmful effects on the response to non surgical and surgical procedures [1].
Paradoxically, smoking tends to mask the gingival inflammation by causing constriction of blood vessels of gingiva [20, 21]. Smoking is known to alter the host response including changes in vascular function, neutrophil activities, adhesion molecule expression, antibody production, release of cytokine inflammatory mediators [33,34].
Biological mechanism of periodontal disease is occurring due to the imbalance between bacterial virulence and host defence activity.[4]. The most possible mechanism that explains the relationship between smoking and periodontal disease is that smoking, an environmental factor, interacts with the host cells and affects the inflammatory changes [25]. These underlying mechanisms can be understood by linking findings of the previous epidemiological studies with in vitro studies.
Biological markers called as biomarkers which are indicative of the status of the disease and have been measured for several studies to reveal the mechanism of disease [27]. For example host immune inflammatory response systems have biomarkers like immune cells, immunoglobulins and metalloproteinase, cytokines, and adhesion molecules. These biomarkers are obtained limitedly particularly from non-diseased smokers. Thus commonly used specimens are saliva, blood serum, gingival crevicular fluid [26].
Gingival crevicular fluid is a fluid present in the sulcus or periodontal pocket between the surface of the tooth and the gingival epithelium [3]. Gingival crevicular fluid is a transudate as well as inflammatory exudates, produced by osmotic gradient containing low protein content. The amount of gingival fluid is greater when inflammation is present. Physiologically the fluid volume increases while masticating, brushing, ovulation etc[23]. Gingival crevicular fluid is a well known marker of gingival health status[1]. This study reviews articles relating the gingival fluid flow in smokers.
SEARCH ENTITY:
This article reviews based on the strategy, keywords like smoking and periodontitis, gingival fluid flow, Gingival crevicular fluid volume in smokers. Many articles reviewed were published in the last 5-7 years. This article constructs the relation between smoking and the gingival crevicular fluid flow rate by reviewing the previously conducted studies.
METHODS OF COLLECTING GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID [7, 9]:
There are several methods to collect Gingival crevicular fluid
- By using absorbent papers
- Brill technique (intra sulcular method) -filter paper strip is placed inside the gingival sulcus until the resistance is felt.
- Loe and Holm-Pedersen technique (extra sulcular technique) -filter paper strip is placed at the entrance of the gingival sulcus.
- Collection of Gingival crevicular fluid using micropipettes
- Micropipettes with standardized length and diameter and uses the capillary action to collect the fluid.
- By using twisted threads
- Pre weighed twisted threads are placed in the crevice and after placing, the threads are measured and measured.
- Collecting Gingival crevicular fluid by using paper points
ESTIMATION OF AMOUNT OF GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID:[7]
- The amount of Gingival crevicular fluid collected in periopaper can be measured by several means
- By weighing the absorbent medium:
 The weight of the twisted threads are measured before and after placing in the gingival crevice and compared.
The weight of the twisted threads are measured before and after placing in the gingival crevice and compared.- By measuring capillary fill of micropipettes
- As the capillary tubes are marked with standardized length and diameter.
- By staining with ninhydrin
 The wetted area with Gingival crevicular fluid becomes more visible by staining with ninhydrin which can be then measured planimetrically on an enlarged photograph or with a microscope.
The wetted area with Gingival crevicular fluid becomes more visible by staining with ninhydrin which can be then measured planimetrically on an enlarged photograph or with a microscope.- Electronic method
- Amount of Gingival crevicular fluidcan be estimated by using an electronic device called as periotron.
COMPOSITION OF GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID:
The contents of Gingival crevicular fluid are usually as a result of interaction between the bacterial biofilm and the periodontal tissues. It contains the products of tissue breakdown, inflammatory mediator and antibody produced against them[7]. From the hypothesis postulated by Pashley which suggested that the initial fluid produced represents interstitial fluid which appears in the crevice as the result of osmotic gradient. This initial, pre-inflammatory fluid is a transudate and on stimulation it becomes as an inflammatory exudates [8].
Composition of Gingival crevicular fluid
 Enzymatic components
Enzymatic components
- Host derived and other products
- Bacteria derived
 Non enzymatic components
Non enzymatic components- Cellular components
- Electrolytes
- Organic components
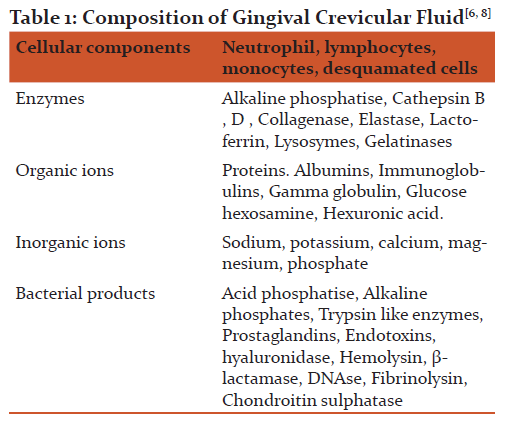
Organic compounds: Glucose hexosamine and hexuronic acid are two main components of Gingival crevicular fluid, where the glucose level of blood do not coincide with the level of glucose in Gingival crevicular fluid, its concentration is three or four times greater than in serum level [6].
COMPOSITION OF CIGARETTES:
Tobacco smoke contains millions of noxious chemicals which comprises of gaseous phase and particulate phase. The gas phase contains carbon monoxide, ammonia, formaldehyde, hydrogen cyanide and 60 known carcinogen such as benzo(a)pyrine, dimethylnitrosamine. The particulate phase includes nicotine, benzene, and tar. Tar is in condensate form, sticky substance that stains the fingers and teeth yellow/brown. Nicotine an alkaloid found in tobacco leaves evaporates when the cigarette is lighted. It's quickly absorbed in the lungs and reaches the brain within 10-19 seconds. Nicotine is highly addictive and causes rise in blood pressure, increased heart rate and respiratory rate with peripheral vasoconstriction. Plasma and saliva cotinine concentration in smokers is approximately 300ng/ml and the urine concentration s approximately 1500 ng/ml. Non-smokers has plasma and saliva concentration
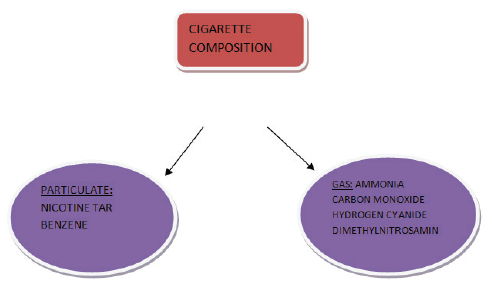
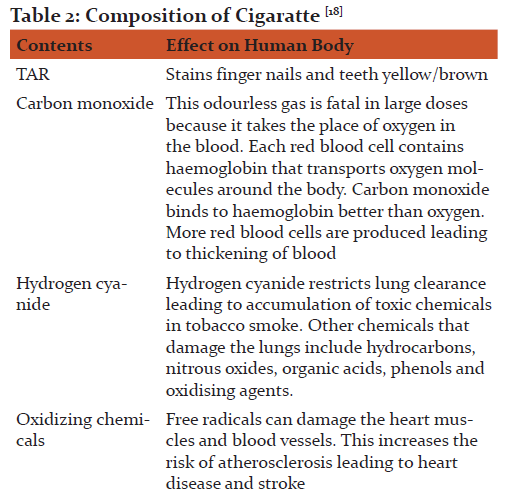
CHANGES IN GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID COMPOSITION ASSOSCIATED WITH SMOKING:
Effect on microvasculature
Smaller number of vessels was observed in inflamed gingival tissues of smokers compared to non smokers. Smoking causes decrease in gingival blood flow and vascular conductance, leading to delay in healing and increases the risk of periodontal health [27,28]. Smoking causes inflammatory activation by inducing endothelial dysfunction which increases the cytokine adhesion molecules [14].
Host immune response
Smoking can affect the neutrophil count in blood in a dose-dependent manner [30]. Smoking reduces the proliferation of T lymphocytic cells and affects B cell function and antibody generation [30].
Connective tissue and bone metabolism:
Crevicular fluid in smokers has increased levels of Interleukins (IL 6, IL 8, IL 4), MMP, and free radicals. Gingival crevicular fluid has decreased levels interleukins (IL 1a), osteoprotegrin, prostaglandins, and gingival fibroblasts [4]

Viability of PMNs was significantly lower in light, moderate and heavy smokers compared to non-smokers. The ability of PMNs to phagocytose was significantly impaired in light, moderate and heavy smokers compared to non-smokers [13]. In periodontally diseased subjects the total amounts of IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 were significantly elevated as compared to healthy subjects, whereas IL-4 showed an inverse relationship to periodontal status and higher amounts were found in the healthy group[14].The levels of calprotectin, a leukocyte protein, in body fluids of patients with some inflammatory diseases are raised. Recently, we detected calprotectin in Gingival crevicular fluid and its concentrations in periodontal pockets were higher than those in healthy gingival crevices[16,17]. Investigations done by Jun-ichi Kido found the correlations between Gingival crevicular fluid calprotectin levels and clinical indicators (probing depth and bleeding on probing, BOP), and the IL-1β and PgE2 levels[14].
DISCUSSION:
Smoking is highly prevalent and can be considered an epidemic both developed and developing nations, smoking was higher in younger groups than older groups. Studies estimate that 1.3 billion people smoke per year worldwide on an average[6]. Smoking is detrimental to body tissues such as lungs, heart muscles, blood vessels, periodontium etc.
The periodontal probing depth and attachment loss were higher in smokers compared to non smokers [3]. Smoking tends to mask gingival inflammation by causing constriction of blood vessels of the gingiva [20,21,22]Smoking decreases oxygen tension in the gingival tissues. Smoking decreases tissue oxygen from from 65  7 to 44 ???????
7 to 44 ??????? 3 mmHg. Oxygen tension of 40-50 mmHg has increased risk of infection [9]. Vasoconstriction of blood vessels leads to reduced clinical signs and suppressed clinical expression of disease[11].A study done by Kemal et al showed that smoking significantly increased Gingival crevicular fluid flow/volume when compared to non-smokers. Purnima et al conducted a study with Gingival crevicular fluid, marginal and sub gingival plaque that revealed early acquisition and colonization of oral biofilm in smokers [12].
3 mmHg. Oxygen tension of 40-50 mmHg has increased risk of infection [9]. Vasoconstriction of blood vessels leads to reduced clinical signs and suppressed clinical expression of disease[11].A study done by Kemal et al showed that smoking significantly increased Gingival crevicular fluid flow/volume when compared to non-smokers. Purnima et al conducted a study with Gingival crevicular fluid, marginal and sub gingival plaque that revealed early acquisition and colonization of oral biofilm in smokers [12].
Cigarette smokers with periodontitis have increased periodontal destruction especially in palatal region of maxilla [35]. Study done by Xia Chen et al showed that 16% of smokers had higher chance of becoming edentulous within 10 years while only 0.3% of non-smokers become edentulous in the same period of time [15].
The research by Kaushal Luthra et al shows a clinically significant decrease in Gingival crevicular fluid volume in smokers when compared to non smokers and an increase in the volume of Gingival crevicular fluid 10 minutes post smoking[1]. Nicotine plays a major role in altering the gingival blood flow which subsequently correlates with the volume of Gingival crevicular fluid in smokers [2]. A similar result was reported by Morozumi et al[1]. There is an immediate increase in Gingival crevicular fluid volume five days after smoking cessation.
CONCLUSION:
The Gingival crevicular fluid volume is known to increase with the degree of inflammation. The increased Gingival crevicular fluid volume shows the presence of masked inflammation in smokers. Smoking alters the gingival blood flow which concomitantly relates to the Gingival crevicular fluid volume. This review concludes that the result may vary according to the pattern of smoking, methods of collection of Gingival crevicular fluid and sample size.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Ustun K, Nilgun A. Alptekin. The effect of tobacco smoking in gingival crevicular fluid. European Journal Dentistry, 1(4): 236-239, 2007.
2. Mokeem SA, Vellappally S , Preethanath RS , Hashem MI , Al-Kheraif AA , Anil S. Influence of Smoking on Clinical Parameters and Gingival Crevicular FluidVolume in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis, OHDM - Vol. 13 - No. 2,2014.
3. Luthra K, Grover HS, Aggarwal N, Luthra S. Smoking swings of gingival crevicular fluid secretion, Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology volume 16(1); 101-103, 2012.
4. Ojima, Hanioka: Destructive effects of smoking on molecular and genetic factors of periodontal disease. Tobacco induced diseases 2010 8: 4.
5. Sabrina C. Gomes, Flávia B. Piccinin, Rui V. Oppermann, Cristiano Susin, Rosemary Adriana C. Marcantonio. The effect of smoking on gingival crevicular fluid volume during the treatment of gingivitis.Acta Odontol. Latinoam Vol. 22 (3); 201-206,2009.
6.Newman, Michael G., Henry H. Takei, and Fermin A. Carranza. Carranza's Clinical Periodontology. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co, 2002.
7. Textbook of periodontics by Jaiganesh, first edition.
8.Griffiths, Formation, collection and significance of Gingival crevicular fluid periodontal 2000:2003; volume 31,32-42.
9. Jensen J, Goodson WH, Hopf H, Hunt TK. Cigarette smoking decreases tissue oxygen. Arch Surg. 1991; 126(9):1131-1134.
10. Andrew J. Delina, origin and function of the cellular components in Gingival crevicular fluid, periodontal 2000:2003; volume 31,55-76.
11. Embery G, Waaddington R, Gingival Crevicular Fluid; Biomarkers of periodontal tissue Activity.Adv Dent Res 1994; 8(2):329-36.
12. Kumar PS, Matthews CR, Joshi V, de Jager M, Aspiras M. Tobacco Smoking Affects Bacterial Acquisition and Colonization in Oral Biofilms. Morrison RP, ed. Infection and Immunity. 2011;79(11):4730-4738.
13. Güntsch A, Erler M, Preshaw PM, Sigusch BW, Klinger G, Glockmann E. (2006), Effect of smoking on crevicular polymorphonuclear neutrophil function in periodontally healthy subjects. Journal of Periodontal Research, 41: 184-188.
14. Giannopoulou C, Kamma JJ, Mombelli A: Effect of inflammation, smoking and stress on gingival crevicular fluid cytokine level. J Clin Periodontol.2003, 30: 145-153.
15. Chen, X., Wolff L., AeppliD., Guo Z., Luan W, Baelum V. and Fejeskov O. (2001), Cigarette smoking, salivary/gingival crevicular fluid cotinine and periodontal status a 10-year longitudinal study. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 28: 331-339.
16. Kido J, Nakamura, T, Kido R, Ohishi K, Yamauchi N, Kataoka M. and Nagata T(1999), Calprotectin in gingival crevicular fluid correlates with clinical and biochemical markers of periodontal disease. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 26: 653-657.
17. Rai B, Kaur J, Anand S C, Laller K, The effect of smoking on gingival crevicular fluid levels of myeloperoxidase, Indian J Dent Res [serial online] 2010; 21:20-2.
18. Jonathan E, Smoking Heath effects and control, NEngl J Med 1985; 313:491-498
19. Preber H, Bergstrom J. The effect of non-surgical treatment on periodontal pockets in smokers and non smokers. J Clin Periodontol 1985; 13:319-23.
20. Bergstrom J, Floderus-Myrhed B. Cotwin control study of the relationship between smoking and some periodontal disease factors. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1983; 11:113-6.
21. Bergstrom J. Oral hygiene compliance and gingivitis expression in cigarette smokers. Scand J Dent Res. 1990; 98:497-503.
22. Baab DA, Oberg PA. The effect of cigarette smoking on gingival blood flow in humans. J Clin Periodontol. 1987; 14:418-24.
23. Preber H, Bergstrom J. occurrence of gingival bleeding in smoker and non smoker patients. Acta Odontol Scand. 1985:43:315-20.
24. Shapiro L, Goldman H, Bloom A. Sulcular exudates flow in gingival inflammation. J Periodontol. 1979; 50:301.
25. Palmer RM, Wilson RF, Hasan AS, Scott DA. Mechanism of action of environmental factors- tobacco smoking. J Clin Periodontol 2005, 32: 180-195.
26. Shield PG. Molecular epidemiology of smoking and lung cancer. Oncogene 2002, 21: 6870-6876.
27. Mavropoulos A, Aars H, Brodin P. Hyperaemic response to cigarette smoking in healthy gingiva. J Clin Periodontol 2003, 30: 214-221.
28. Mavropoulos A, Brodin P, Rosin CK, Aars H. Gingival blood flow in periodontitis patients before and after periodontal surgery assessed in smokers and non smokers. J Periodontol 2007, 78: 1774-1782.
29. Koundouros E, Odell E, Coward P, Wilson R, Palmer RM. Soluble adhesion molecules in serum of smokers and non smokers, with and without periodontitis. J Periodontal Res 1996, 31: 596-599.
30. Loos BG, Roos MTL, Schellekens PTA, Velden van der U, Miedema F. Lymphocyte numbers and function in relation to periodontitis and smoking. J Periodontol 2004, 75: 557-564.
31. Anand PS, Kamath KP, Shekar BR, Anil S. Relationship of smoking and smokeless tobacco use to tooth loss in a central Indian population. Oral Health and Preventive Dentistry. 2012; 10: 243-252.
32. Razali M, Palmer RM, Coward P, Wilson RF. A retrospective study of periodontal disease severity in smokers and non smokers. British Dental Journal. 2005; 198: 495-498; discussion 485.
33. Raulin LA, McPherson JC, 3rd, McQuade MJ, Hanson BS. The effect of nicotine on the attachment of human fibroblasts to glass and human root surfaces in vitro. Journal of Periodontology. 1998; 59: 318-325.
34. Ryder MI, Fujitaki R, Johnson G, Hyun W. Alterations of neutrophil oxidative burst by in vitro smoke exposure: implications for oral and systemic diseases. Annals of Periodontology. 1998; 3: 76-87.
35. Anil S. Study of the patterns of periodontal destruction in smokers with chronic periodontitis, Indian Journal of Dental Research, 2008; 19:124-128.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License