IJCRR - 4(19), October, 2012
Pages: 174-180
Date of Publication: 15-Oct-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
MORBIDITY PROFILE AND HEALTH SEEKING BEHAVIOUR OF THE ELDERLY IN URBAN SLUMS OF HYDERABAD, ANDHRA PRADESH, INDIA - A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY
Author: Vimala Thomas, Lavanya.K.M, Muraleedhar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Elderly or old age consists of ages nearing or surpassing the average life span of human beings. Population ageing is becoming a major concern both in the developed and developing countries. With increase in the aged population, the number of elderly with ailments is also on the rise. The objective of this study is to determine the socio-demographic characteristics of the elderly population, to identify their morbidity profile and to assess their health seeking behavior. Methodology: A community based cross sectional study of 216 subjects over 60 years old from three slums in the urban field practice area of Osmania Medical College (Amberpet, Golnaka, Zinda Tilismaath nagar) was carried out. Results: Of the total sample of 216 elderly persons, 84(38.9%) were males and 132 (61.1%) were females. Among females, 29.8 % and among males 4.7 % were illiterate. Around 43.5% of the elderly were not in any occupation and majority (75%) of them lived in joint families. The most prevalent morbidity was hypertension (46.9%) followed by Arthritis (30.2%), Diabetes (26.5%), Respiratory problem (24.3%) and Cataract (21%). Majority of the elderly went to private clinics for their treatment. Conclusions: The study has highlighted a high prevalence of morbidity among the elderly. As there is a rapid increase in the number of elderly population, there is an urgent need to develop affordable and accessible geriatric health care services.
Keywords: Morbidity, Health seeking behavior, Elderly, Urban slums, India.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
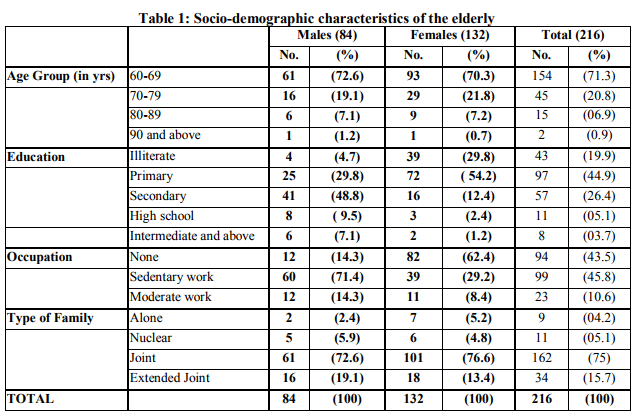
Ageing being a natural process affects each one of us. Discoveries in medical science and improved social conditions during past few decades have increased the lifespan of man. The expectation of life at birth in developed countries is over 70 years. The age structure of the population in the developed countries has so evolved that the number of elderly people is continually on the rise. These trends are appearing in many countries including India. In the year 2002, there were an estimated 605 million old persons in the world, of which 400 million were living in low income countries.1 By the year 2025, the number of elderly people is expected to rise to more than 1.2 billion with 840 million in low-income countries.1 In India, although the percentage of aged persons to the total population is low in comparison to the developed countries, nevertheless, the absolute number of aged population is considerable. According to the NSSO survey for 2007-08, the elderly population aged above 60 years account for 7.5 percent of the total population .2 Health status is an important factor which has a significant impact on the quality of life. Many health problems are known to increase with age. Discrimination in older age plays a vital role in the lowered health status among the elderly people. There are very few studies in India that provide information on the morbidity profile and also the health seeking behavior of the elderly people living in the urban slums. Hence a sincere attempt is made to reveal the same. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES 1. To determine the socio-demographic characteristics of the elderly population in the study area. 2. To identify the morbidity profile of elderly population. 3. To assess the health seeking behavior of elderly population MATERIAL AND METHODS It is a Community based Cross-sectional study. The list of slums was obtained from the Urban Health Centre located in the field practice area of Osmania Medical College. Three slums (Amberpet, Golnaka, Zinda Tilismaath nagar) were randomly selected. The total number of households in all the three slums was 684, each having an average family size of five. Data could be collected from 646 households, the rest being locked at the time of visit. All adults above 60 years age who consented to participate in the study were included. There were 240 (7.4%) persons aged 60 years and above, of whom, 216 (84 males and 132 females) could be contacted. The remaining 24 were either non-co-operative or could not be contacted despite making sincere efforts. Each individual in the study was subjected to personal interview and clinical examination. All the participants were informed about the purpose of the study in the language they could understand and consent was taken from them. The study was carried out over a period of six months from October 2011 to March 2012. A detailed questionnaire containing the demographic profile, socioeconomic data, health status and health seeking behavior was used to collect data by face to face interview. Data was collected from 216 elderly individuals. Physical examination and anthropometric measurement was done. Blood pressure was recorded in sitting position with a mercury sphygmomanometer according to standard guidelines. Average of the three readings five minutes apart was taken. If any-one reading was abnormal, one another reading was taken after ten minutes of rest. Statistical Analysis: Data was entered into an excel spreadsheet and double checked for errors. It was analyzed using Epi-info version 3.5.3. Pearson’s chi-square test was applied to test the relationship of categorized independent and dependent variables. A ???? value (significance) of 0.05). In our study, 29.8 % of females and only 4.7 % of males were illiterate. Among literate females, maximum (54.2%) had primary school education while among literate males; majority (48.8%) had secondary school education. With regards to occupation, 43.5% of the elderly were not in any occupation. A higher percent of females (62.4%) were unoccupied compared to males (14.3%) and this difference was statistically significant (P <0.05). In our study, majority (75%) of the elderly lived in joint families followed by extended joint families (15.7%) (Table 1)
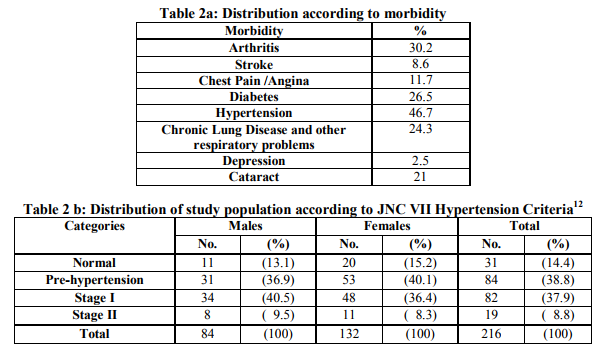
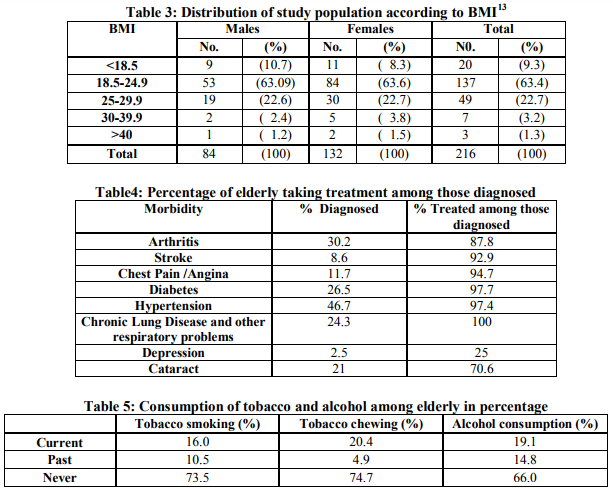
Among the major social problem faced by the elderly, about 73% of the elderly were financially dependent on their family members. Around 40% of them were receiving old age pension. Support for the dependent elderly came mainly from the family i.e., children and spouse. Morbidity profile: Medical history and physical examination revealed that the most common health problems of elders in order of magnitude were Hypertension (46.7%), Arthritis (30.2%), Diabetes (26.5%), Respiratory illness (24.3%), Cataract (21%), Chest pain (11.7%), Stroke (8.6%) and Depression (2.5%). The prevalence of Hypertension (grade 1 and 2 as per JNC VII Hypertension criteria) was higher in males (50%) as compared to females (44.7%), but this difference was statistically not significant (P>0.5). (Table 2 a and 2 b) Among our elderly, 22.7% were overweight (22.6% males and 22.7% females) while 4.5% were obese (3.6% males and 5.3% females), as per BMI classification. Mean BMI of male and female elderly was 22.1 and 24.2 respectively which was statistically not significant (P>0.05). (Table 3) To a question on how the elderly rate their health, majority (56.8%) perceived their health status to be moderate, but 24.1% felt that it was bad and 19.1% felt it was good. Treatment after diagnosis: While it is heartening to note that for most of the diseases more than 90% were treated for their ailments, but for depression hardly 25% were taking treatment. For cataract, still around 30% need eye surgery (Table 4) Habits: In this study, nearly three fourths of the elderly have neither smoked nor chewed tobacco. Alcohol was consumed whether present or past by 34% of the elderly. (Table 5) Majority (79%) of the elderly consumed fruits less than 3 days/week while only 6.8% consumed more than 3 days/week and 14.2 % never consumed fruits at all. Vegetables were taken more than thrice a week by 56.8 % of the elderly. Regarding physical activity, 52.5% of the elderly were sedentary, 43.8% had moderate physical activity and 3.7% were involved in heavy physical activity. Health seeking behavior: Elderly who had at least one hospital/clinic visit in the last one year were 71.6%, of whom 83.6% were accompanied by at least one family member. For out-patient care, 47.2% visited private sectors, 30.3% Government facility, 2.5% RMP and 0.6% Ayush clinics. For in-patient treatment, 19.8% went to private institutions, 16 % went to Government institutions while 64.2% did not go to either. DISCUSSION The present study was undertaken to identify the socio-demographic profile and to assess the various health problems and treatment seeking behavior among the elderly residing in the urban slums of Hyderabad. Out of the 216 elderly, majority were females (61.1%) as was also seen in a study done by Bhatia et. al3 where 57.8% of the elderly studied were females and also similar to a study done by Kishore and Garg where 55% of the elders were females.4 Any person having ability to read and write with an understanding of any language is defined as a literate in India. According to the present study, illiteracy among the elder female was 29.8% and 4.7% in elder males. The majority of female elders had completed only primary school education (54.2%) where as a majority of male elders had completed secondary school education (48.8%). Gurav and Kartikeyan in their study noted that 58.76% of males and 22.85% of female had taken education up to secondary level.5 In India, work area includes mostly the informal sector and there is no fixed age for retirement. Although 43.5% of the elders were not occupied in the present study, a slightly higher percent 45.8% were involved in sedentary work and 10.6% in moderate work. This is similar to a study done by Rajshree J Bhatt et.al, which reported 52.3%
elderly were not in any occupation and 39% were working but in a sedentary way.6 In the urban slums of our study, joint family system was still prevailing since majority (75%) of the elderly lived in joint families followed by extended joint families (15.7%).This is similar to the results of K. Sreenivasa Rao and K.C.M. Eswara Prasad, in urban slums of Tirupathi, in which majority of the elderly (75%) lived in a joint family.7 Srivastava and Mishra’s in their study revealed that the majority of elderly were found living with their spouse and other member.8 Among the major social problems faced by the elderly, the first was the high levels of economic dependence on others, especially for women. The problems faced by women are more critical compared to that of men due to low literacy level and majority of women being not in labor force during their prime age and with only a very few being in the organized sector.2 In this study, only about 37% of the elderly were financially independent and the rest depended on their family members for financial support. About 40% of them were receiving old age pension. This is also as indicated by Gupta et al, based on the 1994-95 Human Development Indicator Survey data where about 76 percent of the women and 42 percent of the males were supported by their family.9 Regarding the presence of health problems in the geriatric population, it was found in the present study that the most prevalent problems of elders were Hypertension, Arthritis, Diabetes, Respiratory problems, Cataract, Chest pain, Stroke and Depression. The morbidity profile is similar to a study conducted by HM Swami et.al, in Chandigarh, where the most common diseases in order of their magnitude were Hypertension (58%) joint pains/arthritis (50.5%), Cataract (19.1%), gastritis (17.7%), deafness (13.5%) followed by Diabetes mellitus (12.2%).10 Similar findings were noted by Rahul P et. al in their study.11 With regard to the treatment received for their health problems, more than 90% were treated for most of the diseases but only about 25% were treated for depression. For cataract, still around 30% need eye surgery. This could be because of financial dependence on other members of their family for their basic health needs. Among our elderly 22.7% were overweight and 3.24% were obese, as per BMI classification.13 Mean BMI of males and females was 22.14 and 24.25 respectively which was statistically not significant (P>0.05). This was similar to the findings of MK Sharma et.al 14 (21.27% elderly were overweight) and Rajshree Bhatt et.al where 21.7% of male and 28.5% of female elderly were overweight and the mean BMI of male and female was 22.8±3.32 and 23.03±3.97 respectively which was statistically not significant. 6 Nearly three fourths of the elderly have neither smoked nor chewed tobacco in the present study which is different from the results of Bala et.al, which revealed that in age group of 65 years or older, 64.73% were smokers and that snuffing was more common especially in women, illiterate and in those involved in household occupation.15 Alcohol was consumed, present or past by 34% of the elderly in our study as was also seen in studies done by Harshal T Pandve and Poonam Deshmukh in Pune 16 and Khokhar and Mehra in Delhi.17 The elderly respondents were asked about how they perceived their health status, majority (56.8%) felt that their health status was moderate but 24.1% felt that it was bad and 19.1% felt it was good. As far as treatment seeking behavior is concerned about 71.6% of the subjects had visited a hospital or clinic at least once either as an outpatient, inpatient or both, hence showing a concern of the elders towards their health. For outpatient treatment nearly half of them went to a private facility and a third went to a government run facility. Even for inpatient treatment a slightly higher percent went to a private facility compared to a Government one, the reason could be location and time convenience. These findings were however different from a study conducted by Harshal T Pandve and Poonam Deshmukh in Pune, where they found that the Government run health centers were more commonly utilized than private clinics.16
CONCLUSIONS
The study among elderly in Hyderabad, India has highlighted a major proportion of the elderly were females, many were not in any occupation, partially or totally financially dependent on others and have one or more health related problems. A high prevalence of morbidity and common existing medical problems like hypertension, arthritis, diabetes mellitus, cataract, cancer, deafness were identified. For treatment services, majority visited the private sectors. As there is a rapid expansion in number of elderly population, there is an urgent need to develop good quality geriatric health care services and provide training to health care providers to manage the commonly existing health problems in the country. Financial assistance and insurance schemes need to be provided for economic independence and better utilization of healthcare services.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors wish to thank the elderly who participated willingly in this study. Authors acknowledge the help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript.The authors are also grateful to the authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Health Action (2004), Eldercare, Feb.2004, Vol. 17, No.2. 2. The Situational Analysis of the Elderly in India. Central Statistics Office, Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, Government of India (June 2011) 3. Bhatia SPS, Swami H M, Thakur J S, Bhatia V. A study of health problem and loneliness among elderly in Chandigarh. Indian Journal of Community Medicine 2007; 32 (4): 255-58. 4. Kishore .S, Garg B S. Socio-medical problems of aged population in a rural area of Wardha District, Indian Journal of Public Health 1997; 41(2): 43-48. 5. Gurav R V, Kartikeyan S. Problem of Geriatric population in urban area, Kalwa Thane. Bombay Hospital Journals 2002 Jan; 44 (1): 47-51. 6. Rajshree Bhatt, Minal S Gadhvi, K N Sonaliya, Anand Solanki, Himanshu Nayak. An Epidemiological study of the morbidity pattern among the elderly population in Ahmedabad, Gujarat. National Journal of Community Medicine, 2011; 2(2): 233-236 7. K. Sreenivasa Rao, K.C.M. Eswara Prasad. Condition of Older Persons Living in Slum in Tirupati, Helpage India–Research and Development Journal October 2009 Vol 15 No. 3; 20-27 8. Srivastava H C, Mishra N R. Living arrangement and morbidity pattern among elderly in rural India. International Institute for population science Mumbai 2005: 1-7. 9. Gupta, I., P. Dasgupta, and M. Sawhney. 2001. Health of the Elderly in India: Some Aspects of Vulnerability. Discussion paper series No 26. Delhi, India: Institute of Economic Growth. 10. HM Swami, Vikas Bhatia, Rekha Dutt, SPS Bhatia. A Community Based Study of the Morbidity Profile among the Elderly in Chandigarh, India - Bahrain Medical Bulletin,2002; 24(1) : 13-16 11. Rahul P, Chaudary S K, Singh V S. A study of Morbidity pattern among geriatric population in an urban area of Udiapur Rajasthan. Indian Journal of Community Medicine 2004; 29 (1): 35-40. 12. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National High Blood Pressure Education Program, NIH Publication No. 04-5230, August 2004. 13. Joshi P. P Integrated Disease Surveillance Project Training Manual for field workers and field supervisors BMI, Waist to Hip ratio. WHO surveillance Handouts The GOI- WHO collaborative Programme : 04-05. 14. M K Sharma, H M Swami, V Bhatia, A Verma, S P S Bhatia, G Kaur. An Epidemiological study of correlates of osteoarthritis in geriatric population of UT Chandigarh. Indian Journal of Community Medicine 2007 ; 32(1): 77-78 15. Bala DV, Bodiwala I, Patel DD, Shah PM, Epidemiological determinants of Tobacco use in Gujarat state. Indian Journal of Community Medicine 2006; 31(3): 173-76. 16. Harshal T Pandve, Poonam Deshmukh. Health Survey among Elderly Population Residing in an Urban Slum of Pune City. Journal of The Indian Academy of Geriatrics, 2010 ; 6 (1): 5- 8 17. Khokhar A, Mehra M. Life style and morbidity profile of geriatric population in an urban community of Delhi. Indian J Med Sci 2001; 55: 609-615.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License