IJCRR - 4(20), October, 2012
Pages: 156-161
Date of Publication: 20-Oct-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
BODY SENSOR NETWORK SECURITY USING CRYPTOGRAPHY APPROACH
Author: Umasankar K., Vetrivendan R.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:A body sensor network (BSN), is a network of sensors de-ployed on a person's body, usually for health care monitoring. Since the sensors collect personal medical data, security and privacy are important components in a body sensor network. At the same time, the collected data has to readily available in the event of an emergency. In this paper, we present IBE-Lite, a lightweight identity-based encryption suitable for sensors, and developed protocols based on IBE-Lite for a BSN.
Keywords: Security, Body Sensor Networks, Identity-based cryptography
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Applying wireless sensors toward health care monitoring allows for new ways to provide quality health care to pa-tents. A diverse array of specialized sensors can be de-ployed to monitor, for instance, at-risk patients with history of heart attacks, or senior citizens living independently at home. These sensors provide continuous, long term monitoring in an unobtrusive manner, allowing doctors to diagnose problems more effectively. A body sensor network, or BSN, is a network of sensors deployed on a person’s body to collect physiological information. In this paper, we focus on a BSN deployed for medical monitoring. We term the person wearing the BSN as the Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page. To copy otherwise, to republish, to post on servers or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission and/or a fee. The term “doctor” is used loosely, and refers to any person wanting to access the data.
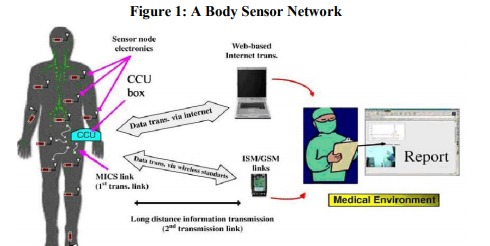
Motivating Example
Privacy and security for a BSN is important since the data collected is directly associated with a particular patient. At the same time, the data must be easily accessible to relevant personal in the event of an emergency. The following scenarios serve to better illustrate such concerns. 1. Alice wears a BSN that monitors her EKG data when she is working out. One day, Alice suddenly falls un-conscious and is sent to the emergency room. The data collected by the BSN should be stored in a public place and made easily accessible in an emergency. 2. After the incident, Alice instructs her BSN to collect some additional data. Alice would like to restrict this information to only physicians in an ER. However, Al-ice cannot predict which doctor or hospital will treat her. Alice may not be physically competent to authenticate anybody when she is admitted to a hospital. ABSN security scheme should be able to tolerate this form of ambiguity. 3. Furthermore, due to privacy reasons, a doctor requiring two days worth of data prior to Alice’s illness should only be able to obtain data collected within those two days. However, since Alice does not know when she might have a relapse, a BSN should be able to limit access to the collected data, even when the data is stored in a public space. 4. Alice’s family and friends are worried about her condition. To allay their concerns, Alice would like some other family members to be able to have partial access to her BSN data. Since the data collected by the BSNbelongs to Alice, a security scheme should be flexible Enough to allow Alice to easily add additional access permissions to people she chooses.
BSN security requirements
While a complete BSN system will have many different components, a crucial factor is that any security design must be lightweight enough to be executed by a sensor in a BSNsince a sensor can be lost or stolen, leaving the data stored within the sensor exposed. From the scenario presented, we derive the following security and privacy requirements for a BSN. 1. Protect patient privacy from the storage site. Since the data is stored on a third party storage site, we cannot trust the storage site with the data. We assume an honest-but-curious storage site that will not maliciously delete the data, but may attempt to learn the contents of a patient’s data. 2. Tolerate compromised BSN sensors. The BSN sensors may be misplaced or stolen, and a compromised BSNsensor should not allow an adversary from obtaining the patient’s data. 3. Prevent unauthorized access to information. This includes a doctor with permissions to access some data and not others. We assume that a doctor may attempt to obtain additional data about a patient beyond what was authorized. Since storage site is not trusted, access control can only be performed by the CA. 4. Flexibility in granting permissions. The patient may decide to allow different people to access the BSN data, and the BSN should be able to generate keys on-the-fly without additional interaction with the CA.
Identity-based encryption
Our solutions are based on a type of cryptographic primitive known as identity-based encryption (IBE). After an initial setup phase, IBE allows a public key to be generated from an arbitrary string. The corresponding secret key can be derived separately by a trusted party. For example, Al-ice may want to encrypt a message for the doctor in charge on Monday. Alice can independently generated a public key using the strings “Monday” and “doctor” to encrypt her data without further contact with the trusted party. To decrypt the message, a doctor will have to convince the trusted party that he is a doctor in charge on Monday. The same doctor working on Tuesday cannot decrypt messages encrypted using the string “Tuesday” and “doctor” even if he knows the secret key from Monday. The simple example cannot be easily accomplished without using IBE. Alice can try to generate many public/secret key pairs, one for each occasion. However, Alice will have to store the secret key created with the trusted party each time a new public/secret key pair is generated. Otherwise, the trusted party cannot derive the secret key on its own. This is inefficient. Another possible alternative is for Alice to include some instructions with each of her message, and encrypt every-thing with the trusted parties’ public key. When a doctor receives an encrypted message, the doctor will forward it to the trusted party. The trusted party can decrypt can obtain Alice’s instructions. The trusted party will release the message to the doctor only if he meets Alice’s instructions. This solution is also inefficient since a BSN may generate many pieces of data, each of which has to be forwarded to the trusted party for decryption. Using IBE, the doctor only needs to be given a single secret key once. Our contributions In this paper, we design protocols based on identity-based encryption (IBE) that provide security and privacy protections to a body sensor network, while allowing flexible access to stored data. However, conventional IBE cannot be efficiently implemented on sensors used in a BSN. In this paper, we propose IBE-Lite, lightweight IBE scheme that is suitable for sensors. We implement a proof-of-concept of our schemes based on IBE-Litton commercially available sensors similar to the ones used in a BSN. While IBE schemes have been suggested by previous researchers to protect medical data, we are the first to present a lightweight IBE suitable for body sensor networks. The rest of the paper is as follows. The next section presents our protocols and Section 3 contains the security analysis. Our schemes are evaluated in Section 4, with related work presented in Section 5. Section 6 concludes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
OUR SOLUTION
Our protocols are based on a lightweight IBE scheme IBE-Lite. IBE-LIE shares two properties with conventional IBE, namely the ability to use an arbitrary string to generate public key, and the ability to generate a public key separately from the corresponding secret key. We begin by first reviewing Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), a public key primitive suitable for BSN [18], followed by the modifications made to derive IBELite. Finally, we present our protocols based on IBE-Lite.
Basic ECC Primitives
To setup ECC, we first select a particular elliptic curve over GF(p), where p is a big prime number. We also denote P as the base point of E and q as the order of P, where q is also a big prime. We then pick a secret key expand the corresponding public key y, where y = x · P, and cryptographic hash function h(). Finally, we have the secret key x and public parameters (y, P, p, q, h(.)).We denote encrypting a message m using public key asEccEncrypt (m, y). The resulting cipher text is denoted. The decryption of cipher text c using the secret key x is given as Eyck Decrypt(c, x). The algorithms for Eyck Encrypt and EccDecrypt are found in Alg. 1 and Alg. 2 respectively. Algorithm 1 EccDecrypt (m, y) 1: Generate a random number r ∈ GF (p). Encrypt m with, Er (m) 2: Calculate Ar = h(r) · y 3: Calculate Br = h(r) · P 4: Calculate _r = r ⊕ _(Ar), where _(Ar) is the x coordinate of Ar 5: Return cipher text c = h_ r, Br, Er (m) i Algorithm 2 EccDecrypt(c, x) 1: Calculate x · Br = x · h(r) · P = h(r) · y = Ar 2: Determine the x coordinate, _(Ar) 3: Derive symmetric key r with _r ⊕_(Ar) = r ⊕_(Ar)⊕ (Ar) = r 4: Apply r to Er(m) to return m IBE-Lite From the basic ECC primitives, we derive the following BE-Lite primitives, setup, and keygen, encrypt and decrypt. For ease of explanation, we assume in this subsection that all primitives are executed by the patient. The actual protocols involving the patient, CA and doctor are explained in the next subsection. The intuition behind is to let a sensor independently generate a public key on-the-fly using an arbitrary string. For example, a sensor collecting EKG readings on Monday 1 Powell first create a string str = (monday|1 pm|EKG). Using this string, the sensor can derive a public key, ystr to en-crypt the data and send it to the storage site. There is no corresponding secret key created. In fact, the sensor cannot create the secret key needed to decrypt the message. When the patient wishes to release this information to a doctor, the patient can derive the corresponding secret key,xstr, by using the same string str = (monday|1pm|EKG). This secret key only allows the doctor to decrypt messages encrypted by a sensor using the same string. This simplifies the key management, since the patient can generate the secret key on-demand without keeping track of which keys were used to encrypt which data. The only requirement is that the string used to describe the event is the same. Setup: We select an elliptic curve E over GF(p), where p is a big prime number. We also denote P as the base point of E and q as the order of P, where q is also a big prime. Asset of n secret keys x1, · · · , xn ∈ GF(q) is chosen to generate the master secret key = (x1, · · · , xn).The n public keys are then generated to make up the master public key = (y1, · · · , yn)where yi = xi · P, 1 ≤ i < n. Finally, a collision resistant one-way hash function h: {0, 1}_ → {0, 1}n is chosen. The parameter shy, P, p, q, h(.)i are released as the system public parameters. Eigen: To derive a secret key xstr corresponding to public key generated by a string str, the patient executes Eigen (str) = xstr, xstr =nXi=1hi (str) · xi, where hi(str) is the i-th bit of h(str).Encrypt: To encrypt a message m using a public key derived from string str, the sensor does Encrypt(m, str) to determine the cipher text c. Alg. 3 shows the process. BSN Security Protocols We first describe the initialization phase where the patient configures the BSN, followed by the data collection phase which outlines how a sensor encrypts the collected data. The data transfer phase describes how a BSN transfers data to storage site, and finally, the query phase which occurs when a doctor needs to obtain data from the storage site. We assume that an agreed upon syntax is used to describe the string needed to derive a public key, and this descriptions termed as STR. For example, the patient deciding to collect data on a hourly basis will set the sensors in the BSN to affix timestamp rounded to the nearest hour when creating strain other words, two EKG readings collected on Monday at1:05 pm and 1:20 pm will both be described using the same string star = {monday|1 pm|EKG}.As mentioned earlier, we assume an honest-but-curious storage site which will try to learn the contents of the stored data, but will otherwise not delete the stored data. We also assume a separate security mechanism is in place so that only the patient can store BSN data onto the storage site. Initialization: The patient first executes Setup to obtain the master secret key X = (x1, · · · , xn), and public parameters hay, P, p, q, h(.)i. The patient loads the parameter shy, P, p, q, h (.)i into every sensor in the BSN. The patient then registers the master secret key together with additional instructions with the CA. Data collection: Let the sensor collect data d at events.
SECURITY ANALYSIS
We begin by examining the basic primitives, followed by an analysis of the protocols themselves. Analysis of Basic Primitives Our Setup is similar to that of the basic ECC setup scheme, except that instead of picking a single secret x, our Setup picks n secrets and n corresponding public keys. Knowing only one star and h(str), the doctor cannot determine the patient’s master secret X since there are n unknown xi. The doctor is only able to determine X when he has in this pos-session n different secret keys x1str, · · · , xnstr.The use of star and yet as the private key and public key derived from string str does not violate the discrete logarithm property of ECC where, given a y = x · P, it is infeasible to determine x given y and P, since both are simply the result of addition of points. Also, both Encrypt and Decrypt are secure since both rely on well established ECC encryption and decryption methods. Analysis of Protocols Our protocols protect the privacy of the patient’s data by encrypting all the information before forwarding the data to the storage site. After a sensor collects the data, the sensor encrypts the data using Encrypt, resulting in the tupleSince all tulles are in cipher text; the storage site learns nothing about the patient’s data. The protocols also prevent unauthorized access to the patient’s data. Each piece of data collected by a sensor is encrypted with a yet, the public key derived from the strings. When the doctor receives permissions to access data encrypted under star, the doctor receives the secret key star, which cannot be used to decrypt any other cipher text not encrypted using yet. A compromised sensor does not allow the adversary to obtain any useful data about a patient from the storage site since the sensor only stores the publicly known parameters. At most the adversary obtains the cipher text pair (c1, c2).The adversary can try to launch a matching attack by first creating many public keys using different strings str. The adversary then encrypts all possible values using the different public keys to determine whether there is a match forth tuple (c1, c2). This is possible since the number of potential EKG readings for example is bounded. However, both c1 and c2 contains a random number n generated by the sensor. Since the adversary cannot predict the value of, the matching attack fails. Finally, our protocols provide flexibility. The string strcan be used to specify access to the data, without using additional certificates. For instance, consider the string str ={Date | ER | Doctor} used to encrypt data. A doctor wanting to obtain the corresponding secret key will have to convince the CA that he is indeed an ER doctor on the given date. The process of specifying what str to construct can be programmed by the patient without additional permissions from the CA. RELATED WORK AND RESULT The motivation behind a BSN is to place low cost sensors directly on the patient for health care monitoring. With this in mind, several research prototypes have been developed [18, 28, 8, 19]. The use of identity-based cryptography (IBE) [25, 2, 5] for medical applications was also suggested by [22, 21], but our work presents practical implementation actual sensors rather than a general architecture. Other applications of IBE include [13, 1, 11].Sensor network security is a widely researched area [24, 12], with solutions focusing on key deployment [7, 14, 17, 16, 4], public key cryptography [15, 23, 9] and management [6, 20, 3]. Unlike prior work, our security protocols incorportateidentity-based cryptography primitives.
CONCLUSION
In this paper, we presented IBE-Lite, a lightweight identity based encryption method suitable for a body sensor net-work. We provided protocols based on IBE-Lite to provide security and privacy support for a BSN. We evaluated our protocols using a combination of security analysis, simulations, and practical implementation on actual sensors.
References:
1. N. Asokan, K. Kostiainen, P. Ginzboorg, J. Otto, and C. Lou. Applicability of identitybased cryptography for disruption-tolerant networking. In MobiOpp 2007.
2. D. Boneh and M. Franklin. Identity-based encryption from the Weil pairing. In CRYPTO 2001.
3. S. Capkun, L. Butty´an, and J.-P. Hubaux.Self-organized public-key management for mobile adhoc networks. IEEE TMC 2003.
4. H. Chan, A. Perrig, and D. Song. Random key redistribution schemes for sensor networks. In IEEESP 2003. 5. C. Cocks. An identity based encryption scheme based on. quadratic residues. In LNCS 2260 (2001).
6. W. Du, R. Wang, and P. Ning. An efficient scheme for authenticating public keys in sensor networks. InMobiHoc 2005.
7. L. Eschenauer and V. D. Gligor. A keymanagement scheme for distributed sensor networks. In CCS 2002.
8. R. Ganti, P. Jayachandran, and T. Abdelzaher. Satire:A software architecture for smart attire. In Mobisys2006.
9. J. Girao, D. Westhoff, E. Mykletun, and T. Araki.Tinypeds: Tiny persistent encrypted data storage in asynchronous wireless sensor networks. Ad HocNetworks 2007.
10. V. Gupta, M. Wurm, Y. Zhu, M. Millard, S. Fung,N. Gura, H. Eberle, and S. C. Shantz. Sizzle: A standards-based end-to-end security architecture forthe embedded internet. In PerCom 2005.
11. U. Hengartner and P. Steenkiste. Exploiting hierarchical identity-based encryption for access control to pervasive computing information. InSecureComm 2005. 12. C. Karlof, N. Sastry, and D. Wagner. Tinysec: a linklayer security architecture for wireless sensor networks. In SenSys 2004.
13. A. Kate, G. Zaverucha, and U. Hengartner. Anonymity and security in delay tolerant networks. InSecureComm 2007.
14. L. Lazos and R. Poovendran. Serloc: Secure range-independent localization for wireless sensor networks. ACM TOSN 2005.
15. A. Liu, P. Kampanakis, and P. Ning. Tinyecc: Elliptic curve cryptography for sensor networks (version 0.3).2007. 16. D. Liu and P. Ning. Establishing pair wise keys in distributed sensor networks. In CCS 2003.
17. D. Liu, P. Ning, S. Zhu, and S. Jajodia. Practical broadcast authentication in sensor networks. InMobiQuitous 2005.
18. B. Lo and G. Z. Yang. Key technical challenges and current implementations of body sensor networks. InBSN 2005.
19. D. Malan, T. Fulford-Jones, M. Welsh, ands. Moulton. Code blue: An ad hoc sensor network infrastructure for emergency medical care. In BSN2004.
20. D. J. Malan, M. Welsh, and M. D. Smith. A public-key infrastructure for key distribution in tinyosbased on elliptic curve cryptography. In SECON 2004.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License