IJCRR - 5(20), October, 2013
Pages: 66-74
Date of Publication: 02-Nov-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF PYRIPROXYFEN ON FUNCTION AND TISSUE OF TESTIS IN ADULT RAT
Author: Ghavami Mehrnoush , Shariati Mehrdad , Khatamsaz Saeid
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: Pyriproxyfen is a pyridine insecticide and used in agriculture widely. Extensive application
of pyriproxyfen to control annual insect pest in agriculture, horticulture and horn garden, leads to
environmental pollution and its entrance into the food chain could have determined effects on human
and other species. In this research the effects of pyriproxyfen on reproductive parameters of the male
rats including serum LH, FSH, testosterone levels, and changes in testicular tissue and body weight
were investigated.
Methods: For this purpose 250 ? 5g male Wistar strain rats (n = 50) were randomly collected and
divided into 5 group of 10, including control, sham (received distilled water 70%+ethanol 20%+aceton
10%as a solvent), and three experimental groups which received 1000, 2000 and 4000 mg/kg/bw
pyriproxyfen orally. After 28 days, body and testis weight were measured and blood samples were
taken from heart and used for measurement of LH, FSH and testosterone levels. To evaluate
histological changes, testes were removed and weighed and, after obtaining tissue section, stained by H
and E method.
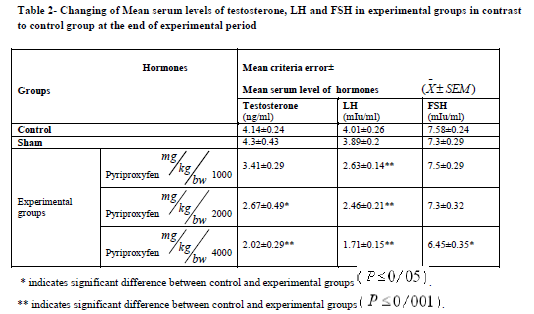
Results: Serum testosterone, FSH, and LH levels showed significant decreasing in experimental groups
(p ? 0.05). There was significant decreasing in the number of germinal and somatic cells in testis in
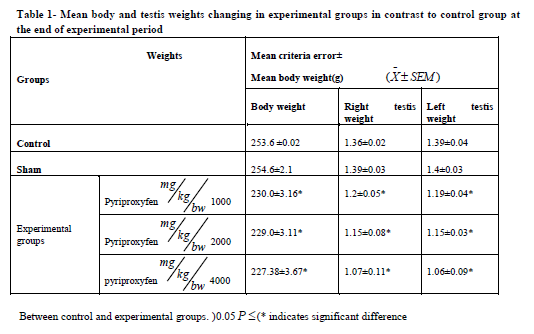
experimental groups. There was also a significant decreasing in body and testis weight in experimental
groups, as compared to control group.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that oral administration of pyriproxyfen could reduction
gonadotropins and testosterone hormone levels and also this insecticide might have hazardous effects
on testis tissue.
Keywords: Pyriproxyfen, Testosterone, Gonadotropins, Testis, Rat
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
One of the most disquieting discoveries in recent years concerns the possible roles of environmental chemicals on endocrine systems (1-3). Endocrine systems coordinate and regulate many important body functions such as growth and maturation, behavior, reproduction and embryo development. They do this by making and releasing hormones which act as "chemical messengers"(1-3)
Endocrine systems can be affected by certain substances outside of the body, both naturally-occurring and artificial. By interfering with the normal communication between the messenger and the cell receptors, the chemical message is misinterpreted, generating abnormal response(s) in the body.
The number of substances believed to act as endocrine disruptors is wide and varied, including both natural and synthetic materials. Concern arises because potential endocrine disruptors may be present in the environment, unrecognized but possibly able to cause effects at low concentrations.
Synthetic chemicals suspected as endocrine disruptors may reach humans and animals in a variety of ways. Some, such as insecticides, are released intentionally (1-3).
These days insecticide usage has become more widespread as new ways to harvest more crops and control weed are used so humans are exposed to a wide variety of insecticides. Therefore it is necessary to notice the possible hazardous effects of these insecticides on human health.
In this article we have investigated the effects of one of the most current insecticides, called pyriproxyfen, on LH, FSH and testosterone hormone levels and testis histological changes in adult rats. Pyriproxyfen is a pyridine insecticide used in agriculture widely. It enters insects and inhibits insect maturation process from cell division to elongation (a juvenile hormone mimic). Extensive application of pyriproxyfen to control annual grasses and broadleaf weeds in agriculture, horticulture and home gardens leads to environmental pollution and its entrance into the food chain could have detrimental effects on human and other species.
We selected pyriproxyfen because of the following important points:
1- Excessive usage of this pesticide in recent years.
2- Low solubility in water and high stability in the environment may lead pyriproxyfen entering into the body via fruits and vegetable feeding by human and domestics.
3- Potential effects of as pyriproxyfen an endocrine disrupting chemical.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In our experimental study, the effects of pyriproxyfen on reproductive parameters of male Wistar strain rats were investigated. For this purpose, 40 adult male rats with the average age of 2.5-3 months and 250 grams weight were randomly divided in 5 groups of 10: control, sham and three experimental groups 1, 2, and 3.
The 5 groups of rats were kept in special polycarbonate cages under the same conditions of unlimited water and special squeezed food. The temperature range and light and dark cycle were between 20-25°C and 12 hours respectively.
The rats in the experimental groups 1, 2, and 3 received 1000, 2000 and 4000 grams pyriproxyfen per kilograms live weight per day (mg⁄kg/day) respectively. The control group left untreated and the sham received solvent (distilled water 70%+ethanol 20%+aceton 10%). Everyday pyriproxyfen was administered orally via syringes equipped with feeder.
The rats were weighed at the end of day 28 and then under anesthesia by ether, blood was taken from the heart. Each group's blood samples were centrifuged at the rate of 5000 per min. in order to separate blood serum.
Serum concentrations of LH, FSH and testosterone were measured by special rat kits using the ELISA method. For histological studies of testis tissue, the testes were removed, weighed and kept in formalin for 17-18 hours and then microscopic slides were prepared and stained by Hematoxylin – Eosin method.
Finally, the data were statistically analyzed using the SPSS software. The means of the sham and experimental groups were compared with the control group using the ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range tests. P<0.05 was considered as a significant difference.
RESULTS
Pyriproxyfen treatment caused a significant decrease in body and testis weights in the experimental groups (Table 1). It also decreased serum LH and FSH levels in all experimental groups. There was also a significant decrease in experimental group 3 compared to the control group (Table 2). Testosterone decreased significantly in experimental groups 2 and 3 compared to the control group (Table 2).
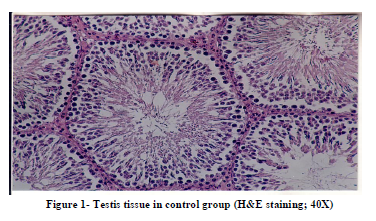
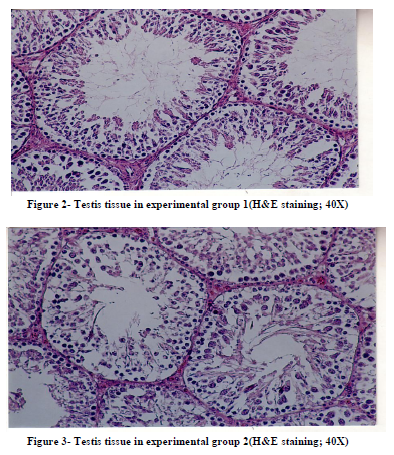
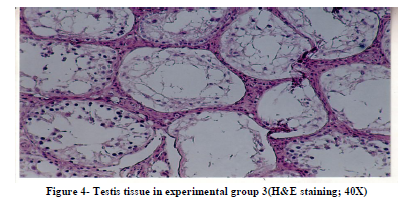
Histological studies of testis tissue demonstrated significant decrease in the number of spermatogonia, primary spermatocytes, spermatids, sertoli cells and leydig cells in all or some of experimental groups compared to the control group (Table 3 and Figures 1,2,3,4). Sperm density declined significantly in all experimental groups and seminiferous tubules showed degeneration and deformation in experimental group 3 (Figure 4).
DISCUSSION
Our findings demonstrated that pyriproxyfen could decrease serum testosterone hormone concentration. Many studies have proven that testosterone has a direct effect on protein synthesis in all tissues and organs of the body and can increase bone and muscle mass in males (4, 5); so in experimental groups decreased testosterone could lead to body weight loss via decreasing protein synthesis and bone/muscle mass.
According to previous studies, pyriproxyfen is a thyroid hormone disruptor and can induce tumor formation or hypertrophy of thyroid follicular cells (6), so probable significant increase in serum T3 and T4 levels lead to proteolysis and decreasing protein mass, followed by severe muscle catabolism (7). Recent data demonstrated that increasing serum T4 and decreasing TSH decrease only BMI (7,8).
Some experimental studies showed that pyriproxyfen increases cortisol significantly. Cortisol increases under following physiologic and pathologic situations:
In physiologic situations (stress, fight and flight,) increasing cortisol leads to increased gluconeogenesis and protein catabolism and decreased glucose oxidation to supply the required energy. Following alleviation of this condition, appetite increases leading to increased weight (9). This probably happened in the sham group under daily stress (see table 1). But pathologic elevation of cortisol leads to decreased protein synthesis, increased protein catabolism, decreased bone mass and finally decreased body weight (9).
According to a previous study on rats and dogs exposed to a compound pesticide containing pyriproxyfen, prostate, seminal vesicle and androgen sensitive organ weights decreased (10).
Researches have demonstrated that physiologic concentrations of testosterone, LH and FSH play an important role in spermatogenesis (4), so a significant decrease of these hormones in our study could decrease the number and function of somatic and germinal cells of testis followed by testis weight reduction.
Some experimental studies have demonstrated that pyriproxyfen can generate free radicals (10) and chromosomal malformations in cells (11), so this could occur in sensitive cells in the testis and result in cell death and testis weight reduction.
Experimental studies on rats demonstrated that pyriproxyfen can decrease pituitary gland weight and size (12), which could be the result of decreasing pituitary secreted hormones like LH and FSH.
Pyriproxyfen causes disorder in adrenal and significant increase in serum cortisol level (5). Findings demonstrated cortisol elevation reduces pulsatile secretion of GnRH and gonadotropins specially (13-17), so it can potentially reduce testis endocrine function (16,17).
Tumor and hypertrophy in follicular cells of thyroid by pyriproxyfen (6) can increase serum T4 and then TRH through negative feedback and therefore causes a long-term increase in prolactin level. Prolactin elevation decreases GnRH and FSH/LH secretion (9)
Significant decrease in interstitial cells number and LH hormone concentration in experimental groups could lead to decreased testosterone secretion from interstitial cells (4,5). As previously states, pyriproxyfen can increase serum cortisol level (10). Cortisol elevation induces negative effects on testosterone synthesis, steroidogenesis, and spermatogenesis, directly (16-21).
According to recent studies, pyriproxyfen leads to activation of a type of nuclear receptor in liver called PXR[1], which is a kind of steroid / xenobiotic sensor (22-24). Many hormone disrupting chemicals that activate PXR have anti androgenic effects (23), so it could be possible that pyriproxyfen has the same effect too. Moreover, PXR induces CYP3A enzyme. This enzyme metabolizes a great number of steroids like testosterone and increases these steroids’ clearance from plasma. Also, CYP3A induction would produce some metabolites which have endocrine disrupting function (24). Recent hypotheses express that PXR activation via xenobiotics leads to iNOS (human gene promoter inducing nitric oxide synthesis) upregulation and then increase nitric oxide synthesis (24-25). Pyriproxyfen elevates blood platelets level (25) and causes release of serotonin and histamine inflammatory factors. These factors can start inflammatory reactions and increase nitric oxide synthesis (9). Nitric oxide prevents steroidogenesis in interstitial cells by the mechanism of CP450scc[2] enzyme prevention which acts as a cholesterol-to-pregnenolone converter (26-28).
An experimental study demonstrated that a herbicide with 26% pyriproxyfen could increase chromosomal malformation in testis germinal cells (11,29). It can be mutagenic (6). On the other hand, the published article by CDC[3] has demonstrated that this herbicide can pass through cytoplasmic membrane and produce free radicals, oxidative stress and damage to biomolecules like DNA and protein (10), so these properties of pyriproxyfen can cause severe damage to or kill sensitive testis cells, especially spermatogonia, primary spermatocytes and spermatids.
Decreasing LH, FSH, and testosterone hormones concentration could be effective in decreasing spermatogenesis and the number of testis germinal cells (4, 5).
Significant increase in serum cortisol and nitric oxide (e.g. by pyriproxyfen in our study) decreases steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis (16,20,21); also nitric oxide is able to decrease spermatocytes and spermatids number and sperm content, due to induction of apoptosis (18,30-32) and can damage seminiferous tubules epithelium(33) too. Moreover, according to some studies, cortisol elevation decreases LH pulsatile secretion and causes oligospermia (13-16).
According to experimental studies on rats, pyriproxyfen has hazardous effects on prostate and seminal vesicle glands (10,17), which have a crucial role in generating most of semen contents and supplying suitable milieu for sperm life (4,5), so this could be an important result of severe oligospermia in the experimental groups in our study.
CONCLUSION
The results obtained from the present study indicated that different doses of pyriproxyfen showed significant reduction in levels of FSH, LH and testosterone. In addition, this compound eliminated spermatogenesis process in seminiferous tubules. Hence, based on foregoing evidence, the present study suggest that usage of pyriproxyfen must be done with consider to different levels of hazard analysis. However, to achieve to this information more investigations are needed.
[1]- Pregnane Xenobiotic Rceptor
Cytochrome P450 type scc- [2]
[3] - Control Diseases Center

References:
- Bervini TA, Zanetto SB, Cillo F. Effect of endocrine disruptors on developmental and reproductive functions .Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord 2005;5(1):1-10.
- Trubo R. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals probed as potential pathway to illness. JAMA 2005; 294 (3):291-293.
- Elobeid MA, Allison DB. Putative environmental endocrine disruptors and obesity .Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2008;15 (5):403-408.
- Zitzmann M. Effect of testosterone replacement and its pharmacogenetics on physical performance and metabolism .Asian J Andrology 2008;10(3):364-372.
- Wade AP, Wilkinson GS, Davis JC, Jeffcoate TN. The metabolism of testosterone, androstendione and oesterone by testes from a case of testicular feminization .J Endocrinol 1968;42(3):391-403.
- Franc M, Genchi C, Bouhsira E, Warin S, Kaltsatos V, Baduel L, Genchi M. Efficacy of dinotefuran,permithin and pyriproxyfen combination spot-on against Ades aegypti mosquitoes on dogs .Vet Parasitol 2012;189(2-4): 333-337.
- Iacobellis G, Ribaudo MC, Zappaterreno A, Iannucci CV, Leonetti F. Relationship of thyroid function with body mass index ,leptin, insulin sensitivity and adiponectin in euthyroid obese woman .Clin Endocrinol(Oxf) 2005;62(4):487-491.
- Knudsen N, Laurberg P, Rasmussen LB, Bulow I, Perrild H, Ovesen L, et al. Small differences in thyroid function may be important for body mass index and the occurrence of obesity in the population .J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90(7):4019-4024.
- Fraser R, Ingram MC, Anderson NH, Morrison C, Davies E, Connell JM. Cortisol effect on body mass, blood pressure and cholesterol in the general population. Hypertension 1999;33(6):1364-1368.
- Choi SM, Lee BM. An alternative mode of action of endocrine disrupting chemicals and chemoprevention. J Toxicol Environ Health 2004;7(6):451-463.
- Sial AA, Brunner JF. Lethal and sublethal effects of an insect growth regulator, pyriproxyfen, on Obliquebanded leafroller (Lepidopetra Torti). J Econ Entomol 2010;103 (2):340-347.
- Toppari J, Larsen GC, Christiansen P, Giwercman A, Grandjean P, Guillette LJ, et al. Male reproductive health and environmental xenoestrogens. Environ Health Perspect 1996;104 (4):741-803.
- Debus N, Breen KM, Barrell GK, Billings HJ, Brown M, Young EA, et al. Does cortisol mediate endotoxin induced inhibition of pulsatile luteinizing hormone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion? Endocrinology 2002;143(10):3748-3758.
- Tassou KT, Schulz R. Effect of the insect growth regulatory pyriproxyfen in a two-generation test with chironomus riparius. Ecotoxicol environment 2009;72 (4):1058-1062.
- Breen KM, Billings HJ, Wagenmaker ER, Wessinger EW, Karsch FG. Endocrine basis for disruptive effects of cortisol on preovulatory events. Endocrinology 2005;146(4):2107-2115.
- Bambino TH, Hsueh AJ. Direct inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids upon testicular luteinizing hormone receptor and steroidogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Endocrinology 1981; 108(6): 2142-2148.
- Juinewicz PE, Johnson BH, Bolt DJ. Effect of adrenal steroids on testosterone and luteinizing hormone secretion in the ram. Andrology 1987; 8(3): 190-196.
- Norman RL. Effect of corticotropin- releasing hormone on luteinizing hormone, testosterone and cortisol secretion in intact male rhesus macaques.Biol Reprod 1993; 79(1): 148-153.
- Hoogeveen AR, Zonderland ML. Relationships between testosterone, cortisol and performance in professional cyclists. Int J Sports Med 1996; 17(6): 423-428
- Shanker DS, Kulkarni RS. Effects of cortisol on testis freshwater fish Notopterus notopterus (pallas).Indian J Expl Biol 2000; 38(12): 1227-1230.
- Consten D, Keuning ED, Terlou M, Lambert JGD, Goos HJT. Cortisol effects on the testicular androgen synthesizing capacity in common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Fish Physiol Biochem 2001; 25(2): 91-98.
- Mikamo E, Harada S, Nishikawa J, Nishihara T. Endocrine disruptors induce cytochrome P450 by affecting transcriptional regulation via pregnane X receptor. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2003;193(1): 66-72.
- Tabb MM, Blumberg B. New modes of action for endocrine-disrupting chemicals .Mol Endocrinol 2006;20(3):475-482.
- Guillette LJ. Endocrine disrupting contaminants beyond the Dogma. Environ Health Perspect 2006; 114(1):9-12.
- Toell A, Kroncke KD, Kleinert H, Carlberg C. Orphan nuclear receptor binding site in the human inducible nitric oxide synthesis promoter mediats responsiveness to steroid and xenobiotic ligands. J Cell Biochem 2002; 85(1): 72-82.
- Del Punta K, Charreau EH, Pignataro OP. Nitric oxide inhibits leydig cell steroidogenesis.Endocrinology 1996; 137(12): 5337-5343.
- Pomerantz DK, Pitelka V. Nitric oxide is a mediator of the inhibitory effect of activated macrophages on production of androgen by the leydig cell of the mouse. Endocrinology 1998; 139(3): 3922-3931.
- O’Bryan MK, Schlatt S, Gerdprasert O, Phillips DJ, Kretser DM, Hedger MP. Inducible nitric oxide synthesis in the rat testis: evidence for potential roles in both normal function and inflammation- mediated infertility. Biol Reprod 2000; 63(5): 1285-1293.
- Pontecorvo G, Fantaccione S. Recombinogenic activity of 10 chemical compounds in male germ cells of Drosophila melanogaster. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2006; 65(1): 93-101.
- Ishikawa T, Kondo Y, Goda K, Fujisawa M. Overexpression of endothelial nitric oxide synthesis in transgenic mice accelerates testicular germ cell apoptosis induced by experimental cryptorchidism.J Androl 2005; 26(2):281-288.
- Lue Y, Shina Hikim AP, Wang C, Leung A, Swerdloff RS. Functional role of inducible nitric oxide synthesis in the induction of male germ cell apoptosis, regulation of sperm number and determination of testes size: evidence from null mutant mice. Endocrinology 2003; 144(7):3092-3100.
- Kavallieratos NG, Athanassiou CG, Vayias BJ, Tomanovi Z. Efficacy of insect growth regulators as grain protectants against two stored-product pests in wheat and maize. J Food Prot 2012;75 (5):945-949.
- Lee NP, Cheng CY. Nitric oxide/nitric oxide synthesis, spermatogenesis and tight junction dynamics. Biol Reprod 2004;70(2):267-276.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License